The pharmaceutical industry stands at an inflection point where artificial intelligence meets regulatory compliance, creating new paradigms for quality decision-making that neither fully automate nor abandon human expertise. The concept of the “missing middle” first articulated by Paul Daugherty and H. James Wilson in their seminal work Human + Machine: Reimagining Work in the Age of AI has found profound resonance in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly as regulators grapple with how to govern AI applications in Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) environments
The recent publication of EU GMP Annex 22 on Artificial Intelligence marks a watershed moment in this evolution, establishing the first dedicated regulatory framework for AI use in pharmaceutical manufacturing while explicitly mandating human oversight in critical decision-making processes. This convergence of the missing middle concept with regulatory reality creates unprecedented opportunities and challenges for pharmaceutical quality professionals, fundamentally reshaping how we approach GMP decision-making in an AI-augmented world.
Understanding the Missing Middle: Beyond the Binary of Human Versus Machine
The missing middle represents a fundamental departure from the simplistic narrative of AI replacing human workers. Instead, it describes the collaborative space where human expertise and artificial intelligence capabilities combine to create outcomes superior to what either could achieve independently. In Daugherty and Wilson’s framework, this space is characterized by fluid, adaptive work processes that can be modified in real-time—a stark contrast to the rigid, sequential workflows that have dominated traditional business operations.
Within the pharmaceutical context, the missing middle takes on heightened significance due to the industry’s unique requirements for safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance. Unlike other sectors where AI can operate with relative autonomy, pharmaceutical manufacturing demands a level of human oversight that ensures patient safety while leveraging AI’s analytical capabilities. This creates what we might call a “regulated missing middle”—a space where human-machine collaboration must satisfy not only business objectives but also stringent regulatory requirements.
Traditional pharmaceutical quality relies heavily on human decision-making supported by deterministic systems and established procedures. However, the complexity of modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, coupled with the vast amounts of data generated throughout the production process, creates opportunities for AI to augment human capabilities in ways that were previously unimaginable. The challenge lies in harnessing these capabilities while maintaining the control, traceability, and accountability that GMP requires.
Annex 22: Codifying Human Oversight in AI-Driven GMP Environments
The draft EU GMP Annex 22, published for consultation in July 2025, represents the first comprehensive regulatory framework specifically addressing AI use in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The annex establishes clear boundaries around acceptable AI applications while mandating human oversight mechanisms that reflect the missing middle philosophy in practice.
Scope and Limitations: Defining the Regulatory Boundaries
Annex 22 applies exclusively to static, deterministic AI models—those that produce consistent outputs when given identical inputs. This deliberate limitation reflects regulators’ current understanding of AI risk and their preference for predictable, controllable systems in GMP environments. The annex explicitly excludes dynamic models that continuously learn during operation, generative AI systems, and large language models (LLMs) from critical GMP applications, recognizing that these technologies present challenges in terms of explainability, reproducibility, and risk control that current regulatory frameworks cannot adequately address.
This regulatory positioning creates a clear delineation between AI applications that can operate within established GMP principles and those that require different governance approaches. The exclusion of dynamic learning systems from critical applications reflects a risk-averse stance that prioritizes patient safety and regulatory compliance over technological capability—a decision that has sparked debate within the industry about the pace of AI adoption in regulated environments.
Human-in-the-Loop Requirements: Operationalizing the Missing Middle
Perhaps the most significant aspect of Annex 22 is its explicit requirement for human oversight in AI-driven processes. The guidance mandates that qualified personnel must be responsible for ensuring AI outputs are suitable for their intended use, particularly in processes that could impact patient safety, product quality, or data integrity. This requirement operationalizes the missing middle concept by ensuring that human judgment remains central to critical decision-making processes, even as AI capabilities expand.
The human-in-the-loop (HITL) framework outlined in Annex 22 goes beyond simple approval mechanisms. It requires that human operators understand the AI system’s capabilities and limitations, can interpret its outputs meaningfully, and possess the expertise necessary to intervene when circumstances warrant. This creates new skill requirements for pharmaceutical quality professionals, who must develop what Daugherty and Wilson term “fusion skills”—capabilities that enable effective collaboration with AI systems.
Validation and Performance Requirements: Ensuring Reliability in the Missing Middle
Annex 22 establishes rigorous validation requirements for AI systems used in GMP contexts, mandating that models undergo testing against predefined acceptance criteria that are at least as stringent as the processes they replace. This requirement ensures that AI augmentation does not compromise existing quality standards while providing a framework for demonstrating the value of human-machine collaboration.
The validation framework emphasizes explainability and confidence scoring, requiring AI systems to provide transparent justifications for their decisions. This transparency requirement enables human operators to understand AI recommendations and exercise appropriate judgment in their implementation—a key principle of effective missing middle operations. The focus on explainability also facilitates regulatory inspections and audits, ensuring that AI-driven decisions can be scrutinized and validated by external parties.
The Evolution of GMP Decision Making: From Human-Centric to Human-AI Collaborative
Traditional GMP decision-making has been characterized by hierarchical approval processes, extensive documentation requirements, and risk-averse approaches that prioritize compliance over innovation. While these characteristics have served the industry well in ensuring product safety and regulatory compliance, they have also created inefficiencies and limited opportunities for continuous improvement.
Traditional GMP Decision Paradigms
Conventional pharmaceutical quality assurance relies on trained personnel making decisions based on established procedures, historical data, and their professional judgment. Quality control laboratories generate data through standardized testing protocols, which trained analysts interpret according to predetermined specifications. Deviation investigations follow structured methodologies that emphasize root cause analysis and corrective action implementation. Manufacturing decisions are made through change control processes that require multiple levels of review and approval.
This approach has proven effective in maintaining product quality and regulatory compliance, but it also has significant limitations. Human decision-makers can be overwhelmed by the volume and complexity of data generated in modern pharmaceutical manufacturing. Cognitive biases can influence judgment, and the sequential nature of traditional decision-making processes can delay responses to emerging issues. Additionally, the reliance on historical precedent can inhibit innovation and limit opportunities for process optimization.
AI-Augmented Decision Making: Expanding Human Capabilities
The integration of AI into GMP decision-making processes offers opportunities to address many limitations of traditional approaches while maintaining the human oversight that regulations require. AI systems can process vast amounts of data rapidly, identify patterns that might escape human observation, and provide data-driven recommendations that complement human judgment.
In quality control laboratories, AI-powered image recognition systems can analyze visual inspections with greater speed and consistency than human inspectors, while still requiring human validation of critical decisions. Predictive analytics can identify potential quality issues before they manifest, enabling proactive interventions that prevent problems rather than merely responding to them. Real-time monitoring systems can continuously assess process parameters and alert human operators to deviations that require attention.
The transformation of deviation management exemplifies the potential of AI-augmented decision-making. Traditional deviation investigations can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, often requiring weeks or months to complete. AI systems can rapidly analyze historical data to identify potential root causes, suggest relevant corrective actions based on similar past events, and even predict the likelihood of recurrence. However, the final decisions about root cause determination and corrective action implementation remain with qualified human personnel, ensuring that professional judgment and regulatory accountability are preserved.
Maintaining Human Accountability in AI-Augmented Processes
The integration of AI into GMP decision-making raises important questions about accountability and responsibility. Annex 22 addresses these concerns by maintaining clear lines of human accountability while enabling AI augmentation. The guidance requires that qualified personnel remain responsible for all decisions that could impact patient safety, product quality, or data integrity, regardless of the level of AI involvement in the decision-making process.
This approach reflects the missing middle philosophy by recognizing that AI augmentation should enhance rather than replace human judgment. Human operators must understand the AI system’s recommendations, evaluate them in the context of their broader knowledge and experience, and take responsibility for the final decisions. This creates a collaborative dynamic where AI provides analytical capabilities that exceed human limitations while humans provide contextual understanding, ethical judgment, and regulatory accountability that AI systems cannot replicate.
Fusion Skills for Pharmaceutical Quality Professionals: Navigating the AI-Augmented Landscape
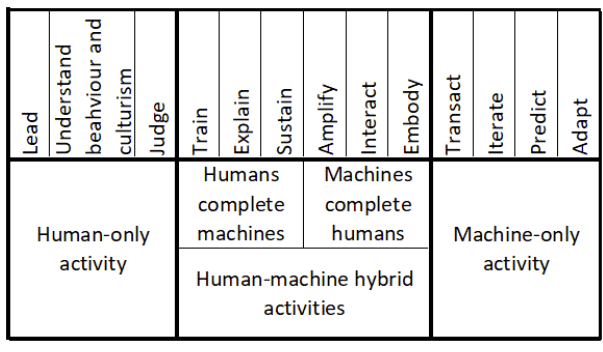
The successful implementation of AI in GMP environments requires pharmaceutical quality professionals to develop new capabilities that enable effective collaboration with AI systems. Daugherty and Wilson identify eight “fusion skills” that are essential for thriving in the missing middle. These skills take on particular significance in the highly regulated pharmaceutical environment, where the consequences of poor decision-making can directly impact patient safety.
Intelligent Interrogation: Optimizing Human-AI Interactions
Intelligent interrogation involves knowing how to effectively query AI systems to obtain meaningful insights. In pharmaceutical quality contexts, this skill enables professionals to leverage AI analytical capabilities while maintaining critical thinking about the results. For example, when investigating a deviation, a quality professional might use AI to analyze historical data for similar events, but must know how to frame queries that yield relevant and actionable insights.
The development of intelligent interrogation skills requires understanding both the capabilities and limitations of specific AI systems. Quality professionals must learn to ask questions that align with the AI system’s training and design while recognizing when human judgment is necessary to interpret or validate the results. This skill is particularly important in GMP environments, where the accuracy and completeness of information can have significant regulatory and safety implications.
Judgment Integration: Combining AI Insights with Human Wisdom
Judgment integration involves combining AI-generated insights with human expertise to make informed decisions. This skill is critical in pharmaceutical quality, where decisions often require consideration of factors that may not be captured in historical data or AI training sets. For instance, an AI system might recommend a particular corrective action based on statistical analysis, but a human professional might recognize unique circumstances that warrant a different approach.
Effective judgment integration requires professionals to maintain a critical perspective on AI recommendations while remaining open to insights that challenge conventional thinking. In GMP contexts, this balance is particularly important because regulatory compliance demands both adherence to established procedures and responsiveness to unique circumstances. Quality professionals must develop the ability to synthesize AI insights with their understanding of regulatory requirements, product characteristics, and manufacturing constraints.
Reciprocal Apprenticing: Mutual Learning Between Humans and AI
Reciprocal apprenticing describes the process by which humans and AI systems learn from each other to improve performance over time. In pharmaceutical quality applications, this might involve humans providing feedback on AI recommendations that helps the system improve its future performance, while simultaneously learning from AI insights to enhance their own decision-making capabilities.
This bidirectional learning process is particularly valuable in GMP environments, where continuous improvement is both a regulatory expectation and a business imperative. Quality professionals can help AI systems become more effective by providing context about why certain recommendations were or were not appropriate in specific situations. Simultaneously, they can learn from AI analysis to identify patterns or relationships that might inform future decision-making.
Additional Fusion Skills: Building Comprehensive AI Collaboration Capabilities
Beyond the three core skills highlighted by Daugherty and Wilson for generative AI applications, their broader framework includes additional capabilities that are relevant to pharmaceutical quality professionals. Responsible normalizing involves shaping the perception and purpose of human-machine interaction in ways that align with organizational values and regulatory requirements. In pharmaceutical contexts, this skill helps ensure that AI implementation supports rather than undermines the industry’s commitment to patient safety and product quality.
Re-humanizing time involves using AI to free up human capacity for distinctly human activities such as creative problem-solving, relationship building, and ethical decision-making. For pharmaceutical quality professionals, this might mean using AI to automate routine data analysis tasks, creating more time for strategic thinking about quality improvements and regulatory strategy.
Bot-based empowerment and holistic melding involve developing mental models of AI capabilities that enable more effective collaboration. These skills help quality professionals understand how to leverage AI systems most effectively while maintaining appropriate skepticism about their limitations.
Real-World Applications: The Missing Middle in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The theoretical concepts of the missing middle and human-AI collaboration are increasingly being translated into practical applications within pharmaceutical manufacturing environments. These implementations demonstrate how the principles outlined in Annex 22 can be operationalized while delivering tangible benefits to product quality, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Quality Control and Inspection: Augmenting Human Visual Capabilities
One of the most established applications of AI in pharmaceutical manufacturing involves augmenting human visual inspection capabilities. Traditional visual inspection of tablets, capsules, and packaging materials relies heavily on human operators who must identify defects, contamination, or other quality issues. While humans excel at recognizing unusual patterns and exercising judgment about borderline cases, they can be limited by fatigue, inconsistency, and the volume of materials that must be inspected.
AI-powered vision systems can process images at speeds far exceeding human capabilities while maintaining consistent performance standards. These systems can identify defects that might be missed by human inspectors and flag potential issues for further review89. However, the most effective implementations maintain human oversight over critical decisions, with AI serving to augment rather than replace human judgment.
Predictive Maintenance: Preventing Quality Issues Through Proactive Intervention
Predictive maintenance represents another area where AI applications align with the missing middle philosophy by augmenting human decision-making rather than replacing it. Traditional maintenance approaches in pharmaceutical manufacturing have relied on either scheduled maintenance intervals or reactive responses to equipment failures. Both approaches can result in unnecessary costs or quality risks.
AI-powered predictive maintenance systems analyze sensor data, equipment performance histories, and maintenance records to predict when equipment failures are likely to occur. This information enables maintenance teams to schedule interventions before failures impact production or product quality. However, the final decisions about maintenance timing and scope remain with qualified personnel who can consider factors such as production schedules, regulatory requirements, and risk assessments that AI systems cannot fully evaluate.
Real-Time Process Monitoring: Enhancing Human Situational Awareness
Real-time process monitoring applications leverage AI’s ability to continuously analyze large volumes of data to enhance human situational awareness and decision-making capabilities. Traditional process monitoring in pharmaceutical manufacturing relies on control systems that alert operators when parameters exceed predetermined limits. While effective, this approach can result in delayed responses to developing issues and may miss subtle patterns that indicate emerging problems.
AI-enhanced monitoring systems can analyze multiple data streams simultaneously to identify patterns that might indicate developing quality issues or process deviations. These systems can provide early warnings that enable operators to take corrective action before problems become critical. The most effective implementations provide operators with explanations of why alerts were generated, enabling them to make informed decisions about appropriate responses.
The integration of AI into Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) exemplifies this approach. AI algorithms can monitor real-time production data to detect deviations in drug formulation, dissolution rates, and environmental conditions. When potential issues are identified, the system alerts qualified operators who can evaluate the situation and determine appropriate corrective actions. This approach maintains human accountability for critical decisions while leveraging AI’s analytical capabilities to enhance situational awareness.
Deviation Management: Accelerating Root Cause Analysis
Deviation management represents a critical area where AI applications can significantly enhance human capabilities while maintaining the rigorous documentation and accountability requirements that GMP mandates. Traditional deviation investigations can be time-consuming processes that require extensive data review, analysis, and documentation.
AI systems can rapidly analyze historical data to identify patterns, potential root causes, and relevant precedents for similar deviations. This capability can significantly reduce the time required for initial investigation phases while providing investigators with comprehensive background information. However, the final determinations about root causes, risk assessments, and corrective actions remain with qualified human personnel who can exercise professional judgment and ensure regulatory compliance.
The application of AI to root cause analysis demonstrates the value of the missing middle approach in highly regulated environments. AI can process vast amounts of data to identify potential contributing factors and suggest hypotheses for investigation, but human expertise remains essential for evaluating these hypotheses in the context of specific circumstances, regulatory requirements, and risk considerations.
Regulatory Landscape: Beyond Annex 22
While Annex 22 represents the most comprehensive regulatory guidance for AI in pharmaceutical manufacturing, it is part of a broader regulatory landscape that is evolving to address the challenges and opportunities presented by AI technologies. Understanding this broader context is essential for pharmaceutical organizations seeking to implement AI applications that align with both current requirements and emerging regulatory expectations.
FDA Perspectives: Encouraging Innovation with Appropriate Safeguards
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has taken a generally supportive stance toward AI applications in pharmaceutical manufacturing, recognizing their potential to enhance product quality and manufacturing efficiency. The agency’s approach emphasizes the importance of maintaining human oversight and accountability while encouraging innovation that can benefit public health.
The FDA’s guidance on Process Analytical Technology (PAT) provides a framework for implementing advanced analytical and control technologies, including AI applications, in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The PAT framework emphasizes real-time monitoring and control capabilities that align well with AI applications, while maintaining requirements for validation, risk assessment, and human oversight that are consistent with the missing middle philosophy.
The agency has also indicated interest in AI applications that can enhance regulatory processes themselves, including automated analysis of manufacturing data for inspection purposes and AI-assisted review of regulatory submissions. These applications could potentially streamline regulatory interactions while maintaining appropriate oversight and accountability mechanisms.
International Harmonization: Toward Global Standards
The development of AI governance frameworks in pharmaceutical manufacturing is increasingly taking place within international forums that seek to harmonize approaches across different regulatory jurisdictions. The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) has begun considering how existing guidelines might need to be modified to address AI applications, particularly in areas such as quality risk management and pharmaceutical quality systems.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has published reflection papers on AI use throughout the medicinal product lifecycle, providing broader context for how AI applications might be governed beyond manufacturing applications. These documents emphasize the importance of human-centric approaches that maintain patient safety and product quality while enabling innovation.
The Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention and Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) has also begun developing guidance on AI applications, recognizing the need for international coordination in this rapidly evolving area. The alignment between Annex 22 and PIC/S approaches suggests movement toward harmonized international standards that could facilitate global implementation of AI applications.
Industry Standards: Complementing Regulatory Requirements
Professional organizations and industry associations are developing standards and best practices that complement regulatory requirements while providing more detailed guidance for implementation. The International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE) has published guidance on AI governance frameworks that emphasize risk-based approaches and lifecycle management principles.
Emerging Considerations: Preparing for Future Developments
The regulatory landscape for AI in pharmaceutical manufacturing continues to evolve as regulators gain experience with specific applications and technologies advance. Several emerging considerations are likely to influence future regulatory developments and should be considered by organizations planning AI implementations.
The potential for AI applications to generate novel insights that challenge established practices raises questions about how regulatory frameworks should address innovation that falls outside existing precedents. The missing middle philosophy provides a framework for managing these situations by maintaining human accountability while enabling AI-driven insights to inform decision-making.
The increasing sophistication of AI technologies, including advances in explainable AI and federated learning approaches, may enable applications that are currently excluded from critical GMP processes. Regulatory frameworks will need to evolve to address these capabilities while maintaining appropriate safeguards for patient safety and product quality.
Challenges and Limitations: Navigating the Complexities of AI Implementation
Despite the promise of AI applications in pharmaceutical manufacturing, significant challenges and limitations must be addressed to realize the full potential of human-machine collaboration in GMP environments. These challenges span technical, organizational, and regulatory dimensions and require careful consideration in the design and implementation of AI systems.
Technical Challenges: Ensuring Reliability and Performance
The implementation of AI in GMP environments faces significant technical challenges related to data quality, system validation, and performance consistency. Pharmaceutical manufacturing generates vast amounts of data from multiple sources, including process sensors, laboratory instruments, and quality control systems. Ensuring that this data is of sufficient quality to train and operate AI systems requires robust data governance frameworks and quality assurance processes.
Data integrity requirements in GMP environments are particularly stringent, demanding that all data be attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate (ALCOA principles). AI systems must be designed to maintain these data integrity principles throughout their operation, including during data preprocessing, model training, and prediction generation phases. This requirement can complicate AI implementations and requires careful attention to system design and validation approaches.
System validation presents another significant technical challenge. Traditional validation approaches for computerized systems rely on deterministic testing methodologies that may not be fully applicable to AI systems, particularly those that employ machine learning algorithms. Annex 22 addresses some of these challenges by focusing on static, deterministic AI models, but even these systems require validation approaches that can demonstrate consistent performance across expected operating conditions.
The black box nature of some AI algorithms creates challenges for meeting explainability requirements. While Annex 22 mandates that AI systems provide transparent justifications for their decisions, achieving this transparency can be technically challenging for complex machine learning models. Organizations must balance the analytical capabilities of sophisticated AI algorithms with the transparency requirements of GMP environments.
Organizational Challenges: Building Capabilities and Managing Change
The successful implementation of AI in pharmaceutical manufacturing requires significant organizational capabilities that many companies are still developing. The missing middle approach demands that organizations build fusion skills across their workforce while maintaining existing competencies in traditional pharmaceutical quality practices.
Skills development represents a particular challenge, as it requires investment in both technical training for AI systems and conceptual training for understanding how to collaborate effectively with AI. Quality professionals must develop capabilities in data analysis, statistical interpretation, and AI system interaction while maintaining their expertise in pharmaceutical science, regulatory requirements, and quality assurance principles.
Change management becomes critical when implementing AI systems that alter established workflows and decision-making processes. Traditional pharmaceutical organizations often have deeply embedded cultures that emphasize risk aversion and adherence to established procedures. Introducing AI systems that recommend changes to established practices or challenge conventional thinking requires careful change management to ensure adoption while maintaining appropriate risk controls.
The integration of AI systems with existing pharmaceutical quality systems presents additional organizational challenges. Many pharmaceutical companies operate with legacy systems that were not designed to interface with AI applications. Integrating AI capabilities while maintaining system reliability and regulatory compliance can require significant investments in system upgrades and integration capabilities.
Regulatory Challenges: Navigating Evolving Requirements
The evolving nature of regulatory requirements for AI applications creates uncertainty for pharmaceutical organizations planning implementations. While Annex 22 provides important guidance, it is still in draft form and subject to change based on consultation feedback. Organizations must balance the desire to implement AI capabilities with the need to ensure compliance with final regulatory requirements.
The international nature of pharmaceutical manufacturing creates additional regulatory challenges, as organizations must navigate different AI governance frameworks across multiple jurisdictions. While there is movement toward harmonization, differences in regulatory approaches could complicate global implementations.
Inspection readiness represents a particular challenge for AI implementations in GMP environments. Traditional pharmaceutical inspections focus on evaluating documented procedures, training records, and system validations. AI systems introduce new elements that inspectors may be less familiar with, requiring organizations to develop new approaches to demonstrate compliance and explain AI-driven decisions to regulatory authorities.
The dynamic nature of AI systems, even static models as defined by Annex 22, creates challenges for maintaining validation status over time. Unlike traditional computerized systems that remain stable once validated, AI systems may require revalidation as they are updated or as their operating environments change. Organizations must develop lifecycle management approaches that maintain validation status while enabling continuous improvement.
Future Implications: The Evolution of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
The integration of AI into pharmaceutical manufacturing represents more than a technological upgrade; it signals a fundamental transformation in how quality assurance is conceptualized and practiced. As AI capabilities continue to advance and regulatory frameworks mature, the implications for pharmaceutical quality assurance extend far beyond current applications to encompass new paradigms for ensuring product safety and efficacy.
The Transformation of Quality Professional Roles
The missing middle philosophy suggests that AI integration will transform rather than eliminate quality professional roles in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Future quality professionals will likely serve as AI collaborators who combine domain expertise with AI literacy to make more informed decisions than either humans or machines could make independently.
These evolved roles will require professionals who can bridge the gap between pharmaceutical science and data science, understanding both the regulatory requirements that govern pharmaceutical manufacturing and the capabilities and limitations of AI systems. Quality professionals will need to develop skills in AI system management, including understanding how to train, validate, and monitor AI applications while maintaining appropriate skepticism about their outputs.
The emergence of new role categories seems likely, including AI trainers who specialize in developing and maintaining AI models for pharmaceutical applications, AI explainers who help interpret AI outputs for regulatory and business purposes, and AI sustainers who ensure that AI systems continue to operate effectively over time. These roles reflect the missing middle philosophy by combining human expertise with AI capabilities to create new forms of value.
| Fusion Skill | Category | Definition | Pharmaceutical Quality Application | Current Skill Level (Typical) | Target Skill Level (AI Era) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Interrogation | Machines Augment Humans | Knowing how to ask the right questions of AI systems across levels of abstraction to get meaningful insights | Querying AI systems for deviation analysis, asking specific questions about historical patterns and root causes | Low – Basic | High – Advanced |
| Judgment Integration | Machines Augment Humans | The ability to combine AI-generated insights with human expertise and judgment to make informed decisions | Combining AI recommendations with regulatory knowledge and professional judgment in quality decisions | Medium – Developing | High – Advanced |
| Reciprocal Apprenticing | Humans + Machines (Both) | Mutual learning where humans train AI while AI teaches humans, creating bidirectional skill development | Training AI on quality patterns while learning from AI insights about process optimization | Low – Basic | High – Advanced |
| Bot-based Empowerment | Machines Augment Humans | Working effectively with AI agents to extend human capabilities and create enhanced performance | Using AI-powered inspection systems while maintaining human oversight and decision authority | Low – Basic | High – Advanced |
| Holistic Melding | Machines Augment Humans | Developing robust mental models of AI capabilities to improve collaborative outcomes | Understanding AI capabilities in predictive maintenance to optimize intervention timing | Low – Basic | Medium – Proficient |
| Re-humanizing Time | Humans Manage Machines | Using AI to free up human capacity for distinctly human activities like creativity and relationship building | Automating routine data analysis to focus on strategic quality improvements and regulatory planning | Medium – Developing | High – Advanced |
| Responsible Normalizing | Humans Manage Machines | Responsibly shaping the purpose and perception of human-machine interaction for individuals and society | Ensuring AI implementations align with GMP principles and patient safety requirements | Medium – Developing | High – Advanced |
| Relentless Reimagining | Humans + Machines (Both) | The discipline of creating entirely new processes and business models rather than just automating existing ones | Redesigning quality processes from scratch to leverage AI capabilities while maintaining compliance | Low – Basic | Medium – Proficient |
Advanced AI Applications: Beyond Current Regulatory Boundaries
While current regulatory frameworks focus on static, deterministic AI models, the future likely holds opportunities for more sophisticated AI applications that could further transform pharmaceutical quality assurance. Dynamic learning systems, currently excluded from critical GMP applications by Annex 22, may eventually be deemed acceptable as our understanding of their risks and benefits improves.
Generative AI applications, while currently limited to non-critical applications, could potentially revolutionize areas such as deviation investigation, regulatory documentation, and training material development. As these technologies mature and appropriate governance frameworks develop, they may enable new forms of human-AI collaboration that further expand the missing middle in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The integration of AI with other emerging technologies, such as digital twins and advanced sensor networks, could create comprehensive pharmaceutical manufacturing ecosystems that continuously optimize quality while maintaining human oversight. These integrated systems could enable unprecedented levels of process understanding and control while preserving the human accountability that regulations require.
Personalized Medicine and Quality Assurance Implications
The trend toward personalized medicine presents unique challenges and opportunities for AI applications in pharmaceutical quality assurance. Traditional GMP frameworks are designed around standardized products manufactured at scale, but personalized therapies may require individualized quality approaches that adapt to specific patient or product characteristics.
AI systems could enable quality assurance approaches that adjust to the unique requirements of personalized therapies while maintaining appropriate safety and efficacy standards. This might involve AI-driven risk assessments that consider patient-specific factors or quality control approaches that adapt to the characteristics of individual therapeutic products.
The regulatory frameworks for these applications will likely need to evolve beyond current approaches, potentially incorporating more flexible risk-based approaches that can accommodate the variability inherent in personalized medicine while maintaining patient safety. The missing middle philosophy provides a framework for managing this complexity by ensuring that human judgment remains central to quality decisions while leveraging AI capabilities to manage the increased complexity of personalized manufacturing.
Global Harmonization and Regulatory Evolution
The future of AI in pharmaceutical manufacturing will likely be shaped by efforts to harmonize regulatory approaches across different jurisdictions. The current patchwork of national and regional guidelines creates complexity for global pharmaceutical companies, but movement toward harmonized international standards could facilitate broader AI adoption.
The development of risk-based regulatory frameworks that focus on outcomes rather than specific technologies could enable more flexible approaches to AI implementation while maintaining appropriate safeguards. These frameworks would need to balance the desire for innovation with the fundamental regulatory imperative to protect patient safety and ensure product quality.
The evolution of regulatory science itself may be influenced by AI applications, with regulatory agencies potentially using AI tools to enhance their own capabilities in areas such as data analysis, risk assessment, and inspection planning. This could create new opportunities for collaboration between industry and regulators while maintaining appropriate independence and oversight.
Recommendations for Industry Implementation
Based on the analysis of current regulatory frameworks, technological capabilities, and industry best practices, several key recommendations emerge for pharmaceutical organizations seeking to implement AI applications that align with the missing middle philosophy and regulatory expectations.
Developing AI Governance Frameworks
Organizations should establish comprehensive AI governance frameworks that address the full lifecycle of AI applications from development through retirement. These frameworks should align with existing pharmaceutical quality systems while addressing the unique characteristics of AI technologies. The governance framework should define roles and responsibilities for AI oversight, establish approval processes for AI implementations, and create mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and risk management.
The governance framework should explicitly address the human oversight requirements outlined in Annex 22, ensuring that qualified personnel remain accountable for all decisions that could impact patient safety, product quality, or data integrity. This includes defining the knowledge and training requirements for personnel who will work with AI systems and establishing procedures for ensuring that human operators understand AI capabilities and limitations.
Risk assessment processes should be integrated throughout the AI lifecycle, beginning with initial feasibility assessments and continuing through ongoing monitoring of system performance. These risk assessments should consider not only technical risks but also regulatory, business, and ethical considerations that could impact AI implementations.
| AI Family | Description | Key Characteristics | Annex 22 Classification | GMP Applications | Validation Requirements | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-Based Systems | If-then logic systems with predetermined decision trees and fixed algorithms | Deterministic, transparent, fully explainable decision logic | Fully Permitted | Automated equipment control, batch processing logic, SOP workflows | Standard CSV approach, logic verification, boundary testing | Low |
| Statistical Models | Traditional statistical methods like regression, ANOVA, time series analysis | Mathematical foundation, well-understood statistical principles | Fully Permitted | Process capability studies, control charting, stability analysis | Statistical validation, model assumptions verification, performance metrics | Low |
| Classical Machine Learning | Support Vector Machines, Random Forest, k-means clustering with fixed training | Fixed model parameters, consistent outputs for identical inputs | Fully Permitted | Quality control classification, batch disposition, trend analysis | Cross-validation, holdout testing, bias assessment, performance monitoring | Medium |
| Static Deep Learning | Neural networks trained once and frozen for deployment (CNNs, RNNs) | Trained once, parameters frozen, deterministic within training scope | Fully Permitted | Tablet defect detection, packaging inspection, equipment monitoring | Comprehensive validation dataset, robustness testing, explainability evidence | Medium |
| Expert Systems | Knowledge-based systems encoding human expertise in specific domains | Codified expertise, logical inference, domain-specific knowledge | Fully Permitted | Regulatory knowledge systems, troubleshooting guides, decision support | Knowledge base validation, inference logic testing, expert review | Low-Medium |
| Computer Vision (Static) | Image recognition, defect detection using pre-trained, static models | Pattern recognition on visual data, consistent classification | Permitted with Human-in-the-Loop | Visual inspection automation, contamination detection, label verification | Image dataset validation, false positive/negative analysis, human oversight protocols | Medium-High |
| Natural Language Processing (Static) | Text analysis, classification using pre-trained models without continuous learning | Text processing, sentiment analysis, document classification | Permitted with Human-in-the-Loop | Deviation report analysis, document classification, regulatory text mining | Text corpus validation, accuracy metrics, bias detection, human review processes | Medium-High |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasting models using historical data with static parameters | Historical pattern analysis, maintenance scheduling, demand forecasting | Permitted with Human-in-the-Loop | Equipment failure prediction, demand planning, shelf-life modeling | Historical data validation, prediction accuracy, drift monitoring, human approval gates | Medium-High |
| Ensemble Methods (Static) | Multiple static models combined for improved predictions | Combining multiple static models, voting or averaging mechanisms | Permitted with Human-in-the-Loop | Combined prediction models for enhanced accuracy in quality decisions | Individual model validation plus ensemble validation, human oversight required | Medium |
| Dynamic/Adaptive Learning | Systems that continue learning and updating during operational use | Model parameters change during operation, non-deterministic evolution | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Adaptive process control, real-time optimization (non-critical only) | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | High |
| Reinforcement Learning | AI that learns through trial and error, adapting behavior based on rewards | Trial-and-error learning, behavior modification through feedback | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Process optimization, resource allocation (non-critical research only) | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | High |
| Generative AI | AI that creates new content (text, images, code) from prompts | Creative content generation, high variability in outputs | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Documentation assistance, training content creation (non-critical only) | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | High |
| Large Language Models (LLMs) | Large-scale language models like GPT, Claude, trained on vast text datasets | Complex language understanding and generation, contextual responses | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Query assistance, document summarization (non-critical support only) | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | High |
| Probabilistic Models | Models that output probability distributions rather than deterministic results | Uncertainty quantification, confidence intervals in predictions | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Risk assessment with uncertainty, quality predictions with confidence | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | High |
| Continuous Learning Systems | Systems that continuously retrain themselves with new operational data | Real-time model updates, evolving decision boundaries | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Self-improving quality models (non-critical applications only) | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | High |
| Federated Learning | Distributed learning across multiple sites while keeping data local | Privacy-preserving distributed training, model aggregation | Prohibited for Critical GMP | Multi-site model training while preserving data privacy | Not applicable – prohibited for critical GMP applications | Medium |
Building Organizational Capabilities
Successful AI implementation requires significant investment in organizational capabilities that enable effective human-machine collaboration. This includes technical capabilities for developing, validating, and maintaining AI systems, as well as human capabilities for collaborating effectively with AI.
Technical capability development should focus on areas such as data science, machine learning, and AI system validation. Organizations may need to hire new personnel with these capabilities or invest in training existing staff. The technical capabilities should be integrated with existing pharmaceutical science and quality assurance expertise to ensure that AI applications align with industry requirements.
Human capability development should focus on fusion skills that enable effective collaboration with AI systems. This includes intelligent interrogation skills for querying AI systems effectively, judgment integration skills for combining AI insights with human expertise, and reciprocal apprenticing skills for mutual learning between humans and AI. Training programs should help personnel understand both the capabilities and limitations of AI systems while maintaining their core competencies in pharmaceutical quality assurance.
Implementing Pilot Programs
Organizations should consider implementing pilot programs that demonstrate AI capabilities in controlled environments before pursuing broader implementations. These pilots should focus on applications that align with current regulatory frameworks while providing opportunities to develop organizational capabilities and understanding.
Pilot programs should be designed to generate evidence of AI effectiveness while maintaining rigorous controls that ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance. This includes comprehensive validation approaches, robust change control processes, and thorough documentation of AI system performance.
The pilot programs should also serve as learning opportunities for developing organizational capabilities and refining AI governance approaches. Lessons learned from pilot implementations should be captured and used to inform broader AI strategies and implementation approaches.
Engaging with Regulatory Authorities
Organizations should actively engage with regulatory authorities to understand expectations and contribute to the development of regulatory frameworks for AI applications. This engagement can help ensure that AI implementations align with regulatory expectations while providing input that shapes future guidance.
Regulatory engagement should begin early in the AI development process, potentially including pre-submission meetings or other formal interaction mechanisms. Organizations should be prepared to explain their AI approaches, demonstrate compliance with existing requirements, and address any novel aspects of their implementations.
Industry associations and professional organizations provide valuable forums for collective engagement with regulatory authorities on AI-related issues. Organizations should participate in these forums to contribute to industry understanding and influence regulatory development.
Conclusion: Embracing the Collaborative Future of Pharmaceutical Quality
The convergence of the missing middle concept with the regulatory reality of Annex 22 represents a defining moment for pharmaceutical quality assurance. Rather than viewing AI as either a replacement for human expertise or a mere automation tool, the industry has the opportunity to embrace a collaborative paradigm that enhances human capabilities while maintaining the rigorous oversight that patient safety demands.
The journey toward effective human-AI collaboration in GMP environments will not be without challenges. Technical hurdles around data quality, system validation, and explainability must be overcome. Organizational capabilities in both AI technology and fusion skills must be developed. Regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve as experience accumulates and understanding deepens. However, the potential benefits—enhanced product quality, improved operational efficiency, and more effective regulatory compliance—justify the investment required to address these challenges.
The missing middle philosophy provides a roadmap for navigating this transformation. By focusing on collaboration rather than replacement, by maintaining human accountability while leveraging AI capabilities, and by developing the fusion skills necessary for effective human-machine partnerships, pharmaceutical organizations can position themselves to thrive in an AI-augmented future while upholding the industry’s fundamental commitment to patient safety and product quality.
Annex 22 represents just the beginning of this transformation. As AI technologies continue to advance and regulatory frameworks mature, new opportunities will emerge for expanding the scope and sophistication of human-AI collaboration in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Organizations that invest now in building the capabilities, governance frameworks, and organizational cultures necessary for effective AI collaboration will be best positioned to benefit from these future developments.
The future of pharmaceutical quality assurance lies not in choosing between human expertise and artificial intelligence, but in combining them in ways that create value neither could achieve alone. The missing middle is not empty space to be filled, but fertile ground for innovation that maintains the human judgment and accountability that regulations require while leveraging the analytical capabilities that AI provides. As we move forward into this new era, the most successful organizations will be those that master the art of human-machine collaboration, creating a future where technology serves to amplify rather than replace the human expertise that has always been at the heart of pharmaceutical quality assurance.
The integration of AI into pharmaceutical manufacturing represents more than a technological evolution; it embodies a fundamental reimagining of how quality is assured, how decisions are made, and how human expertise can be augmented rather than replaced. The missing middle concept, operationalized through frameworks like Annex 22, provides a path forward that honors both the innovative potential of AI and the irreplaceable value of human judgment in ensuring that the medicines we manufacture continue to meet the highest standards of safety, efficacy, and quality that patients deserve.