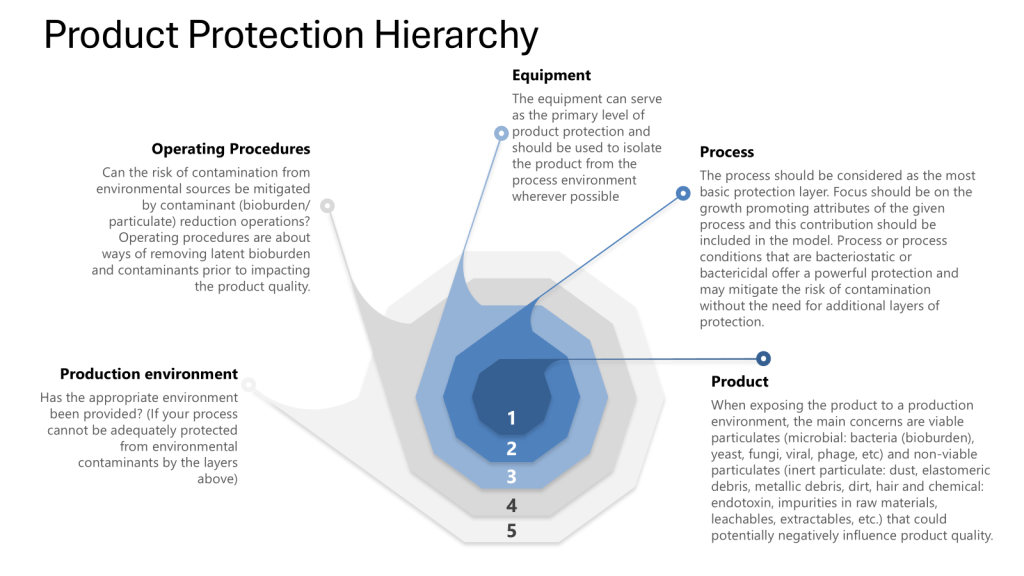
Defining a GMP critical system is an essential aspect of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. A critical system is one that has a direct impact on product quality, safety, and efficacy.
Key Characteristics of GMP Critical Systems
- Direct Impact on Product Quality: A critical system is one that can directly affect the quality, safety, or efficacy of the final product.
- Influence on Patient Safety: Systems that have a direct or indirect influence on patient safety are considered critical. This is where CPPs come in
- Data Integrity: Systems that generate, store, or process data used to determine product SISPQ (e.g. batch quality or are included in batch processing records, stability, data used in a regulatory filing) are critical.
- Decision-Making Role: Systems used in the decision process for product release or a regulatory filing are considered critical.
- Contact with Products: Equipment or devices that may come into contact with products are often classified as critical.
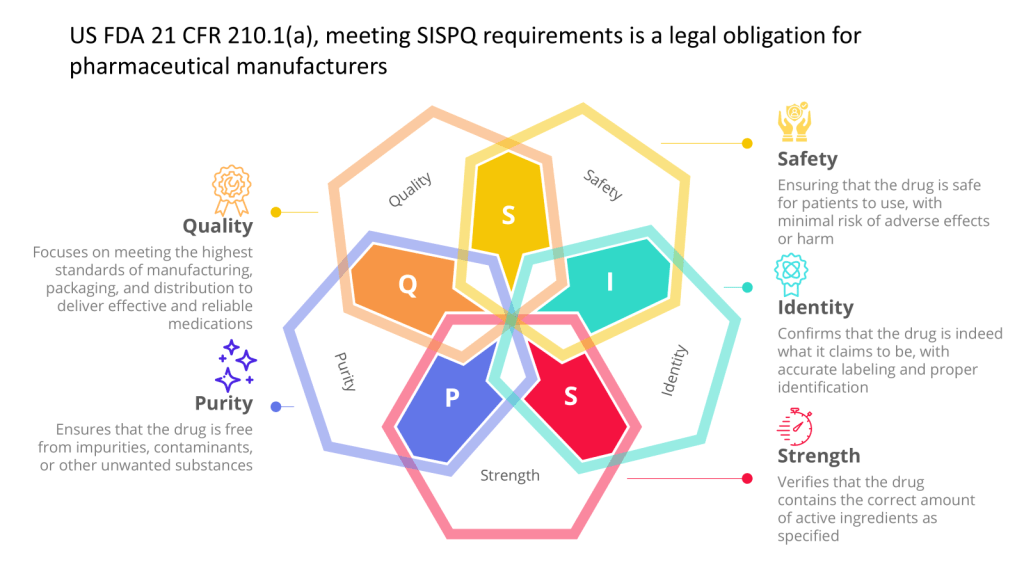
Continuous Evaluation
It’s important to note that the criticality of systems should be periodically evaluated to ensure they remain in a valid state and compliant with GMP requirements. This includes reviewing the current range of functionality, deviation records, incidents, problems, upgrade history, performance, reliability, security, and validation status reports.