The integration of Gigerenzer’s take-the-best heuristic with a causal reasoning framework creates a powerful approach to root cause analysis that addresses one of the most persistent problems in quality investigations: the tendency to generate exhaustive lists of contributing factors without identifying the causal mechanisms that actually drove the event.
Traditional root cause analysis often suffers from what we might call “factor proliferation”—the systematic identification of every possible contributing element without distinguishing between those that were causally necessary for the outcome and those that merely provide context. This comprehensive approach feels thorough but often obscures the most important causal relationships by giving equal weight to diagnostic and non-diagnostic factors.
The take-the-best heuristic offers an elegant solution by focusing investigative effort on identifying the single most causally powerful factor—the factor that, if changed, would have been most likely to prevent the event from occurring. This approach aligns perfectly with causal reasoning’s emphasis on identifying what was actually present and necessary for the outcome, rather than cataloging everything that might have been relevant.
From Counterfactuals to Causal Mechanisms
The most significant advantage of applying take-the-best to causal investigation is its natural resistance to the negative reasoning trap that dominates traditional root cause analysis. When investigators ask “What single factor was most causally responsible for this outcome?” they’re forced to identify positive causal mechanisms rather than falling back on counterfactuals like “failure to follow procedure” or “inadequate training.”
Consider a typical pharmaceutical deviation where a batch fails specification due to contamination. Traditional analysis might identify multiple contributing factors: inadequate cleaning validation, operator error, environmental monitoring gaps, supplier material variability, and equipment maintenance issues. Each factor receives roughly equal attention in the investigation report, leading to broad but shallow corrective actions.
A take-the-best causal approach would ask: “Which single factor, if it had been different, would most likely have prevented this contamination?” The investigation might reveal that the cleaning validation was adequate under normal conditions, but a specific equipment configuration created dead zones that weren’t addressed in the original validation. This equipment configuration becomes the take-the-best factor because changing it would have directly prevented the contamination, regardless of other contributing elements.
This focus on the most causally powerful factor doesn’t ignore other contributing elements—it prioritizes them based on their causal necessity rather than their mere presence during the event.
The Diagnostic Power of Singular Focus
One of Gigerenzer’s key insights about take-the-best is that focusing on the single most diagnostic factor can actually improve decision accuracy compared to complex multivariate approaches. In causal investigation, this translates to identifying the factor that had the greatest causal influence on the outcome—the factor that represents the strongest link in the causal chain.
This approach forces investigators to move beyond correlation and association toward genuine causal understanding. Instead of asking “What factors were present during this event?” the investigation asks “What factor was most necessary and sufficient for this specific outcome to occur?” This question naturally leads to the kind of specific, testable causal statements.
For example, rather than concluding that “multiple factors contributed to the deviation including inadequate procedures, training gaps, and environmental conditions,” a take-the-best causal analysis might conclude that “the deviation occurred because the procedure specified a 30-minute hold time that was insufficient for complete mixing under the actual environmental conditions present during manufacturing, leading to stratification that caused the observed variability.” This statement identifies the specific causal mechanism (insufficient hold time leading to incomplete mixing) while providing the time, place, and magnitude specificity that causal reasoning demands.
Preventing the Generic CAPA Trap
The take-the-best approach to causal investigation naturally prevents one of the most common failures in pharmaceutical quality: the generation of generic, unfocused corrective actions that address symptoms rather than causes. When investigators identify multiple contributing factors without clear causal prioritization, the resulting CAPAs often become diffuse efforts to “improve” everything without addressing the specific mechanisms that drove the event.
By focusing on the single most causally powerful factor, take-the-best investigations generate targeted corrective actions that address the specific mechanism identified as most necessary for the outcome. This creates more effective prevention strategies while avoiding the resource dilution that often accompanies broad-based improvement efforts.
The causal reasoning framework enhances this focus by requiring that the identified factor be described in terms of what actually happened rather than what failed to happen. Instead of “failure to follow cleaning procedures,” the investigation might identify “use of abbreviated cleaning cycle during shift change because operators prioritized production schedule over cleaning thoroughness.” This causal statement directly leads to specific corrective actions: modify shift change procedures, clarify prioritization guidance, or redesign cleaning cycles to be robust against time pressure.
Systematic Application
Implementing take-the-best causal investigation in pharmaceutical quality requires systematic attention to identifying and testing causal hypotheses rather than simply cataloging potential contributing factors. This process follows a structured approach:
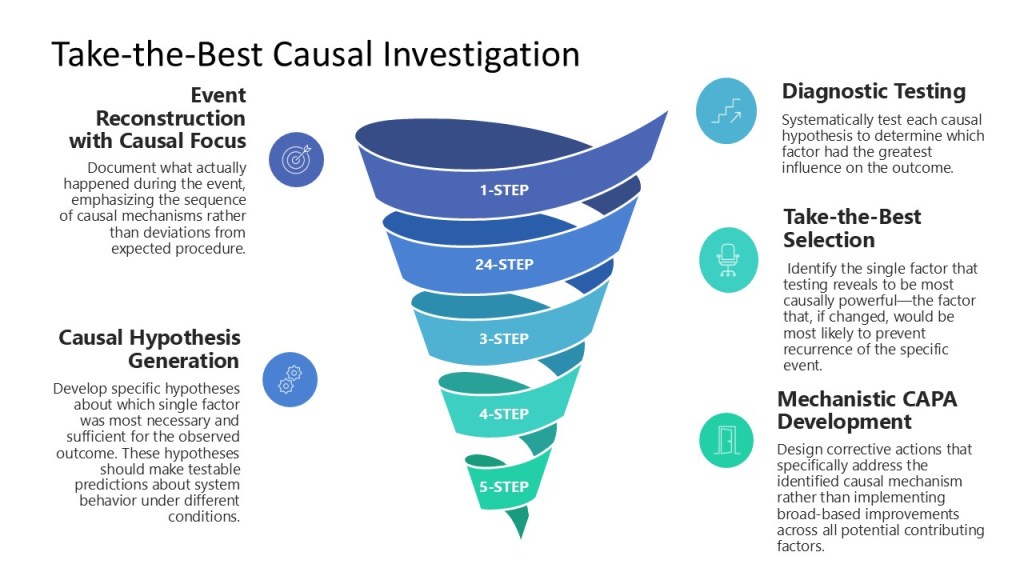
Step 1: Event Reconstruction with Causal Focus – Document what actually happened during the event, emphasizing the sequence of causal mechanisms rather than deviations from expected procedure. Focus on understanding why actions made sense to the people involved at the time they occurred.
Step 2: Causal Hypothesis Generation – Develop specific hypotheses about which single factor was most necessary and sufficient for the observed outcome. These hypotheses should make testable predictions about system behavior under different conditions.
Step 3: Diagnostic Testing – Systematically test each causal hypothesis to determine which factor had the greatest influence on the outcome. This might involve data analysis, controlled experiments, or systematic comparison with similar events.
Step 4: Take-the-Best Selection – Identify the single factor that testing reveals to be most causally powerful—the factor that, if changed, would be most likely to prevent recurrence of the specific event.
Step 5: Mechanistic CAPA Development – Design corrective actions that specifically address the identified causal mechanism rather than implementing broad-based improvements across all potential contributing factors.
Integration with Falsifiable Quality Systems
The take-the-best approach to causal investigation creates naturally falsifiable hypotheses that can be tested and validated over time. When an investigation concludes that a specific factor was most causally responsible for an event, this conclusion makes testable predictions about system behavior that can be validated through subsequent experience.
For example, if a contamination investigation identifies equipment configuration as the take-the-best causal factor, this conclusion predicts that similar contamination events will be prevented by addressing equipment configuration issues, regardless of training improvements or procedural changes. This prediction can be tested systematically as the organization gains experience with similar situations.
This integration with falsifiable quality systems creates a learning loop where investigation conclusions are continuously refined based on their predictive accuracy. Investigations that correctly identify the most causally powerful factors will generate effective prevention strategies, while investigations that miss the key causal mechanisms will be revealed through continued problems despite implemented corrective actions.
The Leadership and Cultural Implications
Implementing take-the-best causal investigation requires leadership commitment to genuine learning rather than blame assignment. This approach often reveals system-level factors that leadership helped create or maintain, requiring the kind of organizational humility that the Energy Safety Canada framework emphasizes.
The cultural shift from comprehensive factor identification to focused causal analysis can be challenging for organizations accustomed to demonstrating thoroughness through exhaustive documentation. Leaders must support investigators in making causal judgments and prioritizing factors based on their diagnostic power rather than their visibility or political sensitivity.
This cultural change aligns with the broader shift toward scientific quality management that both the adaptive toolbox and falsifiable quality frameworks require. Organizations must develop comfort with making specific causal claims that can be tested and potentially proven wrong, rather than maintaining the false safety of comprehensive but non-specific factor lists.
The take-the-best approach to causal investigation represents a practical synthesis of rigorous scientific thinking and adaptive decision-making. By focusing on the single most causally powerful factor while maintaining the specific, testable language that causal reasoning demands, this approach generates investigations that are both scientifically valid and operationally useful—exactly what pharmaceutical quality management needs to move beyond the recurring problems that plague traditional root cause analysis.
