Risk blindness is an insidious loss of organizational perception—the gradual erosion of a company’s ability to recognize, interpret, and respond to threats that undermine product safety, regulatory compliance, and ultimately, patient trust. It is not merely ignorance or oversight; rather, risk blindness manifests as the cumulative inability to see threats, often resulting from process shortcuts, technology overreliance, and the undervaluing of hands-on learning.
Unlike risk aversion or neglect, which involves conscious choices, risk blindness is an unconscious deficiency. It often stems from structural changes like the automation of foundational jobs, fragmented risk ownership, unchallenged assumptions, and excessive faith in documentation or AI-generated reports. At its core, risk blindness breeds a false sense of security and efficiency while creating unseen vulnerabilities.
Pattern Recognition and Risk Blindness: The Cognitive Foundation of Quality Excellence
The Neural Architecture of Risk Detection
Pattern recognition lies at the heart of effective risk management in quality systems. It represents the sophisticated cognitive process by which experienced professionals unconsciously scan operational environments, data trends, and behavioral cues to detect emerging threats before they manifest as full-scale quality events. This capability distinguishes expert practitioners from novices and forms the foundation of what we might call “risk literacy” within quality organizations.
The development of pattern recognition in pharmaceutical quality follows predictable stages. At the most basic level (Level 1 Situational Awareness), professionals learn to perceive individual elements—deviation rates, environmental monitoring trends, supplier performance metrics. However, true expertise emerges at Level 2 (Comprehension), where practitioners begin to understand the relationships between these elements, and Level 3 (Projection), where they can anticipate future system states based on current patterns.
Research in clinical environments demonstrates that expert pattern recognition relies on matching current situational elements with previously stored patterns and knowledge, creating rapid, often unconscious assessments of risk significance. In pharmaceutical quality, this translates to the seasoned professional who notices that “something feels off” about a batch record, even when all individual data points appear within specification, or the environmental monitoring specialist who recognizes subtle trends that precede contamination events.
The Apprenticeship Dividend: Building Pattern Recognition Through Experience
The development of sophisticated pattern recognition capabilities requires what we’ve previously termed the “apprenticeship dividend”—the cumulative learning that occurs through repeated exposure to routine operations, deviations, and corrective actions. This learning cannot be accelerated through technology or condensed into senior-level training programs; it must be built through sustained practice and mentored reflection.
The Stages of Pattern Recognition Development:
Foundation Stage (Years 1-2): New professionals learn to identify individual risk elements—understanding what constitutes a deviation, recognizing out-of-specification results, and following investigation procedures. Their pattern recognition is limited to explicit, documented criteria.
Integration Stage (Years 3-5): Practitioners begin to see relationships between different quality elements. They notice when environmental monitoring trends correlate with equipment issues, or when supplier performance changes precede raw material problems. This represents the emergence of tacit knowledge—insights that are difficult to articulate but guide decision-making.
Mastery Stage (Years 5+): Expert practitioners develop what researchers call “intuitive expertise”—the ability to rapidly assess complex situations and identify subtle risk patterns that others miss. They can sense when a investigation is heading in the wrong direction, recognize when supplier responses are evasive, or detect process drift before it appears in formal metrics.
Tacit Knowledge: The Uncodifiable Foundation of Risk Assessment
Perhaps the most critical aspect of pattern recognition in pharmaceutical quality is the role of tacit knowledge—the experiential wisdom that cannot be fully documented or transmitted through formal training systems. Tacit knowledge encompasses the subtle cues, contextual understanding, and intuitive insights that experienced professionals develop through years of hands-on practice.
In pharmaceutical quality systems, tacit knowledge manifests in numerous ways:
- Knowing which equipment is likely to fail after cleaning cycles, based on subtle operational cues rather than formal maintenance schedules
- Recognizing when supplier audit responses are technically correct but practically inadequate
- Sensing when investigation teams are reaching premature closure without adequate root cause analysis
- Detecting process drift through operator reports and informal observations before it appears in formal monitoring data
This tacit knowledge cannot be captured in standard operating procedures or electronic systems. It exists in the experienced professional’s ability to read “between the lines” of formal data, to notice what’s missing from reports, and to sense when organizational pressures are affecting the quality of risk assessments.
The GI Joe Fallacy: The Dangers of “Knowing is Half the Battle”
A persistent—and dangerous—belief in quality organizations is the idea that simply knowing about risks, standards, or biases will prevent us from falling prey to them. This is known as the GI Joe fallacy—the misguided notion that awareness is sufficient to overcome cognitive biases or drive behavioral change.
What is the GI Joe Fallacy?
Inspired by the classic 1980s G.I. Joe cartoons, which ended each episode with “Now you know. And knowing is half the battle,” the GI Joe fallacy describes the disconnect between knowledge and action. Cognitive science consistently shows that knowing about biases or desired actions does not ensure that individuals or organizations will behave accordingly.
Even the founder of bias research, Daniel Kahneman, has noted that reading about biases doesn’t fundamentally change our tendency to commit them. Organizations often believe that training, SOPs, or system prompts are enough to inoculate staff against error. In reality, knowledge is only a small part of the battle; much larger are the forces of habit, culture, distraction, and deeply rooted heuristics.
GI Joe Fallacy in Quality Risk Management
In pharmaceutical quality risk management, the GI Joe fallacy can have severe consequences. Teams may know the details of risk matrices, deviation procedures, and regulatory requirements, yet repeatedly fail to act with vigilance or critical scrutiny in real situations. Loss aversion, confirmation bias, and overconfidence persist even for those trained in their dangers.
For example, base rate neglect—a bias where salient event data distracts from underlying probabilities—can influence decisions even when staff know better intellectually. This manifests in investigators overreacting to recent dramatic events while ignoring stable process indicators. Knowing about risk frameworks isn’t enough; structures and culture must be designed specifically to challenge these biases in practice, not simply in theory.
Structural Roots of Risk Blindness
The False Economy of Automation and Overconfidence
Risk blindness often arises from a perceived efficiency gained through process automation or the curtailment of on-the-ground learning. When organizations substitute active engagement for passive oversight, staff lose critical exposure to routine deviations and process variables.
Senior staff who only approve system-generated risk assessments lack daily operational familiarity, making them susceptible to unseen vulnerabilities. Real risk assessment requires repeated, active interaction with process data—not just a review of output.
Fragmented Ownership and Deficient Learning Culture
Risk ownership must be robust and proximal. When roles are fragmented—where the “system” manages risk and people become mere approvers—vital warnings can be overlooked. A compliance-oriented learning culture that believes training or SOPs are enough to guard against operational threats falls deeper into the GI Joe fallacy: knowledge is mistaken for vigilance.
Instead, organizations need feedback loops, reflection, and opportunities to surface doubts and uncertainties. Training must be practical and interactive, not limited to information transfer.
Zemblanity: The Shadow of Risk Blindness
Zemblanity is the antithesis of serendipity in the context of pharmaceutical quality—it describes the persistent tendency for organizations to encounter negative, foreseeable outcomes when risk signals are repeatedly ignored, misunderstood, or left unacted upon.
When examining risk blindness, zemblanity stands as the practical outcome: a quality system that, rather than stumbling upon unexpected improvements or positive turns, instead seems trapped in cycles of self-created adversity. Unlike random bad luck, zemblanity results from avoidable and often visible warning signs—deviations that are rationalized, oversight meetings that miss the point, and cognitive biases like the GI Joe fallacy that lull teams into a false sense of mastery
Real-World Manifestations
Case: The Disappearing Deviation
Digital batch records reduced documentation errors and deviation reports, creating an illusion of process control. But when technology transfer led to out-of-spec events, the lack of manually trained eyes meant no one was poised to detect subtle process anomalies. Staff “knew” the process in theory—yet risk blindness set in because the signals were no longer being actively, expertly interpreted. Knowledge alone was not enough.
Case: Supplier Audit Blindness
Virtual audits relying solely on documentation missed chronic training issues that onsite teams would likely have noticed. The belief that checklist knowledge and documentation sufficed prevented the team from recognizing deeper underlying risks. Here, the GI Joe fallacy made the team believe their expertise was shield enough, when in reality, behavioral engagement and observation were necessary.
Counteracting Risk Blindness: Beyond Knowing to Acting
Effective pharmaceutical quality systems must intentionally cultivate and maintain pattern recognition capabilities across their workforce. This requires structured approaches that go beyond traditional training and incorporate the principles of expertise development:
Structured Exposure Programs: New professionals need systematic exposure to diverse risk scenarios—not just successful cases, but also investigations that went wrong, supplier audits that missed problems, and process changes that had unexpected consequences. This exposure must be guided by experienced mentors who can help identify and interpret relevant patterns.
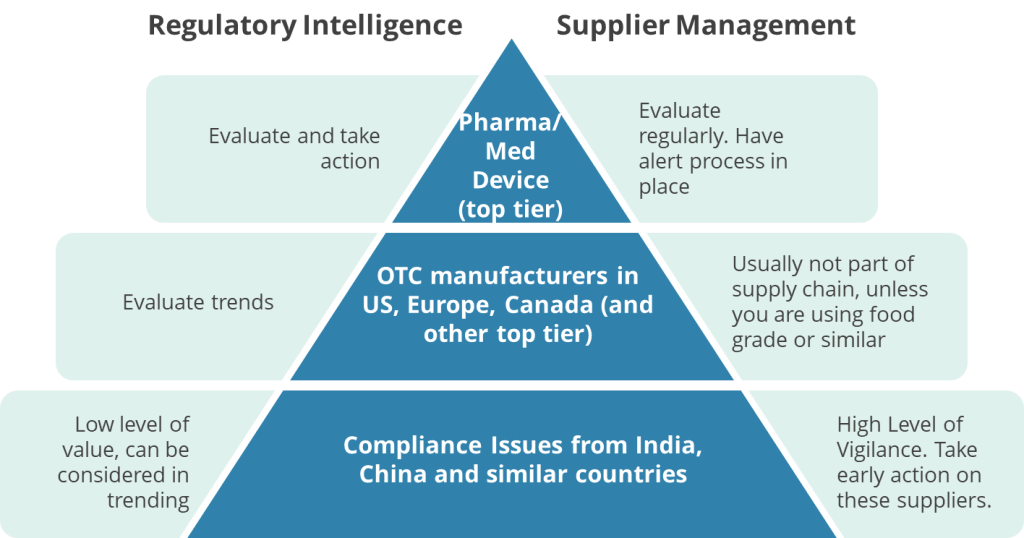
Cross-Functional Pattern Sharing: Different functional areas—manufacturing, quality control, regulatory affairs, supplier management—develop specialized pattern recognition capabilities. Organizations need systematic mechanisms for sharing these patterns across functions, ensuring that insights from one area can inform risk assessment in others.
Cognitive Diversity in Assessment Teams: Research demonstrates that diverse teams are better at pattern recognition than homogeneous groups, as different perspectives help identify patterns that might be missed by individuals with similar backgrounds and experience. Quality organizations should intentionally structure assessment teams to maximize cognitive diversity.
Systematic Challenge Processes: Pattern recognition can become biased or incomplete over time. Organizations need systematic processes for challenging established patterns—regular “red team” exercises, external perspectives, and structured devil’s advocate processes that test whether recognized patterns remain valid.
Reflective Practice Integration: Pattern recognition improves through reflection on both successes and failures. Organizations should create systematic opportunities for professionals to analyze their pattern recognition decisions, understand when their assessments were accurate or inaccurate, and refine their capabilities accordingly.
Using AI as a Learning Accelerator
AI and automation should support, not replace, human risk assessment. Tools can help new professionals identify patterns in data, but must be employed as aids to learning—not as substitutes for judgment or action.
Diagnosing and Treating Risk Blindness
Assess organizational risk literacy not by the presence of knowledge, but by the frequency of active, critical engagement with real risks. Use self-assessment questions such as:
- Do deviation investigations include frontline voices, not just system reviewers?
- Are new staff exposed to real processes and deviations, not just theoretical scenarios?
- Are risk reviews structured to challenge assumptions, not merely confirm them?
- Is there evidence that knowledge is regularly translated into action?
Why Preventing Risk Blindness Matters
Regulators evaluate quality maturity not simply by compliance, but by demonstrable capability to anticipate and mitigate risks. AI and digital transformation are intensifying the risk of the GI Joe fallacy by tempting organizations to substitute data and technology for judgment and action.
As experienced professionals retire, the gap between knowing and doing risks widening. Only organizations invested in hands-on learning, mentorship, and behavioral feedback will sustain true resilience.
Choosing Sight
Risk blindness is perpetuated by the dangerous notion that knowing is enough. The GI Joe fallacy teaches that organizational memory, vigilance, and capability require much more than knowledge—they demand deliberate structures, engaged cultures, and repeated practice that link theory to action.
Quality leaders must invest in real development, relentless engagement, and humility about the limits of their own knowledge. Only then will risk blindness be cured, and resilience secured.