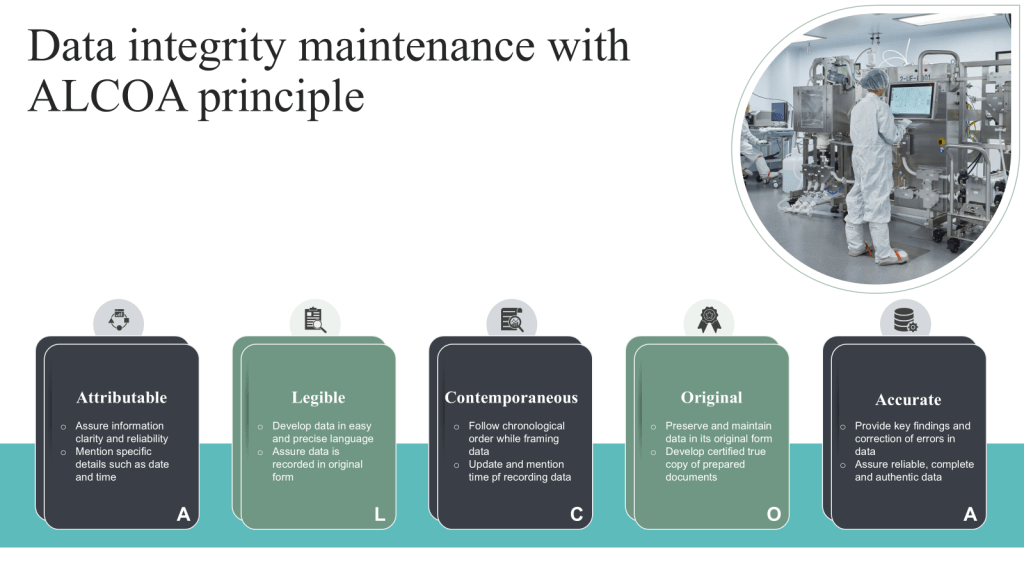
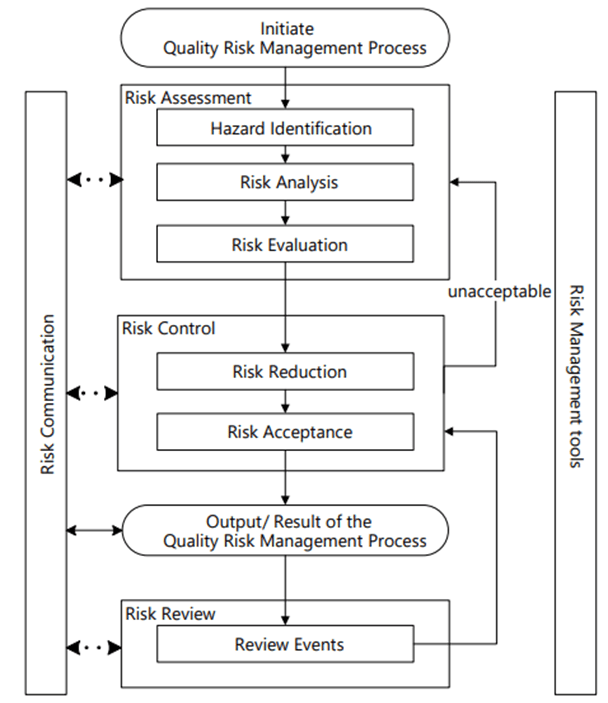
I often joke that as a biotech company employee I am primarily responsible for the manufacture of data (and water) first and foremost, and as a result we get a byproduct of a pharmaceutical drugs.
Many of us face challenges within organizations when it comes to effectively managing data. There tends to be a prevailing mindset that views data handling as a distinct activity, often relegated to the responsibility of someone else, rather than recognizing it as an integral part of everyone’s role. This separation can lead to misunderstandings and missed opportunities for utilizing data to its fullest potential.
Many organizations suffer some multifaceted challenges around data management:
- Lack of ownership: When data is seen as “someone else’s job,” it often falls through the cracks.
- Inconsistent quality: Without a unified approach, data quality can vary widely across departments.
- Missed insights: Siloed data management can result in missed opportunities for valuable insights.
- Inefficient processes: Disconnected data handling often leads to duplicated efforts and wasted resources.
Integrate Data into Daily Work
- Make data part of job descriptions: Clearly define data-related responsibilities for each role, emphasizing how data contributes to overall job performance.
- Provide context: Help employees understand how their data-related tasks directly impact business outcomes and decision-making processes.
- Encourage data-driven decision making: Train employees to use data in their daily work, from small decisions to larger strategic choices.
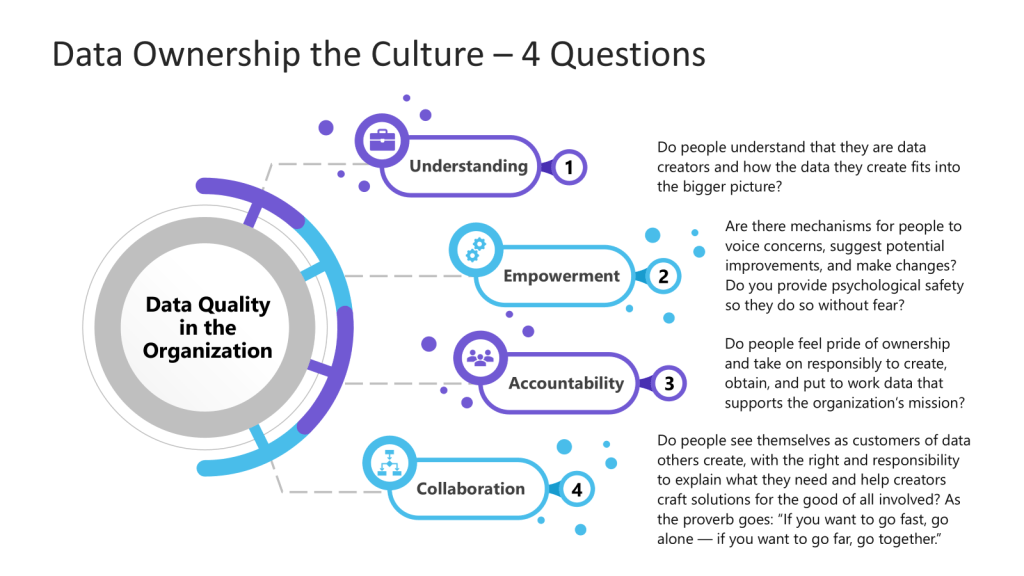
We want to strive to ask four questions.
- Understanding: Do people understand that they are data creators and how the data they create fits into the bigger picture?
- Empowerment: Are there mechanisms for people to voice concerns, suggest potential improvements, and make changes? Do you provide psychological safety so they do so without fear?
- Accountability: Do people feel pride of ownership and take on responsibly to create, obtain, and put to work data that supports the organization’s mission?
- Collaboration: Do people see themselves as customers of data others create, with the right and responsibility to explain what they need and help creators craft solutions for the good of all involved?
Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Fostering a data-driven culture is essential for organizations seeking to leverage the full potential of their data assets. This cultural shift requires a multi-faceted approach that starts at the top and permeates throughout the entire organization.
Leadership by example is crucial in establishing a data-driven culture. Managers and executives must actively incorporate data into their decision-making processes and discussions. By consistently referencing data in meetings, presentations, and communications, leaders demonstrate the value they place on data-driven insights. This behavior sets the tone for the entire organization, encouraging employees at all levels to adopt a similar approach. When leaders ask data-informed questions and base their decisions on factual evidence, it reinforces the importance of data literacy and analytical thinking across the company.
Continuous learning is another vital component of a data-driven culture. Organizations should invest in regular training sessions that enhance data literacy and proficiency with relevant analysis tools. These educational programs should be tailored to each role within the company, ensuring that employees can apply data skills directly to their specific responsibilities. By providing ongoing learning opportunities, companies empower their workforce to make informed decisions and contribute meaningfully to data-driven initiatives. This investment in employee development not only improves individual performance but also strengthens the organization’s overall analytical capabilities.
Creating effective feedback loops is essential for refining and improving data processes over time. Organizations should establish systems that allow employees to provide input on data-related practices and suggest enhancements. This two-way communication fosters a sense of ownership and engagement among staff, encouraging them to actively participate in the data-driven culture. By valuing employee feedback, companies can identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and uncover innovative ways to utilize data more effectively. These feedback mechanisms also help in closing the loop between data insights and actionable outcomes, ensuring that the organization continually evolves its data practices to meet changing needs and challenges.
Build Data as a Core Principle
- Focus on quality: Emphasize the importance of data quality to the mission of the organization
- Continuous improvement: Encourage ongoing refinement of data processes,.
- Pride in workmanship: Foster a sense of ownership and pride in data-related tasks, .
- Break down barriers: Promote cross-departmental collaboration on data initiatives and eliminate silos.
- Drive out fear: Create a safe environment for employees to report data issues or inconsistencies without fear of reprisal.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can effectively tie data to employees’ daily work and create a robust data culture that enhances overall performance and decision-making capabilities.