The draft revision of EU GMP Chapter 4 introduces what can only be described as a revolutionary framework for data governance systems. This isn’t merely an update to existing documentation requirements—it is a keystone document that cements the decade long paradigm shift of data governance as the cornerstone of modern pharmaceutical quality systems.
The Genesis of Systematic Data Governance
The most striking aspect of the draft Chapter 4 is the introduction of sections 4.10 through 4.18, which establish data governance systems as mandatory infrastructure within pharmaceutical quality systems. This comprehensive framework emerges from lessons learned during the past decade of data integrity enforcement actions and reflects the reality that modern pharmaceutical manufacturing operates in an increasingly digital environment where traditional documentation approaches are insufficient.
The requirement that regulated users “establish a data governance system integral to the pharmaceutical quality system” moves far beyond the current Chapter 4’s basic documentation requirements. This integration ensures that data governance isn’t treated as an IT afterthought or compliance checkbox, but rather as a fundamental component of how pharmaceutical companies ensure product quality and patient safety. The emphasis on integration with existing pharmaceutical quality systems builds on synergies that I’ve previously discussed in my analysis of how data governance, data quality, and data integrity work together as interconnected pillars.
The requirement for regular documentation and review of data governance arrangements establishes accountability and ensures continuous improvement. This aligns with my observations about risk-based thinking where effective quality systems must anticipate, monitor, respond, and learn from their operational environment.
Comprehensive Data Lifecycle Management
Section 4.12 represents perhaps the most technically sophisticated requirement in the draft, establishing a six-stage data lifecycle framework that covers creation, processing, verification, decision-making, retention, and controlled destruction. This approach acknowledges that data integrity cannot be ensured through point-in-time controls but requires systematic management throughout the entire data journey.
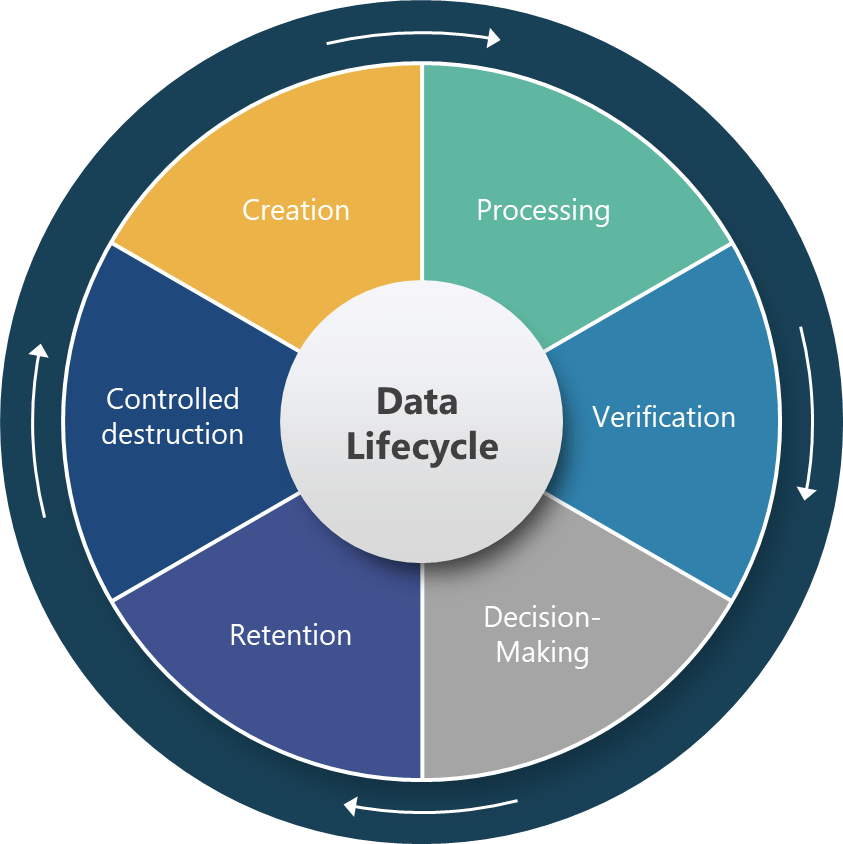
The specific requirement for “reconstruction of all data processing activities” for derived data establishes unprecedented expectations for data traceability and transparency. This requirement will fundamentally change how pharmaceutical companies design their data processing workflows, particularly in areas like process analytical technology (PAT), manufacturing execution systems (MES), and automated batch release systems where raw data undergoes significant transformation before supporting critical quality decisions.
The lifecycle approach also creates direct connections to computerized system validation requirements under Annex 11, as noted in section 4.22. This integration ensures that data governance systems are not separate from, but deeply integrated with, the technical systems that create, process, and store pharmaceutical data. As I’ve discussed in my analysis of computer system validation frameworks, effective validation programs must consider the entire system ecosystem, not just individual software applications.
Risk-Based Data Criticality Assessment
The draft introduces a sophisticated two-dimensional risk assessment framework through section 4.13, requiring organizations to evaluate both data criticality and data risk. Data criticality focuses on the impact to decision-making and product quality, while data risk considers the opportunity for alteration or deletion and the likelihood of detection. This framework provides a scientific basis for prioritizing data protection efforts and designing appropriate controls.
This approach represents a significant evolution from current practices where data integrity controls are often applied uniformly regardless of the actual risk or impact of specific data elements. The risk-based framework allows organizations to focus their most intensive controls on the data that matters most while applying appropriate but proportionate controls to lower-risk information. This aligns with principles I’ve discussed regarding quality risk management under ICH Q9(R1), where structured, science-based approaches reduce subjectivity and improve decision-making.
The requirement to assess “likelihood of detection” introduces a crucial element often missing from traditional data integrity approaches. Organizations must evaluate not only how to prevent data integrity failures but also how quickly and reliably they can detect failures that occur despite preventive controls. This assessment drives requirements for monitoring systems, audit trail analysis capabilities, and incident detection procedures.
Service Provider Oversight and Accountability
Section 4.18 establishes specific requirements for overseeing service providers’ data management policies and risk control strategies. This requirement acknowledges the reality that modern pharmaceutical operations depend heavily on cloud services, SaaS platforms, contract manufacturing organizations, and other external providers whose data management practices directly impact pharmaceutical company compliance.
The risk-based frequency requirement for service provider reviews represents a practical approach that allows organizations to focus oversight efforts where they matter most while ensuring that all service providers receive appropriate attention. For more details on the evolving regulatory expectations around supplier management see the post “draft Annex 11’s supplier oversight requirements“.
The service provider oversight requirement also creates accountability throughout the pharmaceutical supply chain, ensuring that data integrity expectations extend beyond the pharmaceutical company’s direct operations to encompass all entities that handle GMP-relevant data. This approach recognizes that regulatory accountability cannot be transferred to external providers, even when specific activities are outsourced.
Operational Implementation Challenges
The transition to mandatory data governance systems will present significant operational challenges for most pharmaceutical organizations. The requirement for “suitably designed systems, the use of technologies and data security measures, combined with specific expertise” in section 4.14 acknowledges that effective data governance requires both technological infrastructure and human expertise.
Organizations will need to invest in personnel with specialized data governance expertise, implement technology systems capable of supporting comprehensive data lifecycle management, and develop procedures for managing the complex interactions between data governance requirements and existing quality systems. This represents a substantial change management challenge that will require executive commitment and cross-functional collaboration.
The requirement for regular review of risk mitigation effectiveness in section 4.17 establishes data governance as a continuous improvement discipline rather than a one-time implementation project. Organizations must develop capabilities for monitoring the performance of their data governance systems and adjusting controls as risks evolve or new technologies are implemented.
The integration with quality risk management principles throughout sections 4.10-4.22 creates powerful synergies between traditional pharmaceutical quality systems and modern data management practices. This integration ensures that data governance supports rather than competes with existing quality initiatives while providing a systematic framework for managing the increasing complexity of pharmaceutical data environments.
The draft’s emphasis on data ownership throughout the lifecycle in section 4.15 establishes clear accountability that will help organizations avoid the diffusion of responsibility that often undermines data integrity initiatives. Clear ownership models provide the foundation for effective governance, accountability, and continuous improvement.
