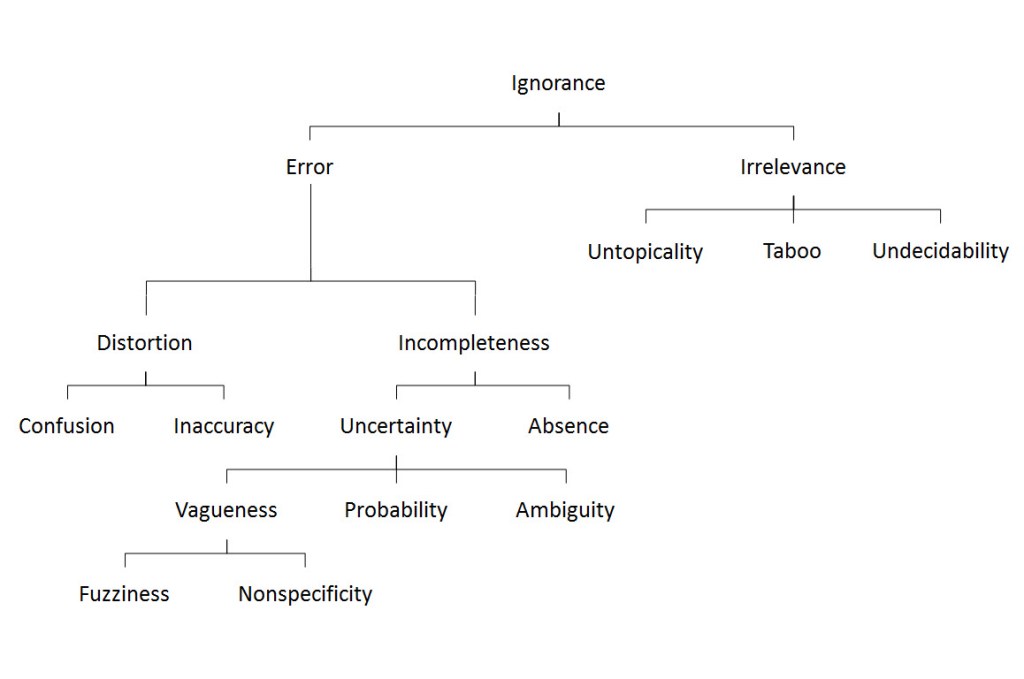
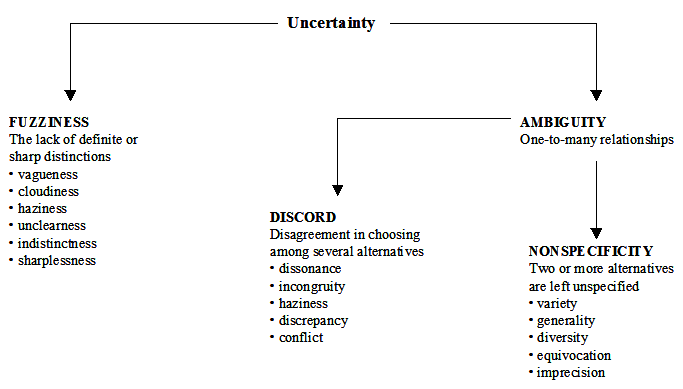
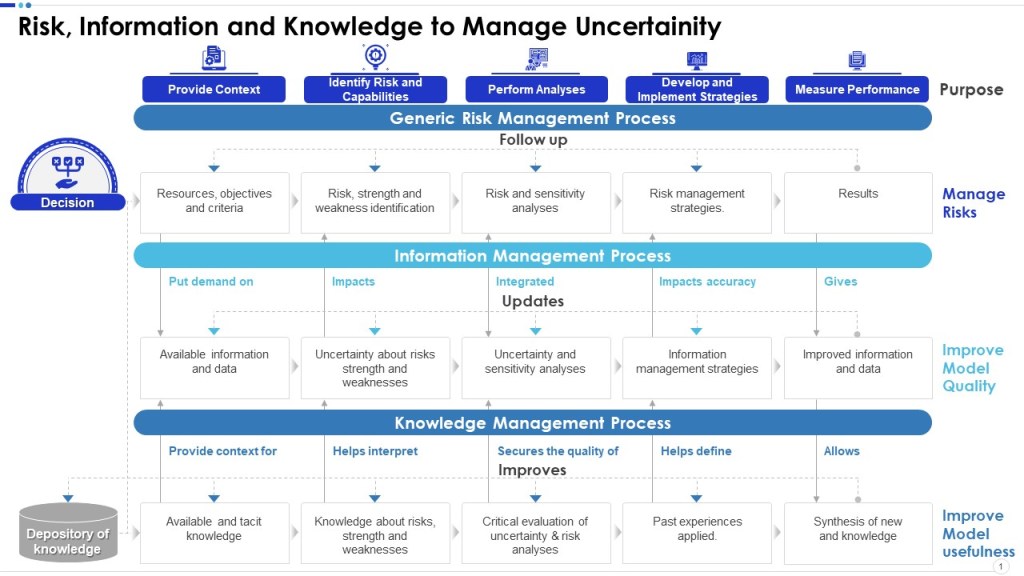
Risk-based thinking is a crucial component of modern quality management systems and consists of four key aspects: anticipate, monitor, respond, and learn. Each aspect ensures an organization can effectively manage and mitigate risks, enhancing overall performance and reliability.

Anticipate
Anticipating risks involves proactively identifying and analyzing potential risks that could impact the organization’s operations or objectives. This step is about foreseeing problems before they occur and planning how to address them. It requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s processes, the external and internal factors that could affect these processes, and the potential consequences of various risks. By anticipating risks, organizations can prepare more effectively and prevent many issues from occurring.
Monitor
Monitoring involves continuously observing and tracking the operational environment to detect risk indicators early. This ongoing process helps catch deviations from expected outcomes or standards, which could indicate the emergence of a risk. Effective monitoring relies on establishing metrics that help to quickly and accurately identify when things are starting to veer off course. This real-time data collection is crucial for enabling timely responses to potential threats.
Respond
Responding to risks is about taking appropriate actions to manage or mitigate identified risks based on their severity and potential impact. This step involves implementing the planned risk responses that were developed during the anticipation phase. The effectiveness of these responses often depends on the speed and decisiveness of the actions taken. Responses can include adjusting processes, reallocating resources, or activating contingency plans. The goal is to minimize the organization’s and its stakeholders’ negative impact.
Learn
Learning from the management of risks is a critical component that closes the loop of risk-based thinking. This aspect involves analyzing the outcomes of risk responses and understanding what worked well and what did not. Learning from these experiences is essential for continuous improvement. It helps organizations refine risk management processes, improve response strategies, and better prepare for future risks. This iterative learning process ensures that risk management efforts are increasingly effective over time.
The four aspects of risk-based thinking—anticipate, monitor, respond, and learn—form a continuous cycle that helps organizations manage uncertainties proactively. This approach protects the organization from potential downsides and enables it to seize opportunities that arise from a well-understood risk landscape. Organizations can enhance their resilience and adaptability by embedding these practices into everyday operations.

Implementing Risk-Based Thinking
1. Understand the Concept of Risk-Based Thinking
Risk-based thinking involves a proactive approach to identifying, analyzing, and addressing risks. This mindset should be ingrained in the organization’s culture and used as a basis for decision-making.
2. Identify Risks and Opportunities
Identify potential risks and opportunities. This can be achieved through various methods such as SWOT analysis, brainstorming sessions, and process mapping. It’s crucial to involve people at all levels of the organization since they can provide diverse perspectives on potential risks and opportunities.
3. Analyze and Prioritize Risks
Once risks and opportunities are identified, they should be analyzed to understand their potential impact and likelihood. This analysis will help prioritize which risks need immediate attention and which opportunities should be pursued.
4. Plan and Implement Responses
After prioritizing, develop strategies to address these risks and opportunities. Plans should include preventive measures for risks and proactive steps to seize opportunities. Integrating these plans into the organization’s overall strategy and daily operations is important to ensure they are effective.
5. Monitor and Review
Implementing risk-based thinking is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and reviewing of risks, opportunities, and the effectiveness of responses are crucial. This can be done through regular audits, performance evaluations, and feedback mechanisms. Adjustments should be made based on these reviews to improve the risk management process.
6. Learn and Improve
Organizations should learn from their experiences in managing risks and opportunities. This involves analyzing what worked well and what didn’t and using this information to improve future risk management efforts. Continuous improvement should be a key goal, aligning with the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle.
7. Documentation and Compliance
Maintaining proper documentation is essential for tracking and managing risk-based thinking activities. Documents such as risk registers, action plans, and review reports should be updated and readily available.
8. Training and Culture
Training and cultural adaptation are necessary to implement risk-based thinking effectively. All employees should be trained on the principles of risk-based thinking and how to apply them in their roles. Creating a culture encouraging open communication about risks and supporting risk-taking within defined limits is also vital.