According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2023, analytical and critical thinking are the 1st and 2nd most needed job skills (Quality Control is #10).
Analytical and critical thinking are two distinct cognitive processes often used interchangeably but have unique characteristics and purposes. Understanding the differences is essential as we hire and develop people.
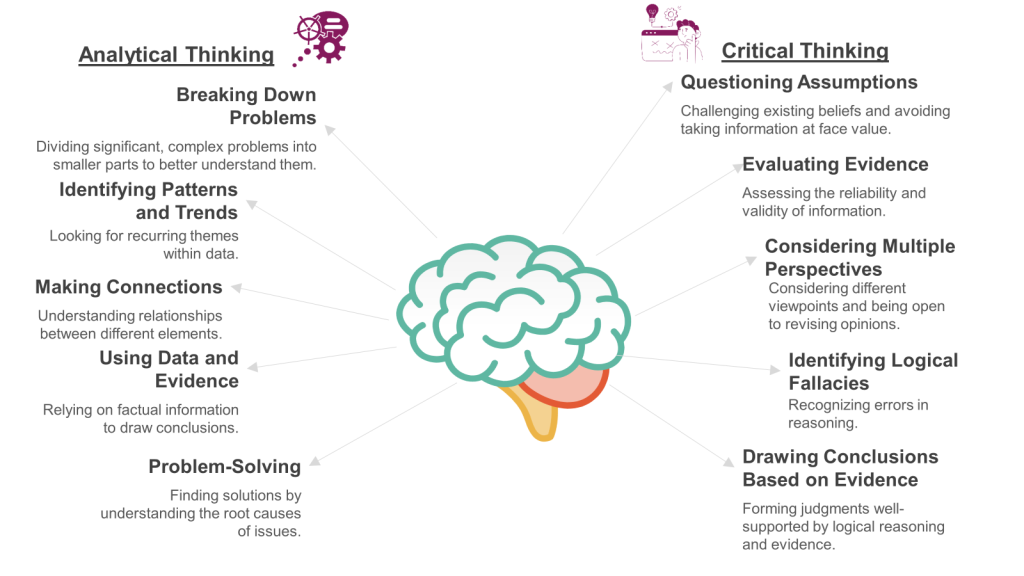
Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking involves separating complex information into smaller, more manageable parts to understand the underlying structure and relationships. It is a linear, step-by-step process that examines each component individually to identify patterns, trends, and cause-and-effect relationships. The goal is to draw logical conclusions based on the available data.
Key Aspects of Analytical Thinking:
- Breaking Down Problems: Dividing significant, complex problems into smaller parts to better understand them.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: Looking for recurring themes within data.
- Making Connections: Understanding relationships between different elements.
- Using Data and Evidence: Relying on factual information to draw conclusions.
- Problem-Solving: Finding solutions by understanding the root causes of issues.
Steps in Analytical Thinking:
- Gathering Relevant Information: Collecting all necessary data.
- Breaking Down Data: Dividing information into smaller, manageable parts.
- Examining Components: Analyzing each part to understand its role and relationship to the whole.
- Identifying Patterns: Looking for trends and cause-and-effect relationships.
- Drawing Conclusions: Making logical deductions based on the analysis[2][4][8].
Critical Thinking
On the other hand, critical thinking is a broader cognitive process that involves evaluating information and making judgments based on evidence. It is more holistic and reflective, considering the context, assumptions, and biases behind the information. Critical thinking aims to form well-reasoned judgments and decisions by synthesizing, evaluating, and reflecting on information from various sources.
Key Aspects of Critical Thinking:
- Questioning Assumptions: Challenging existing beliefs and avoiding taking information at face value.
- Evaluating Evidence: Assessing the reliability and validity of information.
- Considering Multiple Perspectives: Considering different viewpoints and being open to revising opinions.
- Identifying Logical Fallacies: Recognizing errors in reasoning.
- Drawing Conclusions Based on Evidence: Forming judgments well-supported by logical reasoning and evidence.
Steps in Critical Thinking:
- Gathering Relevant Information: Collecting all necessary data.
- Evaluating Information: Assessing the credibility and relevance of the information.
- Asking Questions: Probing more profoundly into the information to uncover hidden biases or unsupported claims.
- Formulating Ideas: Developing theories and ideas based on the evaluation.
- Considering Alternatives: Exploring different possibilities before reaching a conclusion.
- Testing Conclusions: Verifying if the evidence supports the conclusions.
Differences Between Analytical and Critical Thinking
Approach:
- Analytical Thinking: Linear and focused, breaking down problems into smaller components.
- Critical Thinking: Holistic and reflective, evaluating the credibility and relevance of information.
Goal:
- Analytical Thinking: Understand principles and identify patterns.
- Critical Thinking: Evaluate credibility, question assumptions, and make informed decisions.
Outcome:
- Analytical Thinking: Logical conclusions based on data.
- Critical Thinking: Well-reasoned judgments and decisions based on a comprehensive evaluation of information.
While both analytical and critical thinking are essential for effective problem-solving and decision-making, they serve different purposes and involve distinct processes. Analytical thinking focuses on breaking down information to understand its components, whereas critical thinking involves evaluating and synthesizing information to form well-reasoned judgments. Integrating both types of thinking can lead to more robust and informed decision-making.
Here is a table comparing analytical thinking and critical thinking based on the provided information:
| Aspect | Analytical Thinking | Critical Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breaking down complex information into smaller parts to understand its structure. | Evaluating information and making judgments based on evidence and reasoning. |
| Approach | Linear, step-by-step process. | Holistic, reflective, and considers multiple perspectives. |
| Goal | Understand principles, identify patterns, and find connections. | Form well-reasoned judgments and decisions. |
| Process | – Gather relevant information – Break down data – Examine components – Identify patterns – Draw conclusions | – Gather relevant information – Evaluate information – Ask questions – Formulate ideas – Consider alternatives – Test conclusions |
| Focus | Facts and evidence within the information. | Evaluating credibility, questioning assumptions, and considering outside knowledge. |
| Outcome | Logical conclusions based on data. | Well-reasoned judgments and decisions. |
| Use in Problem-Solving | Used to break down and understand complex problems. | Used to evaluate and make informed decisions about problems. |
| Examples of Use | Analyzing reports and scientific data analysis. | Evaluating arguments and making decisions. |
| Traits | – Logical – Detail-oriented – Systematic | – Open-minded – Skeptical – Reflective |


great read.
LikeLike