Empowerment is a foundational element of a quality culture, where workers are entrusted with the authority to make decisions, initiate actions, and take responsibility for the outcomes of their work. This approach not only enhances job satisfaction and productivity but also fosters a culture of autonomy and participation, which is essential for achieving high organizational performance. However, the concept of empowerment has sometimes been misinterpreted within quality management frameworks such as Total Quality Management (TQM), Lean, and Six Sigma. In these contexts, empowerment rhetoric is occasionally used to justify increased work demands and managerial oversight, rather than genuinely empowering workers to contribute to quality improvements. A true quality culture, therefore, requires a genuine commitment to empowering workers, ensuring that they have the autonomy to drive continuous improvement and innovation.
History of Worker Empowerment
The concept of empowerment has its roots in social movements, including the civil rights and women’s rights movements, where it was used to describe the process of gaining autonomy and self-determination for marginalized groups. In the context of management, empowerment gained prominence in the 1980s and 1990s as a way to improve organizational performance by engaging workers more effectively.
Several management thinkers have discussed and advocated for worker empowerment, contributing significantly to the development of this concept. Here are some key figures and their contributions:
Mary Parker Follett
- Autonomy and Collective Power: Follett emphasized the importance of giving workers autonomy to complete their jobs effectively. She believed that when workers have the freedom to work independently, they become happier, more productive, and more engaged. Follett’s “power with” principle suggests that power should be shared among many, rather than concentrated in a few hands, fostering a collaborative environment.
- Collaboration and Flexibility: Follett advocated for establishing personal ownership of company goals while allowing flexibility in achieving them. This approach encourages agile problem-solving and creative solutions that benefit the business.
Tom Peters
- Self-Managing Teams: Peters has been a strong advocate for creating self-managing teams where leadership roles rotate among members. He emphasizes the importance of listening to workers and believing in their unlimited potential. Peters’ philosophy includes empowering front-line staff to act as business teams, which can significantly enhance organizational performance.
- Empowerment through Leadership: Peters suggests that managers should be retrained to become listeners rather than talkers, fostering an environment where every worker feels valued and empowered to contribute.
W. Edwards Deming
- Involvement and Autonomy: Deming’s 14 Points for Management include principles that support worker empowerment, such as removing barriers to pride of workmanship and encouraging collaboration across departments. These principles aim to create an environment where workers feel valued and empowered to improve processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Deming’s emphasis on continuous improvement processes, like kaizen, involves worker participation, which can be seen as a form of empowerment. However, it is crucial to ensure that such participation is genuine and not merely rhetorical.
Rosabeth Moss Kanter
- Change Management: Kanter’s change management theory emphasizes creating a collaborative and transparent work environment. Her approach involves empowering worker by encouraging them to speak up, team up, and continuously work towards positive change within the organization.
- Empowerment through Participation: Kanter’s principles promote worker engagement and loyalty by involving them in organizational changes and decision-making processes.
Elton Mayo
- Human Relations Theory: Mayo’s work highlights the importance of social and relational factors in motivating workers. While not directly focused on empowerment, his theory suggests that workers are more motivated by attention and camaraderie than by monetary rewards alone. This perspective supports the idea that empowering workers involves recognizing their social needs and fostering a supportive work environment.
These thinkers have contributed to the understanding and implementation of worker empowerment by emphasizing autonomy, collaboration, and the importance of recognizing employee contributions. Their ideas continue to influence management practices today.
Dimensions of Empowerment
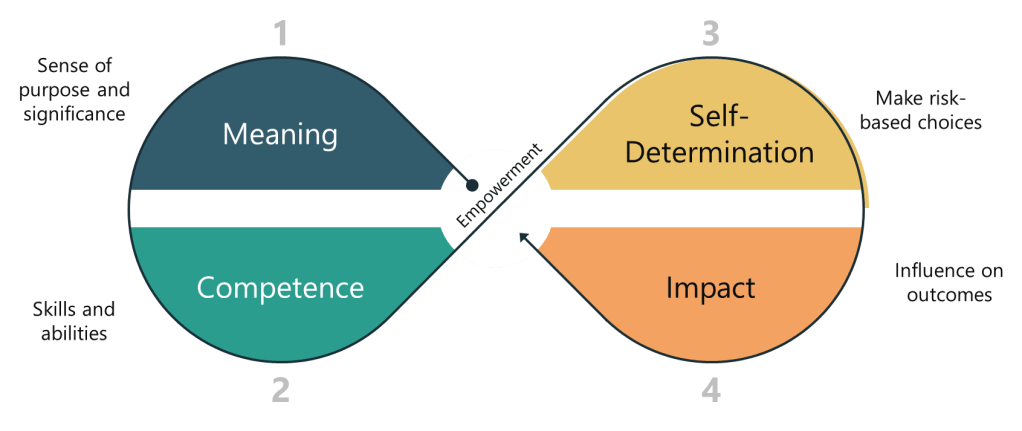
Empowerment can be understood through several key dimensions:
- Meaning: This refers to the sense of purpose and significance that employees derive from their work. When employees feel that their work is meaningful, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged.
- Competence: This dimension involves the skills and abilities that employees need to perform their jobs effectively. Empowerment requires that employees have the necessary competencies to make decisions and take actions.
- Self-Determination: This is the ability of employees to make choices and decisions about their work. Self-determination is crucial for empowerment, as it allows employees to feel in control of their tasks and outcomes.
- Impact: This dimension refers to the influence that employees have on organizational outcomes. When employees feel that their actions can make a difference, they are more likely to be empowered and motivated.
Implementation Practices
Implementing empowerment effectively requires several key practices:
- Clear Communication: Employees need clear expectations and goals to understand how their work contributes to the organization’s objectives.
- Training and Development: Providing employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to make informed decisions is essential for empowerment.
- Autonomy and Decision-Making Authority: Employees should have the freedom to make decisions within their scope of work.
- Feedback and Recognition: Regular feedback and recognition of employee contributions help reinforce empowerment by acknowledging their impact.
Deming’s Involvement in Worker Empowerment
W. Edwards Deming, a pioneer in quality management, emphasized the importance of employee involvement and empowerment through his 14 Points for Management. Specifically:
- Point 3: Cease dependence on inspection to achieve quality. Eliminate the need for inspection on a mass basis by building quality into the product in the first place. This point encourages organizations to empower workers by giving them the tools and training needed to ensure quality during production.
- Point 9: Break down barriers between departments. People in research, design, sales, and production must work as a team to foresee problems of production and in use that may be encountered with the product or service. This emphasizes collaboration and cross-functional teamwork, which is a form of empowerment.
- Point 12: Remove barriers that rob the hourly worker of his right to pride of workmanship. The responsibility of supervisors must be changed from sheer numbers to quality. This point directly addresses the need to empower workers by removing obstacles that prevent them from taking pride in their work.
Deming’s philosophy aligns with genuine empowerment by focusing on building quality into processes, fostering teamwork, and recognizing the value of worker pride and autonomy.
Denison and Organizational Culture
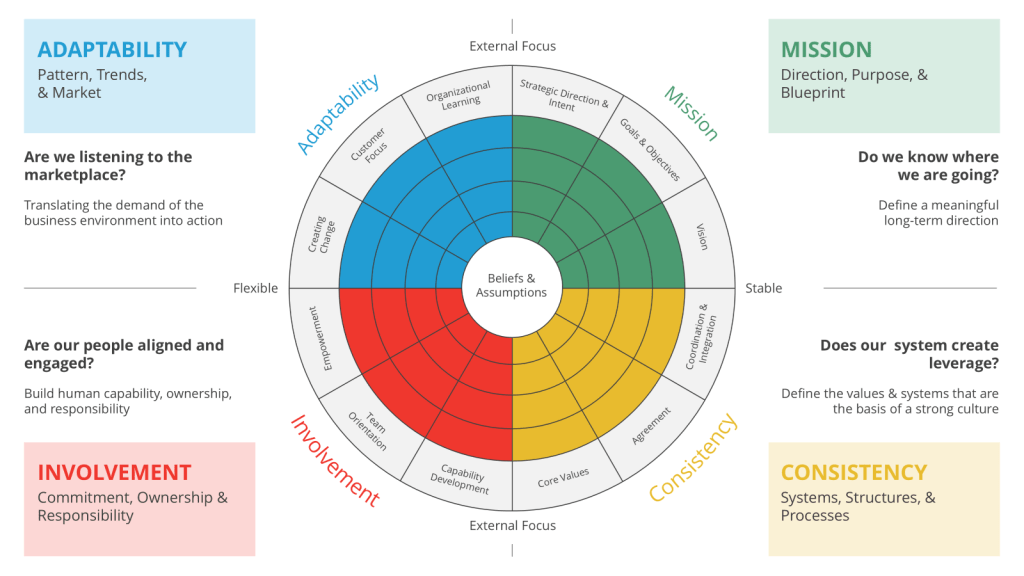
Daniel Denison’s work on organizational culture, particularly through the Denison Model, assesses culture across four critical traits: Mission, Involvement, Adaptability, and Consistency. Each of these traits is further divided into three indexes, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding and improving organizational culture.
Involvement and Empowerment
Denison’s model emphasizes the importance of Involvement, which is the degree to which individuals at all levels are engaged and feel a sense of ownership in the organization. This trait is crucial for empowerment, as it involves aligning employees with the business direction and positioning them to contribute to its success. The indexes under Involvement include aspects such as empowerment, team orientation, and capability development, all of which are essential for creating a culture where employees feel valued and empowered.
Empowerment through Cultural Alignment
Denison suggests that empowerment is not just about giving employees authority but also about ensuring they are aligned with and committed to the organization’s mission. By fostering a culture where workers are engaged and capable, organizations can enhance their performance metrics such as innovation, customer satisfaction, and worker satisfaction. Denison’s approach emphasizes the need for leaders to manage culture effectively, recognizing that culture can either support or hinder organizational goals.
Leadership and Empowerment
Denison’s model implies that leaders should focus on creating an environment where workers feel empowered to contribute. This involves not only setting a clear mission but also ensuring that systems and processes support worker involvement and adaptability. By doing so, leaders can foster a culture where workers are motivated to drive organizational success. Denison’s philosophy underscores the importance of balancing internal consistency with external adaptability, ensuring that organizations remain responsive to market changes while maintaining internal cohesion.
Denison’s work provides a structured framework for understanding how empowerment fits into a broader organizational culture. By emphasizing involvement and alignment, organizations can create an environment where workers feel empowered to contribute to success.
Misuse of Empowerment Rhetoric in Quality Methodologies
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM emphasizes worker involvement and empowerment as part of its comprehensive approach to quality improvement. However, the emphasis on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction can sometimes lead to increased workloads and stress for workers, undermining genuine empowerment.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency, often using empowerment rhetoric to encourage workers to participate in continuous improvement processes like kaizen. However, this can result in workers being manipulated into accepting intensified workloads without real control over their conditions.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma uses a structured approach to quality improvement, relying on trained professionals like Green and Black Belts. While it involves worker participation, the focus on defect reduction and process optimization can lead to a narrow definition of empowerment that serves managerial goals rather than worker autonomy.
Avoiding the Misuse of Empowerment Rhetoric
To avoid misusing empowerment rhetoric, organizations should focus on creating a genuine culture of empowerment by:
Ensuring Autonomy
Ensuring autonomy in the workplace is crucial for empowering workers. This involves providing them with real decision-making authority and the freedom to act within their roles. When workers have autonomy, they are more likely to feel a sense of ownership over their work, which can lead to increased motivation and productivity. Autonomy allows workers to make decisions that align with their expertise and judgment, reducing the need for constant managerial oversight. This not only speeds up decision-making processes but also fosters a culture of trust and responsibility. To implement autonomy effectively, organizations should clearly define the scope of decision-making authority for each role, ensure that workers understand their responsibilities, and provide the necessary resources and support to facilitate independent action. By doing so, organizations can create an environment where workers feel valued and empowered to contribute to organizational success.
Fostering Meaningful Work
Fostering meaningful work is essential for creating a sense of purpose and engagement among workers. This involves aligning worker tasks with organizational goals and ensuring that work contributes to a broader sense of purpose. When workers understand how their tasks fit into the larger picture, they are more likely to be motivated and committed to their work. Meaningful work encourages workers to see beyond their immediate tasks and understand the impact of their contributions on the organization and its stakeholders. To foster meaningful work, organizations should communicate clearly about organizational objectives and how individual roles contribute to these goals. Additionally, providing opportunities for workers to participate in goal-setting and strategic planning can enhance their sense of purpose and connection to the organization’s mission. By making work meaningful, organizations can create a workforce that is not only productive but also passionate about achieving shared objectives.
Developing Competence
Developing competence is a critical aspect of empowering workers . This involves investing in training and development to enhance their skills and abilities. When workers feel competent in their roles, they are more confident and capable of making decisions and taking initiatives. Competence development should be tailored to the needs of both the organization and the individual worker, ensuring that training programs are relevant and effective. Organizations should also provide ongoing opportunities for learning and growth, recognizing that competence is not static but rather something that evolves over time. By investing in worker development, organizations can create a skilled and adaptable workforce that is better equipped to handle challenges and drive innovation. Moreover, when workers see that their employer is committed to their growth, they are more likely to feel valued and committed to the organization.
Recognizing Impact
Recognizing the impact of workers contributions is vital for reinforcing their sense of empowerment. Regularly acknowledging and rewarding worker achievements helps to demonstrate that their work is valued and appreciated. This can be done through various means, such as public recognition, bonuses, or promotions. However, recognition should be genuine and specific, highlighting the specific contributions and outcomes that workers have achieved. Generic or superficial recognition can undermine its effectiveness and lead to skepticism among workers. To make recognition meaningful, organizations should establish clear criteria for what constitutes impactful work and ensure that recognition is timely and consistent. By acknowledging workers contributions, organizations can foster a culture of appreciation and motivation, encouraging workers to continue striving for excellence and making significant contributions to organizational success.
Encouraging Self-Determination
Encouraging self-determination is essential for empowering workers to take ownership of their work processes and outcomes. This involves supporting workers in making choices about how they complete their tasks and achieve their objectives. Self-determination allows workers to work in ways that best suit their skills and work styles, leading to increased job satisfaction and productivity. To encourage self-determination, organizations should provide workers with the flexibility to design their work processes and set their own goals, as long as these align with organizational objectives. Additionally, organizations should foster an environment where workers feel comfortable suggesting improvements and innovations, without fear of criticism or reprisal. By giving workers the autonomy to make decisions about their work, organizations can tap into their creativity and initiative, leading to more effective and efficient work processes. This approach not only empowers workers but also contributes to a more agile and responsive organization.
By focusing on these aspects, organizations can move beyond rhetorical empowerment and create a truly empowered workforce.
Conclusion
Worker empowerment is a powerful concept that, when implemented genuinely, can lead to significant improvements in organizational performance and worker satisfaction. However, its misuse in quality methodologies like TQM, Lean, and Six Sigma can undermine its potential benefits. By understanding the dimensions of empowerment and aligning practices with Deming’s principles, organizations can foster a culture of true empowerment that benefits both workers and the organization as a whole.
