Reading Strukmyer LLC’s recent FDA Warning Letter, and reflecting back to last year’s Colgate-Palmolive/Tom’s of Maine, Inc. Warning Letter, has me thinking of common language In both warning letters where the FDA asks for “A comprehensive, independent assessment of the design and control of your firm’s manufacturing operations, with a detailed and thorough review of all microbiological hazards.”
It is hard to read that as anything else than a clarion call to use a HACCP.
If that isn’t a HACCP, I don’t know what is. Given the FDA’s rich history and connection to the tool, it is difficult to imagine them thinking of any other tool. Sure, I can invent about 7 other ways to do that, but why bother when there is a great tool, full of powerful uses, waiting to be used that the regulators pretty much have in their DNA.
The Evolution of HACCP in FDA Regulation: A Journey to Enhanced Food Safety
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system has a fascinating history that is deeply intertwined with FDA regulations. Initially developed in the 1960s by NASA, the Pillsbury Company, and the U.S. Army, HACCP was designed to ensure safe food for space missions. This pioneering collaboration aimed to prevent food safety issues by identifying and controlling critical points in food processing. The success of HACCP in space missions soon led to its application in commercial food production.
In the 1970s, Pillsbury applied HACCP to its commercial operations, driven by incidents such as the contamination of farina with glass. This prompted Pillsbury to adopt HACCP more widely across its production lines. A significant event in 1971 was a panel discussion at the National Conference on Food Protection, which led to the FDA’s involvement in promoting HACCP for food safety inspections. The FDA recognized the potential of HACCP to enhance food safety standards and began to integrate it into its regulatory framework.
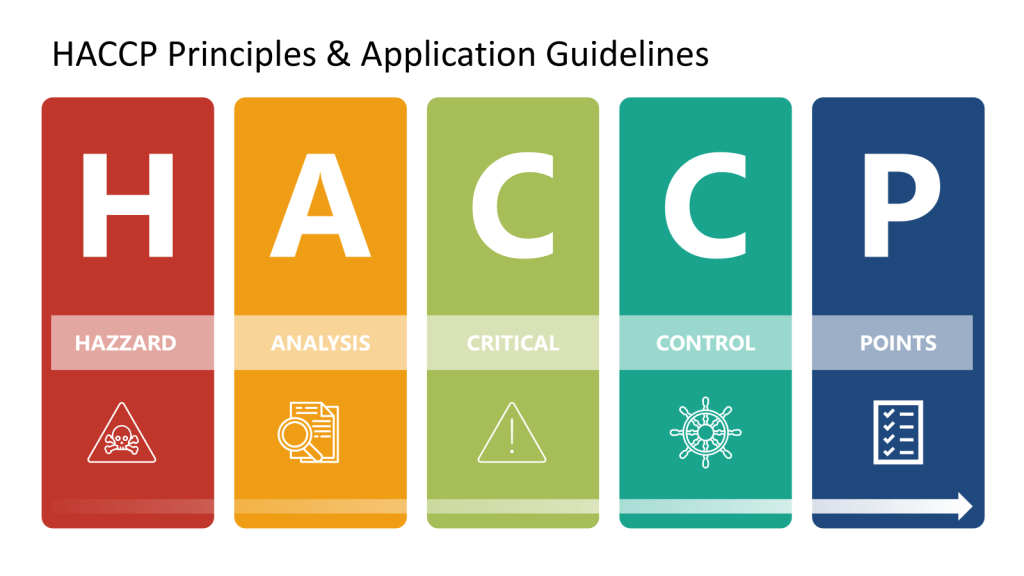
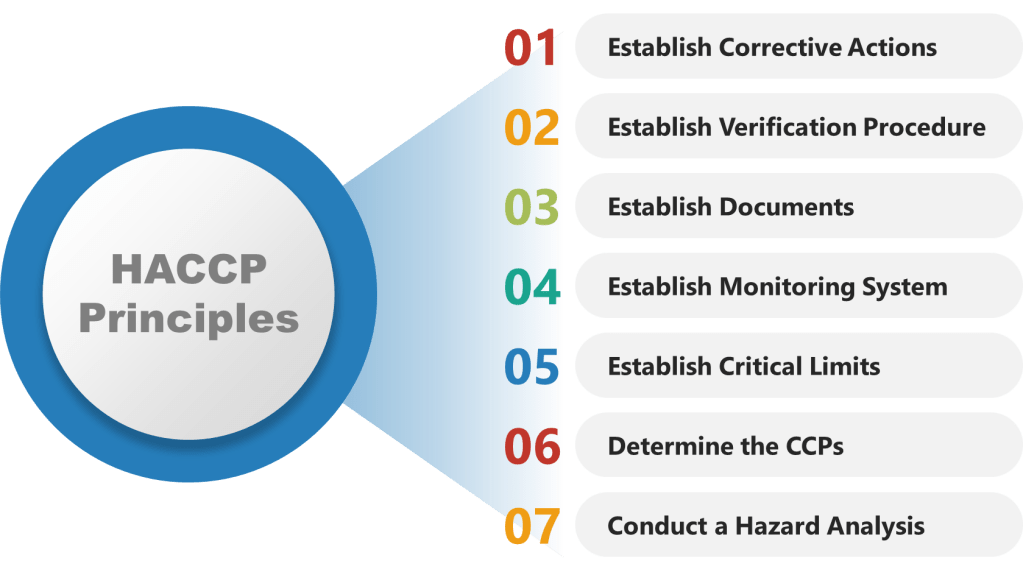
As HACCP gained prominence as a food safety standard in the 1980s and 1990s, the National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Criteria for Foods (NACMCF) refined its principles. The committee added preliminary steps and solidified the seven core principles of HACCP, which include hazard analysis, critical control points identification, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification procedures, and record-keeping. This structured approach helped standardize HACCP implementation across different sectors of the food industry.
A major milestone in the history of HACCP was the implementation of the Pathogen Reduction/HACCP Systems rule by the USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) in 1996. This rule mandated HACCP in meat and poultry processing facilities, marking a significant shift towards preventive food safety measures. By the late 1990s, HACCP became a requirement for all food businesses, with some exceptions for smaller operations. This widespread adoption underscored the importance of proactive food safety management.
The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) of 2011 further emphasized preventive controls, including HACCP, to enhance food safety across the industry. FSMA shifted the focus from responding to food safety issues to preventing them, aligning with the core principles of HACCP. Today, HACCP remains a cornerstone of food safety management globally, with ongoing training and certification programs available to ensure compliance with evolving regulations. The FDA continues to support HACCP as part of its broader efforts to protect public health through safe food production and processing practices. As the food industry continues to evolve, the principles of HACCP remain essential for maintaining high standards of food safety and quality.
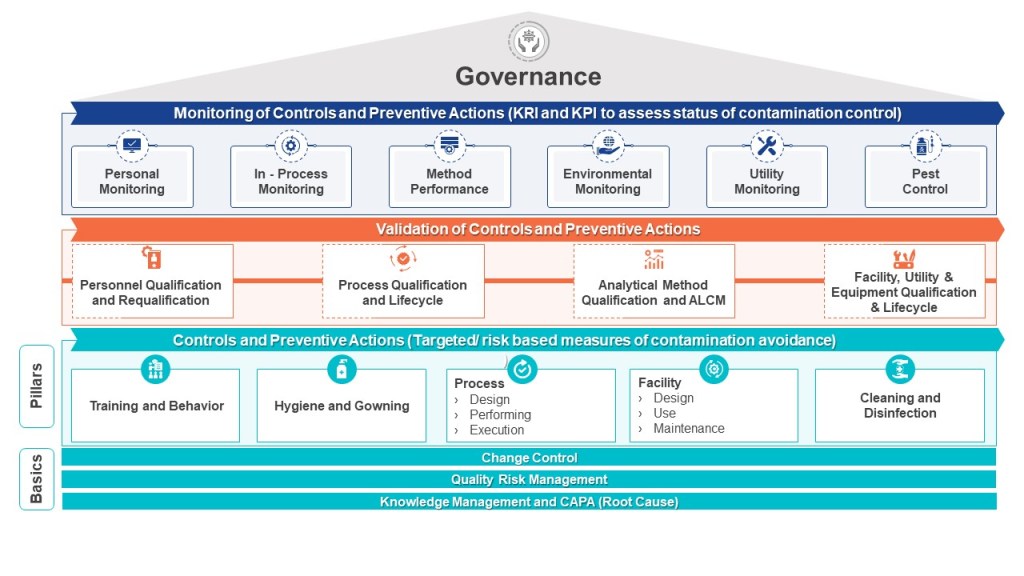
Why is a HACCP Useful in Biotech Manufacturing
The HACCP seeks to map a process – the manufacturing process, one cleanroom, a series of interlinked cleanrooms, or the water system – and identifies hazards (a point of contamination) by understanding the personnel, material, waste, and other parts of the operational flow. These hazards are assessed at each step in the process for their likelihood and severity. Mitigations are taken to reduce the risk the hazard presents (“a contamination control point”). Where a risk cannot be adequately minimized (either in terms of its likelihood of occurrence, the severity of its nature, or both), this “contamination control point” should be subject to a form of detection so that the facility has an understanding of whether the microbial hazard was potentially present at a given time, for a given operation. In other words, the “critical control point” provides a reasoned area for selecting a monitoring location. For aseptic processing, for example, the target is elimination, even if this cannot be absolutely demonstrated.
The HACCP approach can easily be applied to pharmaceutical manufacturing where it proves very useful for microbial control. Although alternative risk tools exist, such as Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, the HACCP approach is better for microbial control.
The HACCP is a core part of an effective layers of control analysis.
Conducting a HACCP
HACCP provides a systematic approach to identifying and controlling potential hazards throughout the production process.
Step 1: Conduct a Hazard Analysis
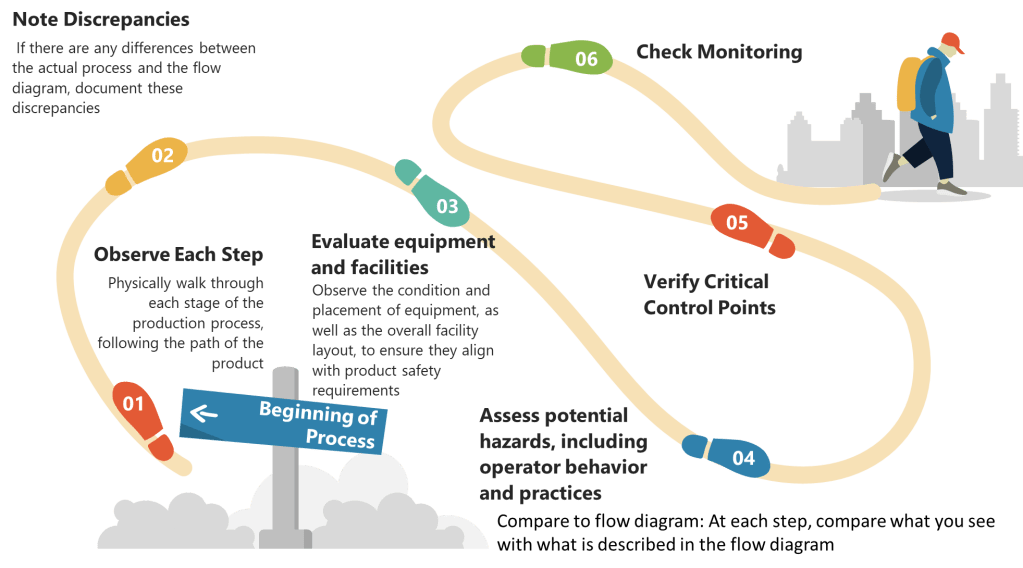
- List All Process Steps: Begin by detailing every step involved in your biotech manufacturing process, from raw material sourcing to final product packaging. Make sure to walk down the process thoroughly.
- Identify Potential Hazards: At each step, identify potential biological, chemical, and physical hazards. Biological hazards might include microbial contamination, while chemical hazards could involve chemical impurities or inappropriate reagents. Physical hazards might include particulates or inappropriate packaging materials.
- Evaluate Severity and Likelihood: Assess the severity and likelihood of each identified hazard. This evaluation helps prioritize which hazards require immediate attention.
- Determine Preventive Measures: Develop strategies to control significant hazards. This might involve adjusting process conditions, improving cleaning protocols, or enhancing monitoring systems.
- Document Justifications: Record the rationale behind including or excluding hazards from your analysis. This documentation is essential for transparency and regulatory compliance.
Step 2: Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs)
- Identify Control Points: Any step where biological, chemical, or physical factors can be controlled is considered a control point.
- Determine CCPs: Use a decision tree to identify which control points are critical. A CCP is a step at which control can be applied and is essential to prevent or eliminate a hazard or reduce it to an acceptable level.
- Establish Critical Limits: For each CCP, define the maximum or minimum values to which parameters must be controlled. These limits ensure that hazards are effectively managed.
| Control Points | Critical Control Points |
| Process steps where a control measure (mitigation activity) is necessary to prevent the hazard from occurring | Process steps where both control and monitoring are necessary to assure product quality and patient safety |
| Are not necessarily critical control points (CCPs) | Are also control points |
| Determined from the risk associated with the hazard | Determined through a decision tree |
Step 3: Establish Monitoring Procedures
- Develop Monitoring Plans: Create detailed plans for monitoring each CCP. This includes specifying what to monitor, how often, and who is responsible.
- Implement Monitoring Tools: Use appropriate tools and equipment to monitor CCPs effectively. This might include temperature sensors, microbial testing kits, or chemical analyzers.
- Record Monitoring Data: Ensure that all monitoring data is accurately recorded and stored for future reference.
Step 4: Establish Corrective Actions
- Define Corrective Actions: Develop procedures for when monitoring indicates that a CCP is not within its critical limits. These actions should restore control and prevent hazards.
- Proceduralize: You are establishing alternative control strategies here so make sure they are appropriately verified and controlled by process/procedure in the quality system.
- Train Staff: Ensure that all personnel understand and can implement corrective actions promptly.
Step 5: Establish Verification Procedures
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to verify that the HACCP system is functioning correctly. This includes reviewing monitoring data and observing process operations.
- Validation Studies: Perform validation studies to confirm that CCPs are effective in controlling hazards.
- Continuous Improvement: Use audit findings to improve the HACCP system over time.
Step 6: Establish Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Maintain Detailed Records: Keep comprehensive records of all aspects of the HACCP system, including hazard analyses, CCPs, monitoring data, corrective actions, and verification activities.
- Ensure Traceability: Use documentation to ensure traceability throughout the production process, facilitating quick responses to any safety issues.
Step 7: Implement and Review the HACCP Plan
- Implement the Plan: Ensure that all personnel involved in biotech manufacturing understand and follow the HACCP plan.
- Regular Review: Regularly review and update the HACCP plan to reflect changes in processes, new hazards, or lessons learned from audits and incidents.