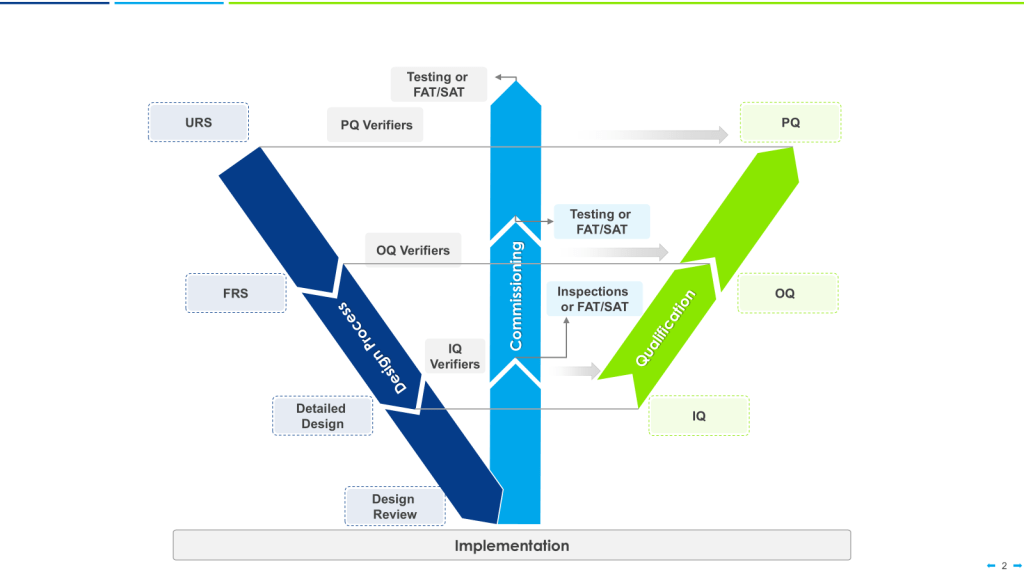
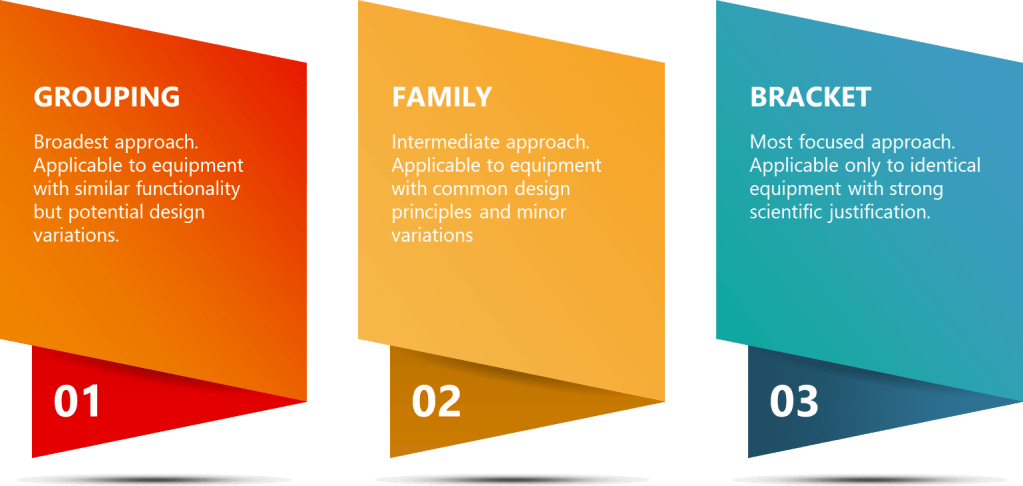
Strategic approaches like grouping, family classification, and bracketing are invaluable tools in the validation professional’s toolkit. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they represent distinct strategies with specific applications and regulatory considerations.
Equipment Grouping – The Broader Approach
Equipment grouping (sometimes called matrixing) represents a broad risk-based approach where multiple equipment items are considered equivalent for validation purposes. This strategy allows companies to optimize validation efforts by categorizing equipment based on design, functionality, and risk profiles. The key principle behind grouping is that equipment with similar characteristics can be validated using a common approach, reducing redundancy in testing and documentation.
Example – Manufacturing
Equipment grouping might apply to multiple buffer preparation tanks that share fundamental design characteristics but differ in volume or specific features. For example, a facility might have six 500L buffer preparation tanks from the same manufacturer, used for various buffer preparations throughout the purification process. These tanks might have identical mixing technologies, materials of construction, and cleaning processes.
Under a grouping approach, the manufacturer could develop one validation plan covering all six tanks. This plan would outline the overall validation strategy, including the rationale for grouping, the specific tests to be performed, and how results will be evaluated across the group. The plan might specify that while all tanks will undergo full Installation Qualification (IQ) to verify proper installation and utility connections, certain Operational Qualification (OQ) and Performance Qualification (PQ) tests can be consolidated.
The mixing efficiency test might be performed on only two tanks (e.g., the first and last installed), with results extrapolated to the entire group. However, critical parameters like temperature control accuracy would still be tested individually for each tank. The grouping approach would also allow for the application of the same cleaning validation protocol across all tanks, with appropriate justification. This might involve developing a worst-case scenario for cleaning validation based on the most challenging buffer compositions and applying the results across all tanks in the group.
Examples – QC
In the QC laboratory setting, equipment grouping might involve multiple identical analytical instruments such as HPLCs used for release testing. For instance, five HPLC systems of the same model, configured with identical detectors and software versions, might be grouped for qualification purposes.
The QC group could justify standardized qualification protocols across all five systems. This would involve developing a comprehensive protocol that covers all aspects of HPLC qualification but allows for efficient execution across the group. For example, software validation might be performed once and applied to all systems, given that they use identical software versions and configurations.
Consolidated performance testing could be implemented where appropriate. This might involve running system suitability tests on a representative sample of HPLCs rather than exhaustively on each system. However, critical performance parameters like detector linearity would still be verified individually for each HPLC to ensure consistency across the group.
Uniform maintenance and calibration schedules could be established for the entire group, simplifying ongoing management and reducing the risk of overlooking maintenance tasks for individual units. This approach ensures consistent performance across all grouped HPLCs while optimizing resource utilization.
Equipment grouping provides broad flexibility but requires careful consideration of which validation elements truly can be shared versus those that must remain equipment-specific. The key to successful grouping lies in thorough risk assessment and scientific justification for any shared validation elements.
Family Approach: Categorizing Based on Common Characteristics
The family approach represents a more structured categorization methodology where equipment is grouped based on specific common characteristics including identical risk classification, common intended purpose, and shared design and manufacturing processes. Family grouping typically applies to equipment from the same manufacturer with minor permissible variations. This approach recognizes that while equipment within a family may not be identical, their core functionalities and critical quality attributes are sufficiently similar to justify a common validation approach with specific considerations for individual variations.
Example – Manufacturing
A family approach might apply to chromatography skids designed for different purification steps but sharing the same basic architecture. For example, three chromatography systems from the same manufacturer might have different column sizes and flow rates but identical control systems, valve technologies, and sensor types.
Under a family approach, base qualification protocols would be identical for all three systems. This core protocol would cover common elements such as control system functionality, alarm systems, and basic operational parameters. Each system would undergo full IQ verification to ensure proper installation, utility connections, and compliance with design specifications. This individual IQ is crucial as it accounts for the specific installation environment and configuration of each unit.
OQ testing would focus on the specific operating parameters for each unit while leveraging a common testing framework. All systems might undergo the same sequence of tests (e.g., flow rate accuracy, pressure control, UV detection linearity), but the acceptance criteria and specific test conditions would be tailored to each system’s operational range. This approach ensures that while the overall qualification strategy is consistent, each system is verified to perform within its specific design parameters.
Shared control system validation could be leveraged across the family. Given that all three systems use identical control software and hardware, a single comprehensive software validation could be performed and applied to all units. This might include validation of user access controls, data integrity features, and critical control algorithms. However, system-specific configuration settings would still need to be verified individually.
Example – QC
In QC testing, a family approach could apply to dissolution testers that serve the same fundamental purpose but have different configurations. For instance, four dissolution testers might have the same underlying technology and control systems but different numbers of vessels or sampling configurations.
The qualification strategy could include common template protocols with configuration-specific appendices. This approach allows for a standardized core qualification process while accommodating the unique features of each unit. The core protocol might cover elements common to all units, such as temperature control accuracy, stirring speed precision, and basic software functionality.
Full mechanical verification would be performed for each unit to account for the specific configuration of vessels and sampling systems. This ensures that despite being part of the same family, each unit’s unique physical setup is thoroughly qualified.
A shared software validation approach could be implemented, focusing on the common control software used across all units. This might involve validating core software functions, data processing algorithms, and report generation features. However, configuration-specific software settings and any unique features would require individual verification.
Configuration-specific performance testing would be conducted to address the unique aspects of each unit. For example, a dissolution tester with automated sampling would undergo additional qualification of its sampling system, while units with different numbers of vessels might require specific testing to ensure uniform performance across all vessels.
The family approach provides a middle ground, recognizing fundamental similarities while still acknowledging equipment-specific variations that must be qualified independently. This strategy is particularly useful in biologics manufacturing and QC, where equipment often shares core technologies but may have variations to accommodate different product types or analytical methods.
Bracketing Approach: Strategic Testing Reduction
Bracketing represents the most targeted approach, involving the selective testing of representative examples from a group of identical equipment to reduce the overall validation burden. This approach requires rigorous scientific justification and risk assessment to demonstrate that the selected “brackets” truly represent the performance of all units. Bracketing is based on the principle that if the extreme cases (brackets) meet acceptance criteria, units falling within these extremes can be assumed to comply as well.
Example – Manufacturing
Bracketing might apply to multiple identical bioreactors. For example, a facility might have six 2000L single-use bioreactors of identical design, from the same manufacturing lot, installed in similar environments, and operated by the same control system.
Under a bracketing approach, all bioreactors would undergo basic installation verification to ensure proper setup and connection to utilities. This step is crucial to confirm that each unit is correctly installed and ready for operation, regardless of its inclusion in comprehensive testing.
Only two bioreactors (typically the minimum and maximum in the installation sequence) might undergo comprehensive OQ testing. This could include detailed evaluation of temperature control systems, agitation performance, gas flow accuracy, and pH/DO sensor functionality. The justification for this approach would be based on the identical design and manufacturing of the units, with the assumption that any variation due to manufacturing or installation would be most likely to manifest in the first or last installed unit.
Temperature mapping might be performed on only two units with justification that these represent “worst-case” positions. For instance, the units closest to and farthest from the HVAC outlets might be selected for comprehensive temperature mapping studies. These studies would involve placing multiple temperature probes throughout the bioreactor vessel and running temperature cycles to verify uniform temperature distribution and control.
Process performance qualification might be performed on a subset of reactors. This could involve running actual production processes (or close simulations) on perhaps three of the six reactors – for example, the first installed, the middle unit, and the last installed. These runs would evaluate critical process parameters and quality attributes to demonstrate consistent performance across the bracketed group.
Example – QC
Bracketing might apply to a set of identical incubators used for microbial testing. For example, eight identical incubators might be installed in the same laboratory environment.
The bracketing strategy could include full IQ documentation for all units to ensure proper installation and basic functionality. This step verifies that each incubator is correctly set up, connected to appropriate utilities, and passes basic operational checks.
Comprehensive temperature mapping would be performed for only the first and last installed units. This intensive study would involve placing calibrated temperature probes throughout the incubator chamber and running various temperature cycles to verify uniform heat distribution and precise temperature control. The selection of the first and last units is based on the assumption that any variations due to manufacturing or installation would be most likely to appear in these extreme cases.
Challenge testing on a subset representing different locations in the laboratory might be conducted. This could involve selecting incubators from different areas of the lab (e.g., near windows, doors, or HVAC vents) for more rigorous performance testing. These tests might include recovery time studies after door openings, evaluation of temperature stability under various load conditions, and assessment of humidity control (if applicable).
Ongoing monitoring that continuously verifies the validity of the bracketing approach would be implemented. This might involve rotating additional performance tests among all units over time or implementing a program of periodic reassessment to confirm that the bracketed approach remains valid. For instance, annual temperature distribution studies might be rotated among all incubators, with any significant deviations triggering a reevaluation of the bracketing strategy.
Key Differences and Selection Criteria
The primary differences between these approaches can be summarized in several key areas:
Scope and Application
Grouping is the broadest approach, applicable to equipment with similar functionality but potential design variations. This strategy is most useful when dealing with a wide range of equipment that serves similar purposes but may have different manufacturers or specific features. For example, in a large biologics facility, grouping might be applied to various types of pumps used throughout the manufacturing process. While these pumps may have different flow rates or pressure capabilities, they could be grouped based on their common function of fluid transfer and similar cleaning requirements.
The Family approach is an intermediate strategy, applicable to equipment with common design principles and minor variations. This is particularly useful for equipment from the same manufacturer or product line, where core technologies are shared but specific configurations may differ. In a QC laboratory, a family approach might be applied to a range of spectrophotometers from the same manufacturer. These instruments might share the same fundamental optical design and software platform but differ in features like sample capacity or specific wavelength ranges.
Bracketing is the most focused approach, applicable only to identical equipment with strong scientific justification. This strategy is best suited for situations where multiple units of the exact same equipment model are installed under similar conditions. For example, in a fill-finish operation, bracketing might be applied to a set of identical lyophilizers installed in the same clean room environment.
Testing Requirements
In a Grouping approach, each piece typically requires individual testing, but with standardized protocols. This means that while the overall validation strategy is consistent across the group, specific tests are still performed on each unit to account for potential variations. For instance, in a group of buffer preparation tanks, each tank would undergo individual testing for critical parameters like temperature control and mixing efficiency, but using a standardized testing protocol developed for the entire group.
The Family approach involves core testing that is standardized, with variations to address equipment-specific features. This allows for a more efficient validation process where common elements are tested uniformly across the family, while specific features of each unit are addressed separately. In the case of a family of chromatography systems, core functions like pump operation and detector performance might be tested using identical protocols, while specific column compatibility or specialized detection modes would be validated individually for units that possess these features.
Bracketing involves selective testing of representative units with extrapolation to the remaining units. This approach significantly reduces the overall testing burden but requires robust justification. For example, in a set of identical bioreactors, comprehensive performance testing might be conducted on only the first and last installed units, with results extrapolated to the units in between. However, this approach necessitates ongoing monitoring to ensure the continued validity of the extrapolation.
Documentation Needs
Grouping requires individual documentation with cross-referencing to shared elements. Each piece of equipment within the group would have its own validation report, but these reports would reference a common validation master plan and shared testing protocols. This approach ensures that while each unit is individually accounted for, the efficiency gains of the grouping strategy are reflected in the documentation.
The Family approach typically involves standardized core documentation with equipment-specific supplements. This might manifest as a master validation report for the entire family, with appendices or addenda addressing the specific features or configurations of individual units. This structure allows for efficient document management while still providing a complete record for each piece of equipment.
Bracketing necessitates a comprehensive justification document plus detailed documentation for tested units. This approach requires the most rigorous upfront documentation to justify the bracketing strategy, including risk assessments and scientific rationale. The validation reports for the tested “bracket” units would be extremely detailed, as they serve as the basis for qualifying the entire set of equipment.
Risk Assessment
In a Grouping approach, the risk assessment is focused on demonstrating equivalence for specific validation purposes. This involves a detailed analysis of how variations within the group might impact critical quality attributes or process parameters. The risk assessment must justify why certain tests can be standardized across the group and identify any equipment-specific risks that need individual attention.
For the Family approach, risk assessment is centered on evaluating permissible variations within the family. This involves a thorough analysis of how differences in specific features or configurations might impact equipment performance or product quality. The risk assessment must clearly delineate which aspects of validation can be shared across the family and which require individual consideration.
Bracketing requires the most rigorous risk assessment to justify the extrapolation of results from tested units to non-tested units. This involves a comprehensive evaluation of potential sources of variation between units, including manufacturing tolerances, installation conditions, and operational factors. The risk assessment must provide a strong scientific basis
| Criteria | Group Approach | Family Approach | Bracket Approach |
| Scope and Application | Broadest approach. Applicable to equipment with similar functionality but potential design variations. | Intermediate approach. Applicable to equipment with common design principles and minor variations. | Most focused approach. Applicable only to identical equipment with strong scientific justification. |
| Equipment Similarity | Similar functionality, potentially different manufacturers or features. | Same manufacturer or product line, core technologies shared, specific configurations may differ. | Identical equipment models installed under similar conditions. |
| Testing Requirements | Each piece requires individual testing, but with standardized protocols. | Core testing is standardized, with variations to address equipment-specific features. | Selective testing of representative units with extrapolation to the remaining units. |
| Documentation Needs | Individual documentation with cross-referencing to shared elements. | Standardized core documentation with equipment-specific supplements. | Comprehensive justification document plus detailed documentation for tested units. |
| Risk Assessment Focus | Demonstrating equivalence for specific validation purposes. | Evaluating permissible variations within the family. | Most rigorous assessment to justify extrapolation of results. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to accommodate various equipment types. | Moderate flexibility within a defined family of equipment. | Low flexibility, requires high degree of equipment similarity. |
| Resource Efficiency | Moderate efficiency gains through standardized protocols. | High efficiency for core validation elements, with specific testing as needed. | Highest potential for efficiency, but requires strong justification. |
| Regulatory Considerations | Generally accepted with proper justification. | Well-established approach, often preferred for equipment from same manufacturer. | Requires most robust scientific rationale and ongoing verification. |
| Ideal Use Case | Large facilities with diverse equipment serving similar functions. | Product lines with common core technology but varying features. | Multiple identical units in same facility or laboratory. |