One thing we should all agree with is that we need reliable reliable, accurate, and trustworthy data. Which is why we strive for the principles of data governance, data quality, and data integrity, three interconnected concepts that work together to create a robust data management framework.

Overarching Framework: Data Governance
Data governance serves as the overarching framework that establishes the policies, procedures, and standards for managing data within an organization. It provides the structure and guidance necessary for effective data management, including:
- Defining roles and responsibilities for data management
- Establishing data policies and standards
- Creating processes for data handling and decision-making
- Ensuring compliance with regulations and internal policies
Data governance sets the stage for both data quality and data integrity initiatives by providing the necessary organizational structure and guidelines.
Data Quality: Ensuring Fitness for Purpose
Within the data governance framework, data quality focuses on ensuring that data is fit for its intended use. This involves:
- Assessing data against specific quality dimensions (e.g., accuracy, completeness, consistency, validity, timeliness)
- Implementing data cleansing and standardization processes
- Monitoring and measuring data quality metrics
- Continuously improving data quality through feedback loops and corrective actions
Data quality initiatives are guided by the policies and standards set forth in the data governance framework, ensuring that quality efforts align with organizational goals and requirements.
Data Integrity: Maintaining Trustworthiness
Data integrity works in tandem with data quality to ensure that data remains accurate, complete, consistent, and reliable throughout its lifecycle. The ALCOA+ principles, widely used in regulated industries, provide a comprehensive framework for ensuring data integrity.
ALCOA+ Principles
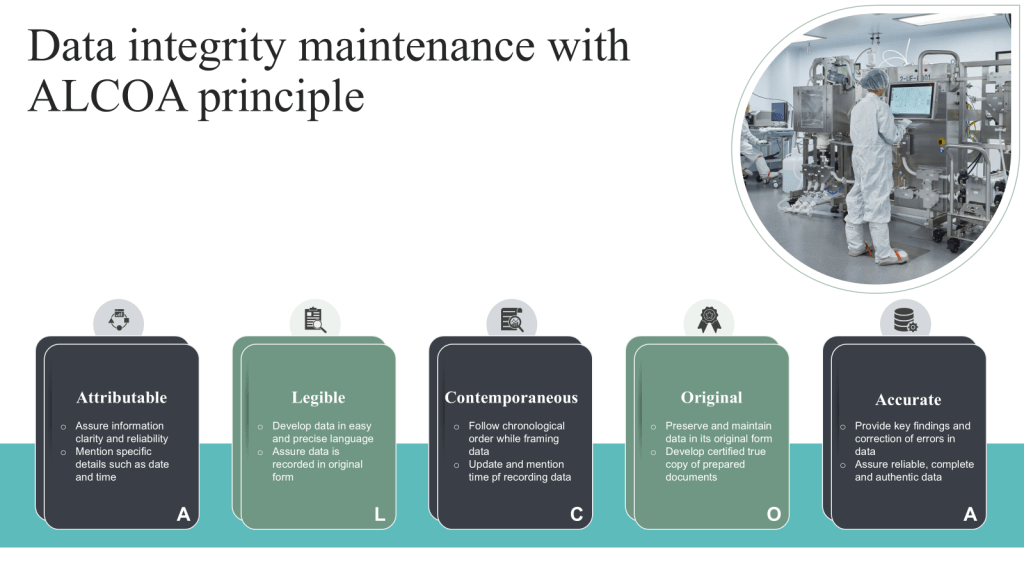
Attributable: Ensuring that data can be traced back to its origin and the individual responsible for its creation or modification.
Legible: Maintaining data in a clear, readable format that is easily understandable.
Contemporaneous: Recording data at the time of the event or observation to ensure accuracy and prevent reliance on memory.
Original: Preserving the original record or a certified true copy to maintain data authenticity.
Accurate: Ensuring data correctness and freedom from errors.
Complete: Capturing all necessary information without omissions.
Consistent: Maintaining data coherence across different systems and over time.
Enduring: Preserving data for the required retention period in a format that remains accessible.
Available: Ensuring data is readily accessible when needed for review or inspection.
Additional Data Integrity Measures
Security Measures: Implementing robust security protocols to protect data from unauthorized access, modification, or deletion.
Data Lineage Tracking: Establishing systems to monitor and document data transformations and origins throughout its lifecycle.
Auditability: Ensuring data changes are traceable through comprehensive logging and change management processes.
Data Consistency: Maintaining uniformity of data across various systems and databases.
Data integrity measures are often defined and enforced through data governance policies, while also supporting data quality objectives by preserving the accuracy and reliability of data. By adhering to the ALCOA+ principles and implementing additional integrity measures, organizations can ensure their data remains trustworthy and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Synergy in Action
The collaboration between these three elements can be illustrated through a practical example:
- Data Governance Framework: An organization establishes a data governance committee that defines policies for GxP data management, including data quality standards and security requirements.
- Data Quality Initiative: Based on the governance policies, the organization implements data quality checks to ensure GxP information is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. This includes:
- Regular data profiling to identify quality issues
- Data cleansing processes to correct errors
- Validation rules to prevent the entry of incorrect data
- Data Integrity Measures: To maintain the trustworthiness of GxP data, the organization:
- Implements access controls to prevent unauthorized modifications
- Qualifies system to meet ALCOA+ requirements
- Establishes audit trails to track changes to GxP records
By working together, these elements ensure that:
- GxP data meets quality standards (data quality)
- The data remains has a secure and unaltered lineage (data integrity)
- All processes align with organizational policies and regulatory requirements (data governance)
Continuous Improvement Cycle
The relationship between data governance, quality, and integrity is not static but forms a continuous improvement cycle:
- Data governance policies inform data quality and integrity standards.
- Data quality assessments and integrity checks provide feedback on the effectiveness of governance policies.
- This feedback is used to refine and improve governance policies, which in turn enhance data quality and integrity practices.
This ongoing cycle ensures that an organization’s data management practices evolve to meet changing business needs and technological advancements.
Data governance, data quality, and data integrity work together as a cohesive system to ensure that an organization’s data is not only accurate and reliable but also properly managed, protected, and utilized in alignment with business objectives and regulatory requirements. This integrated approach is essential for organizations seeking to maximize the value of their data assets while minimizing risks associated with poor data management.
A GMP Application based on ISA S88.01
A great example of Data governance is applying ISA S88.01 to enhance batch control processes and improve overall manufacturing operations.
Data Standardization and Structure
ISA S88.01 provides a standardized framework for batch control, including models and terminology that define the physical, procedural, and recipe aspects of batch manufacturing. This standardization directly supports data governance efforts by:
- Establishing a common language for batch processes across the organization
- Defining consistent data structures and hierarchies
- Facilitating clear communication between different departments and systems
Improved Data Quality
By following the ISA S88.01 standard, organizations can ensure higher data quality throughout the batch manufacturing process:
- Consistent Data Collection: The standard defines specific data points to be collected at each stage of the batch process, ensuring comprehensive and uniform data capture.
- Traceability: ISA S88.01 enables detailed tracking of each phase of the batch process, including raw materials used, process parameters, and quality data.
- Data Integrity: The structured approach helps maintain data integrity by clearly defining data sources, formats, and relationships.
Enhanced Data Management
The ISA S88.01 model supports effective data management practices:
- Modular Approach: The standard’s modular structure allows for easier management of data related to specific equipment, procedures, or recipes.
- Scalability: As processes or equipment change, the modular nature of ISA S88.01 facilitates easier updates to data structures and governance policies.
- Data Lifecycle Management: The standard’s clear delineation of process stages aids in managing data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to archival.
Regulatory Compliance
ISA S88.01 supports data governance efforts related to regulatory compliance:
- Audit Trails: The standard’s emphasis on traceability aligns with regulatory requirements for maintaining detailed records of batch processes.
- Consistent Documentation: Standardized terminology and structures facilitate the creation of consistent, compliant documentation.
Decision Support and Analytics
The structured data approach of ISA S88.01 enhances data governance initiatives aimed at improving decision-making:
- Data Integration: The standard facilitates easier integration of batch data with other enterprise systems, supporting comprehensive analytics.
- Performance Monitoring: Standardized data structures enable more effective monitoring and comparison of batch processes across different units or sites.
Continuous Improvement
Both data governance and ISA S88.01 support continuous improvement efforts:
- Process Optimization: The structured data from ISA S88.01 compliant systems can be more easily analyzed to identify areas for process improvement.
- Knowledge Management: The standard terminology and models facilitate better knowledge sharing and retention within the organization.
By leveraging ISA S88.01 in conjunction with robust data governance practices, organizations can create a powerful framework for managing batch processes, ensuring data quality, and driving operational excellence in manufacturing environments.