Building on our foundational exploration of process mapping as a scaling solution and the interplay of methodologies, frameworks, and tools in quality management, it is essential to position Business Process Management (BPM) as a dynamic discipline that harmonizes structural guidance with actionable execution. At its core, BPM functions as both an adaptive enterprise framework and a prescriptive methodology, with process architecture as the linchpin connecting strategic vision to operational reality. By integrating insights from our prior examinations of process landscapes, SIPOC analysis, and systems thinking principles, we unravel how organizations can leverage BPM’s dual nature to drive scalable, sustainable transformation.
BPM’s Dual Identity: Structural Framework and Execution Pathway
Business Process Management operates simultaneously as a conceptual framework and an implementation methodology. As a framework, BPM establishes the scaffolding for understanding how processes interact across an organization. It provides standardized visualization templates like BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) and value chain models, which create a common language for cross-functional collaboration. This framework perspective aligns with our earlier discussion of process landscapes, where hierarchical diagrams map core processes to supporting activities, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
Yet BPM transcends abstract structuring by embedding methodological rigor through its improvement lifecycle. This lifecycle-spanning scoping, modeling, automation, monitoring, and optimization-mirrors the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) approach applied in quality initiatives. For instance, the “As-Is” modeling phase employs swimlane diagrams to expose inefficiencies in handoffs between departments, while the “To-Be” design phase leverages BPMN simulations to stress-test proposed workflows. These methodological steps operationalize the framework, transforming architectural blueprints into executable workflows.
The interdependence between BPM’s framework and methodology becomes evident in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, where process architectures must align with ICH Q10 guidelines while methodological tools like change control protocols ensure compliance during execution. This duality enables organizations to maintain strategic coherence while adapting tactical approaches to shifting demands.
Process Architecture: The Structural Catalyst for Scalable Operations
Process architecture transcends mere process cataloging; it is the engineered backbone that ensures organizational processes collectively deliver value without redundancy or misalignment. Drawing from our exploration of process mapping as a scaling solution, effective architectures integrate three critical layers:
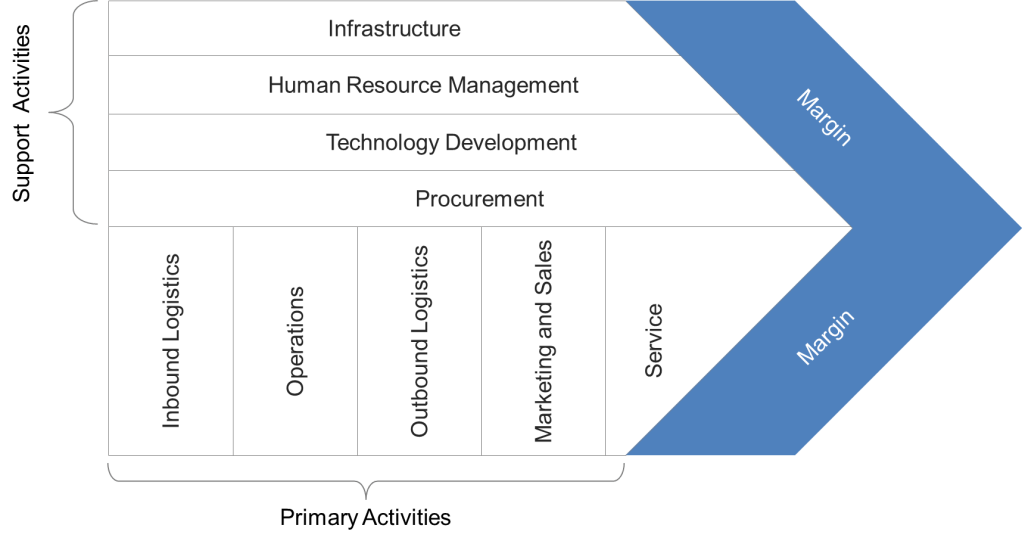
- Strategic Layer: Anchored in Porter’s Value Chain, this layer distinguishes primary activities (e.g., manufacturing, service delivery) from support processes (e.g., HR, IT). By mapping these relationships through high-level process landscapes, leaders can identify which activities directly impact competitive advantage and allocate resources accordingly.
- Operational Layer: Here, SIPOC (Supplier-Input-Process-Output-Customer) diagrams define process boundaries, clarifying dependencies between internal workflows and external stakeholders. For example, a SIPOC analysis in a clinical trial supply chain might reveal that delayed reagent shipments from suppliers (an input) directly impact patient enrollment timelines (an output), prompting architectural adjustments to buffer inventory.
- Execution Layer: Detailed swimlane maps and BPMN models translate strategic and operational designs into actionable workflows. These tools, as discussed in our process mapping series, prevent scope creep by explicitly assigning responsibilities (via RACI matrices) and specifying decision gates.
Implementing Process Architecture: A Phased Approach
Developing a robust process architecture requires methodical execution:
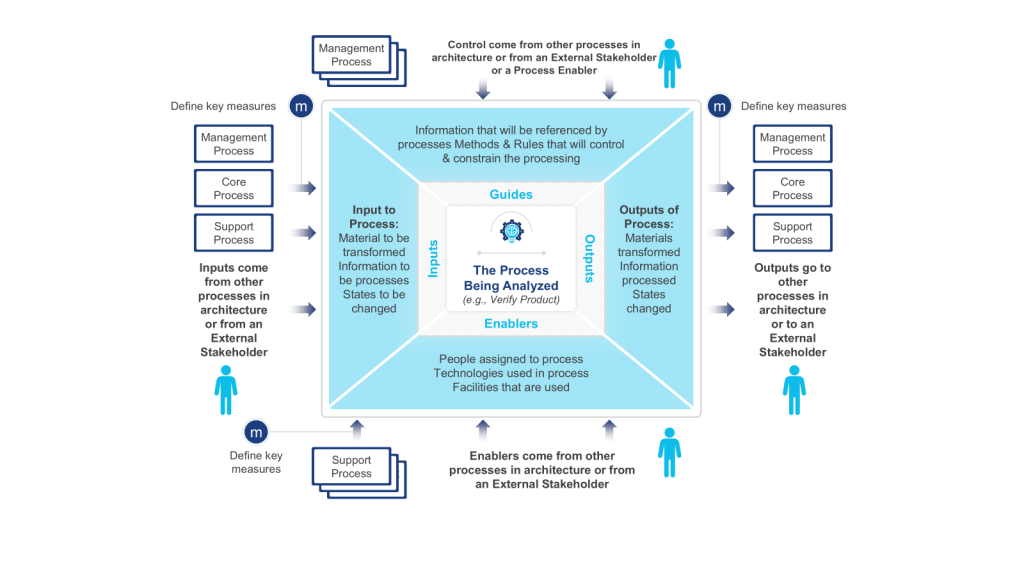
- Value Identification: Begin with value chain analysis to isolate core customer-facing processes. IGOE (Input-Guide-Output-Enabler) diagrams help validate whether each architectural component contributes to customer value. For instance, a pharmaceutical company might use IGOEs to verify that its clinical trial recruitment process directly enables faster drug development (a strategic objective).
- Interdependency Mapping: Cross-functional workshops map handoffs between departments using BPMN collaboration diagrams. These sessions often reveal hidden dependencies-such as quality assurance’s role in batch release decisions-that SIPOC analyses might overlook. By embedding RACI matrices into these models, organizations clarify accountability at each process juncture.
- Governance Integration: Architectural governance ties process ownership to performance metrics. A biotech firm, for example, might assign a Process Owner for drug substance manufacturing, linking their KPIs (e.g., yield rates) to architectural review cycles. This mirrors our earlier discussions about sustaining process maps through governance protocols.
Sustaining Architecture Through Dynamic Process Mapping
Process architectures are not static artifacts; they require ongoing refinement to remain relevant. Our prior analysis of process mapping as a scaling solution emphasized the need for iterative updates-a principle that applies equally to architectural maintenance:
- Quarterly SIPOC Updates: Revisiting supplier and customer relationships ensures inputs/outputs align with evolving conditions. A medical device manufacturer might adjust its SIPOC for component sourcing post-pandemic, substituting single-source suppliers with regional alternatives to mitigate supply chain risks.
- Biannual Landscape Revisions: Organizational restructuring (e.g., mergers, departmental realignments) necessitates value chain reassessment. When a diagnostics lab integrates AI-driven pathology services, its process landscape must expand to include data governance workflows, ensuring compliance with new digital health regulations.
- Trigger-Based IGOE Analysis: Regulatory changes or technological disruptions (e.g., adopting blockchain for data integrity) demand rapid architectural adjustments. IGOE diagrams help isolate which enablers (e.g., IT infrastructure) require upgrades to support updated processes.
This maintenance cycle transforms process architecture from a passive reference model into an active decision-making tool, echoing our findings on using process maps for real-time operational adjustments.
Unifying Framework and Methodology: A Blueprint for Execution
The true power of BPM emerges when its framework and methodology dimensions converge. Consider a contract manufacturing organization (CMO) implementing BPM to reduce batch release timelines:
- Framework Application:
- A value chain model prioritizes “Batch Documentation Review” as a critical path activity.
- SIPOC analysis identifies regulatory agencies as key customers of the release process.
- Methodological Execution:
- Swimlane mapping exposes delays in quality control’s document review step.
- BPMN simulation tests a revised workflow where parallel document checks replace sequential approvals.
- The organization automates checklist routing, cutting review time by 40%.
- Architectural Evolution:
- Post-implementation, the process landscape is updated to reflect QC’s reduced role in routine reviews.
- KPIs shift from “Documents Reviewed per Day” to “Right-First-Time Documentation Rate,” aligning with strategic goals for quality culture.
Strategic Insights for Practitioners
Architecture-Informed Problem Solving
A truly effective approach to process improvement begins with a clear understanding of the organization’s process architecture. When inefficiencies arise, it is vital to anchor any improvement initiative within the specific architectural layer where the issue is most pronounced. This means that before launching a solution, leaders and process owners should first diagnose whether the root cause of the problem lies at the strategic, operational, or tactical level of the process architecture. For instance, if an organization is consistently experiencing raw material shortages, the problem is situated within the operational layer. Addressing this requires a granular analysis of the supply chain, often using tools like SIPOC (Supplier, Input, Process, Output, Customer) diagrams to map supplier relationships and identify bottlenecks or gaps. The solution might involve renegotiating contracts with suppliers, diversifying the supplier base, or enhancing inventory management systems. On the other hand, if the organization is facing declining customer satisfaction, the issue likely resides at the strategic layer. Here, improvement efforts should focus on value chain realignment-re-examining how the organization delivers value to its customers, possibly by redesigning service offerings, improving customer touchpoints, or shifting strategic priorities. By anchoring problem-solving efforts in the appropriate architectural layer, organizations ensure that solutions are both targeted and effective, addressing the true source of inefficiency rather than just its symptoms.
Methodology Customization
No two organizations are alike, and the maturity of an organization’s processes should dictate the methods and tools used for business process management (BPM). Methodology customization is about tailoring the BPM lifecycle to fit the unique needs, scale, and sophistication of the organization. For startups and rapidly growing companies, the priority is often speed and adaptability. In these environments, rapid prototyping with BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) can be invaluable. By quickly modeling and testing critical workflows, startups can iterate and refine their processes in real time, responding nimbly to market feedback and operational challenges. Conversely, larger enterprises with established Quality Management Systems (QMS) and more complex process landscapes require a different approach. Here, the focus shifts to integrating advanced tools such as process mining, which enables organizations to monitor and analyze process performance at scale. Process mining provides data-driven insights into how processes actually operate, uncovering hidden inefficiencies and compliance risks that might not be visible through manual mapping alone. In these mature organizations, BPM methodologies are often more formalized, with structured governance, rigorous documentation, and continuous improvement cycles embedded in the organizational culture. The key is to match the BPM approach to the organization’s stage of development, ensuring that process management practices are both practical and impactful.
Metrics Harmonization
For process improvement initiatives to drive meaningful and sustainable change, it is essential to align key performance indicators (KPIs) with the organization’s process architecture. This harmonization ensures that metrics at each architectural layer support and inform one another, creating a cascade of accountability that links day-to-day operations with strategic objectives. At the strategic layer, high-level metrics such as Time-to-Patient provide a broad view of organizational performance and customer impact. These strategic KPIs should directly influence the targets set at the operational layer, such as Batch Record Completion Rates, On-Time Delivery, or Defect Rates. By establishing this alignment, organizations can ensure that improvements made at the operational level contribute directly to strategic goals, rather than operating in isolation. Our previous work on dashboards for scaling solutions illustrates how visualizing these relationships can enhance transparency and drive performance. Dashboards that integrate metrics from multiple architectural layers enable leaders to quickly identify where breakdowns are occurring and to trace their impact up and down the value chain. This integrated approach to metrics not only supports better decision-making but also fosters a culture of shared accountability, where every team understands how their performance contributes to the organization’s overall success.