The allure of shiny new tools in quality management is undeniable. Like magpies drawn to glittering objects, professionals often collect methodologies and technologies without a cohesive strategy. This “magpie syndrome” creates fragmented systems—FMEA here, 5S there, Six Sigma sprinkled in—that resemble disjointed toolkits rather than coherent ecosystems. The result? Confusion, wasted resources, and quality systems that look robust on paper but crumble under scrutiny. The antidote lies in reimagining quality systems not as static machines but as living organizations that evolve, adapt, and thrive.
The Shift from Machine Logic to Organic Design
Traditional quality systems mirror 20th-century industrial thinking: rigid hierarchies, linear processes, and documents that gather dust. These systems treat organizations as predictable machines, relying on policies to command and procedures to control. Yet living systems—forests, coral reefs, cities—operate differently. They self-organize around shared purpose, adapt through feedback, and balance structure with spontaneity. Deming foresaw this shift. His System of Profound Knowledge—emphasizing psychology, variation, and systems thinking—aligns with principles of living systems: coherence without control, stability with flexibility.
At the heart of this transformation is the recognition that quality emerges not from compliance checklists but from the invisible architecture of relationships, values, and purpose. Consider how a forest ecosystem thrives: trees communicate through fungal networks, species coexist through symbiotic relationships, and resilience comes from diversity, not uniformity. Similarly, effective quality systems depend on interconnected elements working in harmony, guided by a shared “DNA” of purpose.
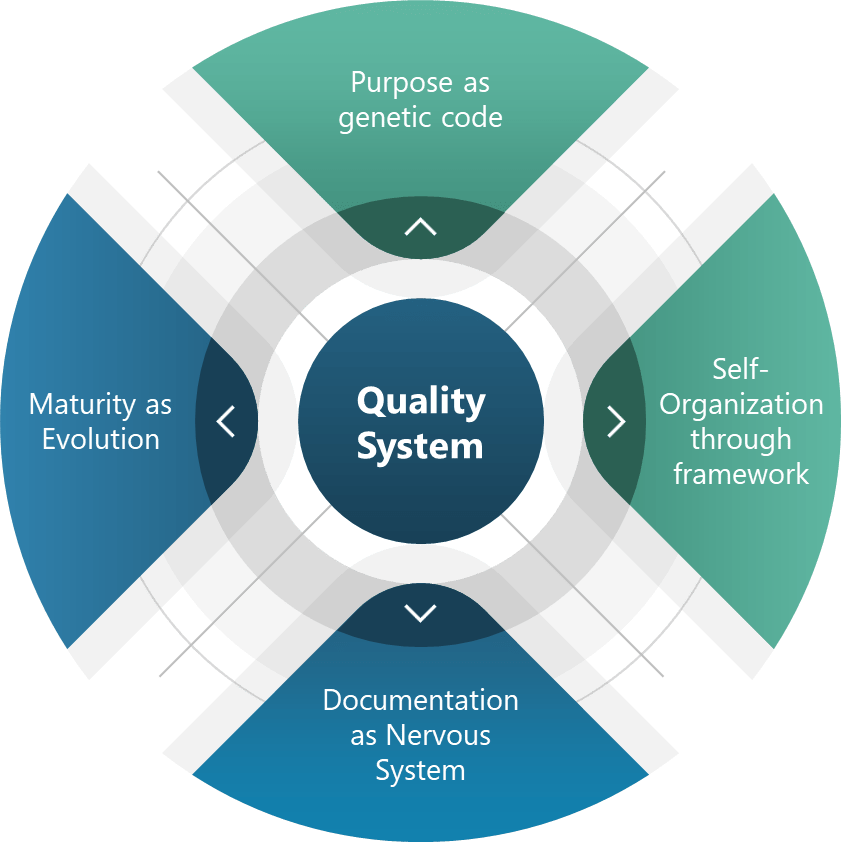
The Four Pillars of Living Quality Systems
- Purpose as Genetic Code
Every living system has inherent telos—an aim that guides adaptation. For quality systems, this translates to policies that act as genetic non-negotiables. For pharmaceuticals and medical devices this is “patient safety above all.”. This “DNA” allowed teams to innovate while maintaining adherence to core requirements, much like genes express differently across environments without compromising core traits. - Self-Organization Through Frameworks
Complex systems achieve order through frameworks as guiding principles. Coherence emerges from shared intent. Deming’s PDSA cycles and emphasis on psychological safety create similar conditions for self-organization. - Documentation as a Nervous System
The enhanced document pyramid—policies, programs, procedures, work instructions, records—acts as an organizational nervous system. Adding a “program” level between policies and procedures bridges the gap between intent and action and can transform static documents into dynamic feedback loops. - Maturity as Evolution
Living systems evolve through natural selection. Maturity models serve as evolutionary markers:- Ad-hoc (Primordial): Tools collected like random mutations.
- Managed (Organized): Basic processes stabilize.
- Standardized (Complex): Methodologies cohere.
- Predictable (Adaptive): Issues are anticipated.
- Optimizing (Evolutionary): Improvement fuels innovation.
Cultivating Organizational Ecosystems: Eight Principles
Living quality systems thrive when guided by eight principles:
- Balance: Serving patients, employees, and regulators equally.
- Congruence: Aligning tools with culture.
- Human-Centered: Designing for joy—automating drudgery, amplifying creativity.
- Learning: Treating deviations as data, not failures.
- Sustainability: Planning for decade-long impacts, not quarterly audits.
- Elegance: Simplifying until it hurts, then relaxing slightly.
- Coordination: Cross-pollinating across the organization
- Convenience: Making compliance easier than non-compliance.
These principles operationalize Deming’s wisdom. Driving out fear (Point 8) fosters psychological safety, while breaking down barriers (Point 9) enables cross-functional symbiosis.
The Quality Professional’s New Role: Gardener, Not Auditor
Quality professionals must embrace a transformative shift in their roles. Instead of functioning as traditional enforcers or document controllers, we are now called to act as stewards of living systems. This evolution requires a mindset change from one of rigid oversight to one of nurturing growth and adaptability. The modern quality professional takes on new identities such as coach, data ecologist, and systems immunologist—roles that emphasize collaboration, learning, and resilience.
To thrive in this new capacity, practical steps must be taken. First, it is essential to prune toxic practices by eliminating fear-driven reporting mechanisms and redundant tools that stifle innovation and transparency. Quality professionals should focus on fostering trust and streamlining processes to create healthier organizational ecosystems. Next, they must plant feedback loops by embedding continuous learning into daily workflows. For instance, incorporating post-meeting retrospectives can help teams reflect on successes and challenges, ensuring ongoing improvement. Lastly, cross-pollination is key to cultivating diverse perspectives and skills. Rotating staff between quality assurance, operations, and research and development encourages knowledge sharing and breaks down silos, ultimately leading to more integrated and innovative solutions.
By adopting this gardener-like approach, quality professionals can nurture the growth of resilient systems that are better equipped to adapt to change and complexity. This shift not only enhances organizational performance but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration.
Thriving, Not Just Surviving
Quality systems that mimic life—not machinery—turn crises into growth opportunities. As Deming noted, “Learning is not compulsory… neither is survival.” By embracing living system principles, we create environments where survival is the floor, and excellence is the emergent reward.
Start small: Audit one process using living system criteria. Replace one control mechanism with a self-organizing principle. Share learnings across your organizational “species.” The future of quality isn’t in thicker binders—it’s in cultivating systems that breathe, adapt, and evolve.