In a past post discussing the program level in the document hierarchy, I outlined how program documents serve as critical connective tissue between high-level policies and detailed procedures. Today, I’ll explore three distinct but related approaches to control strategies: the Annex 1 Contamination Control Strategy (CCS), the ICH Q8 Process Control Strategy, and a Technology Platform Control Strategy. Understanding their differences and relationships allows us to establish a comprehensive quality system in pharmaceutical manufacturing, especially as regulatory requirements continue to evolve and emphasize more scientific, risk-based approaches to quality management.
Control strategies have evolved significantly and are increasingly central to pharmaceutical quality management. As I noted in my previous article, program documents create an essential mapping between requirements and execution, demonstrating the design thinking that underpins our quality processes. Control strategies exemplify this concept, providing comprehensive frameworks that ensure consistent product quality through scientific understanding and risk management.
The pharmaceutical industry has gradually shifted from reactive quality testing to proactive quality design. This evolution mirrors the maturation of our document hierarchies, with control strategies occupying that critical program-level space between overarching quality policies and detailed operational procedures. They serve as the blueprint for how quality will be achieved, maintained, and improved throughout a product’s lifecycle.
This evolution has been accelerated by increasing regulatory scrutiny, particularly following numerous drug recalls and contamination events resulting in significant financial losses for pharmaceutical companies.
Annex 1 Contamination Control Strategy: A Facility-Focused Approach
The Annex 1 Contamination Control Strategy represents a comprehensive, facility-focused approach to preventing chemical, physical and microbial contamination in pharmaceutical manufacturing environments. The CCS takes a holistic view of the entire manufacturing facility rather than focusing on individual products or processes.
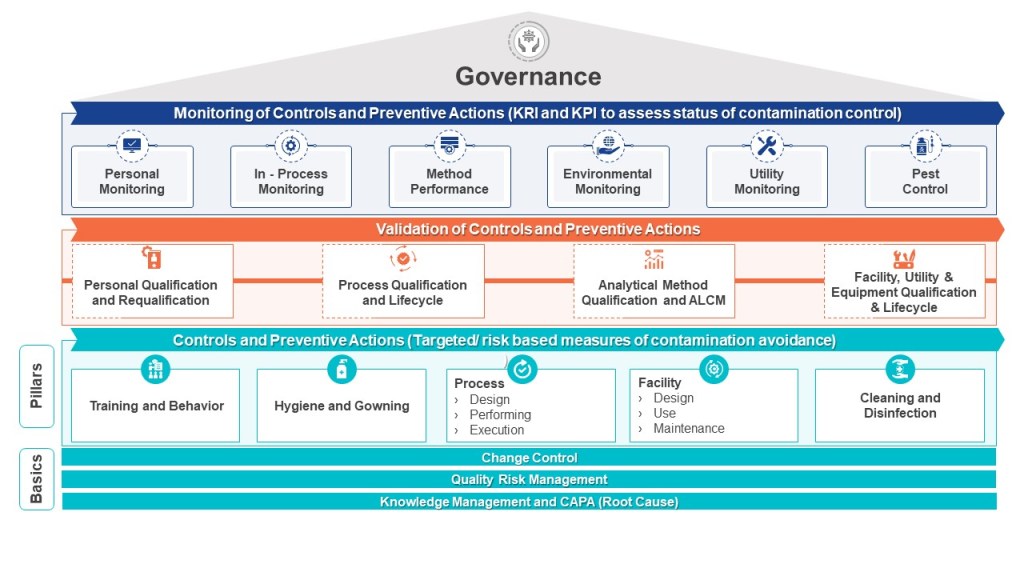
A properly implemented CCS requires a dedicated cross-functional team representing technical knowledge from production, engineering, maintenance, quality control, microbiology, and quality assurance. This team must systematically identify contamination risks throughout the facility, develop mitigating controls, and establish monitoring systems that provide early detection of potential issues. The CCS must be scientifically formulated and tailored specifically for each manufacturing facility’s unique characteristics and risks.
What distinguishes the Annex 1 CCS is its infrastructural approach to Quality Risk Management. Rather than focusing solely on product attributes or process parameters, it examines how facility design, environmental controls, personnel practices, material flow, and equipment operate collectively to prevent contamination. The CCS process involves continual identification, scientific evaluation, and effective control of potential contamination risks to product quality.
Critical Factors in Developing an Annex 1 CCS
The development of an effective CCS involves several critical considerations. According to industry experts, these include identifying the specific types of contaminants that pose a risk, implementing appropriate detection methods, and comprehensively understanding the potential sources of contamination. Additionally, evaluating the risk of contamination and developing effective strategies to control and minimize such risks are indispensable components of an efficient contamination control system.
When implementing a CCS, facilities should first determine their critical control points. Annex 1 highlights the importance of considering both plant design and processes when developing a CCS. The strategy should incorporate a monitoring and ongoing review system to identify potential lapses in the aseptic environment and contamination points in the facility. This continuous assessment approach ensures that contamination risks are promptly identified and addressed before they impact product quality.
ICH Q8 Process Control Strategy: The Quality by Design Paradigm
While the Annex 1 CCS focuses on facility-wide contamination prevention, the ICH Q8 Process Control Strategy takes a product-centric approach rooted in Quality by Design (QbD) principles. The ICH Q8(R2) guideline introduces control strategy as “a planned set of controls derived from current product and process understanding that ensures process performance and product quality”. This approach emphasizes designing quality into products rather than relying on final testing to detect issues.
The ICH Q8 guideline outlines a set of key principles that form the foundation of an effective process control strategy. At its core is pharmaceutical development, which involves a comprehensive understanding of the product and its manufacturing process, along with identifying critical quality attributes (CQAs) that impact product safety and efficacy. Risk assessment plays a crucial role in prioritizing efforts and resources to address potential issues that could affect product quality.
The development of an ICH Q8 control strategy follows a systematic sequence: defining the Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP), identifying Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs), determining Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) and Critical Material Attributes (CMAs), and establishing appropriate control methods. This scientific framework enables manufacturers to understand how material attributes and process parameters affect product quality, allowing for more informed decision-making and process optimization.
Design Space and Lifecycle Approach
A unique aspect of the ICH Q8 control strategy is the concept of “design space,” which represents a range of process parameters within which the product will consistently meet desired quality attributes. Developing and demonstrating a design space provides flexibility in manufacturing without compromising product quality. This approach allows manufacturers to make adjustments within the established parameters without triggering regulatory review, thus enabling continuous improvement while maintaining compliance.
What makes the ICH Q8 control strategy distinct is its dynamic, lifecycle-oriented nature. The guideline encourages a lifecycle approach to product development and manufacturing, where continuous improvement and monitoring are carried out throughout the product’s lifecycle, from development to post-approval. This approach creates a feedback-feedforward “controls hub” that integrates risk management, knowledge management, and continuous improvement throughout the product lifecycle.
Technology Platform Control Strategies: Leveraging Prior Knowledge
As pharmaceutical development becomes increasingly complex, particularly in emerging fields like cell and gene therapies, technology platform control strategies offer an approach that leverages prior knowledge and standardized processes to accelerate development while maintaining quality standards. Unlike product-specific control strategies, platform strategies establish common processes, parameters, and controls that can be applied across multiple products sharing similar characteristics or manufacturing approaches.
The importance of maintaining state-of-the-art technology platforms has been highlighted in recent regulatory actions. A January 2025 FDA Warning Letter to Sanofi, concerning a facility that had previously won the ISPE’s Facility of the Year award in 2020, emphasized the requirement for “timely technological upgrades to equipment/facility infrastructure”. This regulatory focus underscores that even relatively new facilities must continually evolve their technological capabilities to maintain compliance and product quality.
Developing a Comprehensive Technology Platform Roadmap
A robust technology platform control strategy requires a well-structured technology roadmap that anticipates both regulatory expectations and technological advancements. According to recent industry guidance, this roadmap should include several key components:
At its foundation, regular assessment protocols are essential. Organizations should conduct comprehensive annual evaluations of platform technologies, examining equipment performance metrics, deviations associated with the platform, and emerging industry standards that might necessitate upgrades. These assessments should be integrated with Facility and Utility Systems Effectiveness (FUSE) metrics and evaluated through structured quality governance processes.
The technology roadmap must also incorporate systematic methods for monitoring industry trends. This external vigilance ensures platform technologies remain current with evolving expectations and capabilities.
Risk-based prioritization forms another critical element of the platform roadmap. By utilizing living risk assessments, organizations can identify emerging issues and prioritize platform upgrades based on their potential impact on product quality and patient safety. These assessments should represent the evolution of the original risk management that established the platform, creating a continuous thread of risk evaluation throughout the platform’s lifecycle.
Implementation and Verification of Platform Technologies
Successful implementation of platform technologies requires robust change management procedures. These should include detailed documentation of proposed platform modifications, impact assessments on product quality across the portfolio, appropriate verification activities, and comprehensive training programs. This structured approach ensures that platform changes are implemented systematically with full consideration of their potential implications.
Verification activities for platform technologies must be particularly thorough, given their application across multiple products. The commissioning, qualification, and validation activities should demonstrate not only that platform components meet predetermined specifications but also that they maintain their intended performance across the range of products they support. This verification must consider the variability in product-specific requirements while confirming the platform’s core capabilities.
Continuous monitoring represents the final essential element of platform control strategies. By implementing ongoing verification protocols aligned with Stage 3 of the FDA’s process validation model, organizations can ensure that platform technologies remain in a state of control during routine commercial manufacture. This monitoring should anticipate and prevent issues, detect unplanned deviations, and identify opportunities for platform optimization.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies in Platform Strategies
Modern technology platforms increasingly incorporate advanced capabilities that enhance their flexibility and performance. Single-Use Systems (SUS) reduce cleaning and validation requirements while improving platform adaptability across products. Modern Microbial Methods (MMM) offer advantages over traditional culture-based approaches in monitoring platform performance. Process Analytical Technology (PAT) enables real-time monitoring and control, enhancing product quality and process understanding across the platform. Data analytics and artificial intelligence tools identify trends, predict maintenance needs, and optimize processes across the product portfolio.
The implementation of these advanced technologies within platform strategies creates significant opportunities for standardization, knowledge transfer, and continuous improvement. By establishing common technological foundations that can be applied across multiple products, organizations can accelerate development timelines, reduce validation burdens, and focus resources on understanding the unique aspects of each product while maintaining a robust quality foundation.
How Control Strategies Tie Together Design, Qualification/Validation, and Risk Management
Control strategies serve as the central nexus connecting design, qualification/validation, and risk management in a comprehensive quality framework. This integration is not merely beneficial but essential for ensuring product quality while optimizing resources. A well-structured control strategy creates a coherent narrative from initial concept through on-going production, ensuring that design intentions are preserved through qualification activities and ongoing risk management.
During the design phase, scientific understanding of product and process informs the development of the control strategy. This strategy then guides what must be qualified and validated and to what extent. Rather than validating everything (which adds cost without necessarily improving quality), the control strategy directs validation resources toward aspects most critical to product quality.
The relationship works in both directions—design decisions influence what will require validation, while validation capabilities and constraints may inform design choices. For example, a process designed with robust, well-understood parameters may require less extensive validation than one operating at the edge of its performance envelope. The control strategy documents this relationship, providing scientific justification for validation decisions based on product and process understanding.
Risk management principles are foundational to modern control strategies, informing both design decisions and priorities. A systematic risk assessment approach helps identify which aspects of a process or facility pose the greatest potential impact on product quality and patient safety. The control strategy then incorporates appropriate controls and monitoring systems for these high-risk elements, ensuring that validation efforts are proportionate to risk levels.
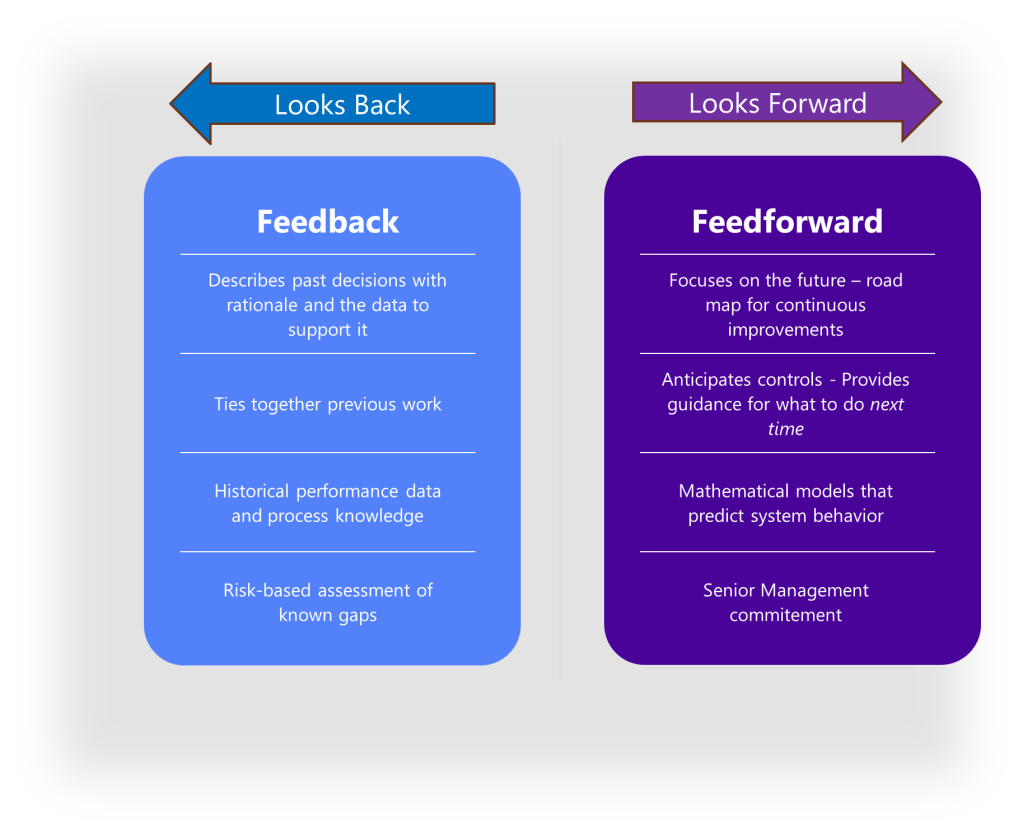
The Feedback-Feedforward Mechanism
One of the most powerful aspects of an integrated control strategy is its ability to function as what experts call a feedback-feedforward controls hub. As a product moves through its lifecycle, from development to commercial manufacturing, the control strategy evolves based on accumulated knowledge and experience. Validation results, process monitoring data, and emerging risks all feed back into the control strategy, which in turn drives adjustments to design parameters and validation approaches.
Comparing Control Strategy Approaches: Similarities and Distinctions
While these three control strategy approaches have distinct focuses and applications, they share important commonalities. All three emphasize scientific understanding, risk management, and continuous improvement. They all serve as program-level documents that connect high-level requirements with operational execution. And all three have gained increasing regulatory recognition as pharmaceutical quality management has evolved toward more systematic, science-based approaches.
| Aspect | Annex 1 CCS | ICH Q8 Process Control Strategy | Technology Platform Control Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Facility-wide contamination prevention | Product and process quality | Standardized approach across multiple products |
| Scope | Microbial, pyrogen, and particulate contamination (a good one will focus on physical, chemical and biologic hazards) | All aspects of product quality | Common technology elements shared across products |
| Regulatory Foundation | EU GMP Annex 1 (2022 revision) | ICH Q8(R2) | Emerging FDA guidance (Platform Technology Designation) |
| Implementation Level | Manufacturing facility | Individual product | Technology group or platform |
| Key Components | Contamination risk identification, detection methods, understanding of contamination sources | QTPP, CQAs, CPPs, CMAs, design space | Standardized technologies, processes, and controls |
| Risk Management Approach | Infrastructural (facility design, processes, personnel) – great for a HACCP | Product-specific (process parameters, material attributes) | Platform-specific (shared technological elements) |
| Team Structure | Cross-functional (production, engineering, QC, QA, microbiology) | Product development, manufacturing and quality | Technology development and product adaptation |
| Lifecycle Considerations | Continuous monitoring and improvement of facility controls | Product lifecycle from development to post-approval | Evolution of platform technology across multiple products |
| Documentation | Facility-specific CCS with ongoing monitoring records | Product-specific control strategy with design space definition | Platform master file with product-specific adaptations |
| Flexibility | Low (facility-specific controls) | Medium (within established design space) | High (adaptable across multiple products) |
| Primary Benefit | Contamination prevention and control | Consistent product quality through scientific understanding | Efficiency and knowledge leverage across product portfolio |
| Digital Integration | Environmental monitoring systems, facility controls | Process analytical technology, real-time release testing | Platform data management and cross-product analytics |
These approaches are not mutually exclusive; rather, they complement each other within a comprehensive quality management system. A manufacturing site producing sterile products needs both an Annex 1 CCS for facility-wide contamination control and ICH Q8 process control strategies for each product. If the site uses common technology platforms across multiple products, platform control strategies would provide additional efficiency and standardization.
Control Strategies Through the Lens of Knowledge Management: Enhancing Quality and Operational Excellence
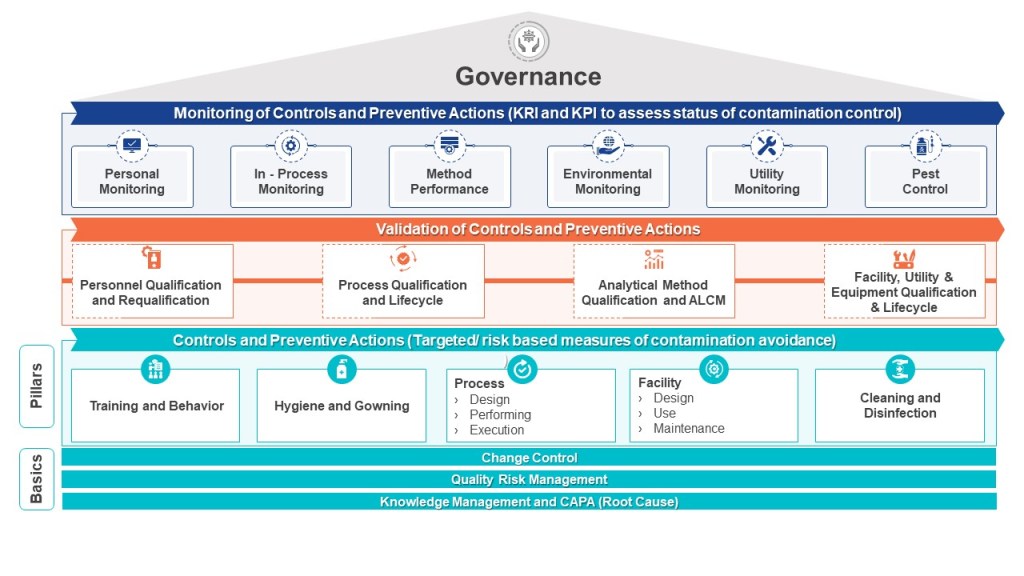
The pharmaceutical industry’s approach to control strategies has evolved significantly in recent years, with systematic knowledge management emerging as a critical foundation for their effectiveness. Control strategies—whether focused on contamination prevention, process control, or platform technologies—fundamentally depend on how knowledge is created, captured, disseminated, and applied across an organization. Understanding the intersection between control strategies and knowledge management provides powerful insights into building more robust pharmaceutical quality systems and achieving higher levels of operational excellence.
The Knowledge Foundation of Modern Control Strategies
Control strategies represent systematic approaches to ensuring consistent pharmaceutical quality by managing various aspects of production. While these strategies differ in focus and application, they share a common foundation in knowledge—both explicit (documented) and tacit (experiential).
Knowledge Management as the Binding Element
The ICH Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System model positions knowledge management alongside quality risk management as dual enablers of pharmaceutical quality. This pairing is particularly significant when considering control strategies, as it establishes what might be called a “Risk-Knowledge Infinity Cycle”—a continuous process where increased knowledge leads to decreased uncertainty and therefore decreased risk. Control strategies represent the formal mechanisms through which this cycle is operationalized in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Effective control strategies require comprehensive knowledge visibility across functional areas and lifecycle phases. Organizations that fail to manage knowledge effectively often experience problems like knowledge silos, repeated issues due to lessons not learned, and difficulty accessing expertise or historical product knowledge—all of which directly impact the effectiveness of control strategies and ultimately product quality.
The Feedback-Feedforward Controls Hub: A Knowledge Integration Framework
As described above, the heart of effective control strategies lies is the “feedback-feedforward controls hub.” This concept represents the integration point where knowledge flows bidirectionally to continuously refine and improve control mechanisms. In this model, control strategies function not as static documents but as dynamic knowledge systems that evolve through continuous learning and application.
The feedback component captures real-time process data, deviations, and outcomes that generate new knowledge about product and process performance. The feedforward component takes this accumulated knowledge and applies it proactively to prevent issues before they occur. This integrated approach creates a self-reinforcing cycle where control strategies become increasingly sophisticated and effective over time.
For example, in an ICH Q8 process control strategy, process monitoring data feeds back into the system, generating new understanding about process variability and performance. This knowledge then feeds forward to inform adjustments to control parameters, risk assessments, and even design space modifications. The hub serves as the central coordination mechanism ensuring these knowledge flows are systematically captured and applied.
Knowledge Flow Within Control Strategy Implementation
Knowledge flows within control strategies typically follow the knowledge management process model described in the ISPE Guide, encompassing knowledge creation, curation, dissemination, and application. For control strategies to function effectively, this flow must be seamless and well-governed.
The systematic management of knowledge within control strategies requires:
- Methodical capture of knowledge through various means appropriate to the control strategy context
- Proper identification, review, and analysis of this knowledge to generate insights
- Effective storage and visibility to ensure accessibility across the organization
- Clear pathways for knowledge application, transfer, and growth
When these elements are properly integrated, control strategies benefit from continuous knowledge enrichment, resulting in more refined and effective controls. Conversely, barriers to knowledge flow—such as departmental silos, system incompatibilities, or cultural resistance to knowledge sharing—directly undermine the effectiveness of control strategies.
Annex 1 Contamination Control Strategy Through a Knowledge Management Lens
The Annex 1 Contamination Control Strategy represents a facility-focused approach to preventing microbial, pyrogen, and particulate contamination. When viewed through a knowledge management lens, the CCS becomes more than a compliance document—it emerges as a comprehensive knowledge system integrating multiple knowledge domains.
Effective implementation of an Annex 1 CCS requires managing diverse knowledge types across functional boundaries. This includes explicit knowledge documented in environmental monitoring data, facility design specifications, and cleaning validation reports. Equally important is tacit knowledge held by personnel about contamination risks, interventions, and facility-specific nuances that are rarely fully documented.
The knowledge management challenges specific to contamination control include ensuring comprehensive capture of contamination events, facilitating cross-functional knowledge sharing about contamination risks, and enabling access to historical contamination data and prior knowledge. Organizations that approach CCS development with strong knowledge management practices can create living documents that continuously evolve based on accumulated knowledge rather than static compliance tools.
Knowledge mapping is particularly valuable for CCS implementation, helping to identify critical contamination knowledge sources and potential knowledge gaps. Communities of practice spanning quality, manufacturing, and engineering functions can foster collaboration and tacit knowledge sharing about contamination control. Lessons learned processes ensure that insights from contamination events contribute to continuous improvement of the control strategy.
ICH Q8 Process Control Strategy: Quality by Design and Knowledge Management
The ICH Q8 Process Control Strategy embodies the Quality by Design paradigm, where product and process understanding drives the development of controls that ensure consistent quality. This approach is fundamentally knowledge-driven, making effective knowledge management essential to its success.
The QbD approach begins with applying prior knowledge to establish the Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP) and identify Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs). Experimental studies then generate new knowledge about how material attributes and process parameters affect these quality attributes, leading to the definition of a design space and control strategy. This sequence represents a classic knowledge creation and application cycle that must be systematically managed.
Knowledge management challenges specific to ICH Q8 process control strategies include capturing the scientific rationale behind design choices, maintaining the connectivity between risk assessments and control parameters, and ensuring knowledge flows across development and manufacturing boundaries. Organizations that excel at knowledge management can implement more robust process control strategies by ensuring comprehensive knowledge visibility and application.
Particularly important for process control strategies is the management of decision rationale—the often-tacit knowledge explaining why certain parameters were selected or why specific control approaches were chosen. Explicit documentation of this decision rationale ensures that future changes to the process can be evaluated with full understanding of the original design intent, avoiding unintended consequences.
Technology Platform Control Strategies: Leveraging Knowledge Across Products
Technology platform control strategies represent standardized approaches applied across multiple products sharing similar characteristics or manufacturing technologies. From a knowledge management perspective, these strategies exemplify the power of knowledge reuse and transfer across product boundaries.
The fundamental premise of platform approaches is that knowledge gained from one product can inform the development and control of similar products, creating efficiencies and reducing risks. This depends on robust knowledge management practices that make platform knowledge visible and available across product teams and lifecycle phases.
Knowledge management challenges specific to platform control strategies include ensuring consistent knowledge capture across products, facilitating cross-product learning, and balancing standardization with product-specific requirements. Organizations with mature knowledge management practices can implement more effective platform strategies by creating knowledge repositories, communities of practice, and lessons learned processes that span product boundaries.
Integrating Control Strategies with Design, Qualification/Validation, and Risk Management
Control strategies serve as the central nexus connecting design, qualification/validation, and risk management in a comprehensive quality framework. This integration is not merely beneficial but essential for ensuring product quality while optimizing resources. A well-structured control strategy creates a coherent narrative from initial concept through commercial production, ensuring that design intentions are preserved through qualification activities and ongoing risk management.
The Design-Validation Continuum
Control strategies form a critical bridge between product/process design and validation activities. During the design phase, scientific understanding of the product and process informs the development of the control strategy. This strategy then guides what must be validated and to what extent. Rather than validating everything (which adds cost without necessarily improving quality), the control strategy directs validation resources toward aspects most critical to product quality.
The relationship works in both directions—design decisions influence what will require validation, while validation capabilities and constraints may inform design choices. For example, a process designed with robust, well-understood parameters may require less extensive validation than one operating at the edge of its performance envelope. The control strategy documents this relationship, providing scientific justification for validation decisions based on product and process understanding.
Risk-Based Prioritization
Risk management principles are foundational to modern control strategies, informing both design decisions and validation priorities. A systematic risk assessment approach helps identify which aspects of a process or facility pose the greatest potential impact on product quality and patient safety. The control strategy then incorporates appropriate controls and monitoring systems for these high-risk elements, ensuring that validation efforts are proportionate to risk levels.
The Feedback-Feedforward Mechanism
The feedback-feedforward controls hub represents a sophisticated integration of two fundamental control approaches, creating a central mechanism that leverages both reactive and proactive control strategies to optimize process performance. This concept emerges as a crucial element in modern control systems, particularly in pharmaceutical manufacturing, chemical processing, and advanced mechanical systems.
To fully grasp the concept of a feedback-feedforward controls hub, we must first distinguish between its two primary components. Feedback control works on the principle of information from the outlet of a process being “fed back” to the input for corrective action. This creates a loop structure where the system reacts to deviations after they occur. Fundamentally reactive in nature, feedback control takes action only after detecting a deviation between the process variable and setpoint.
In contrast, feedforward control operates on the principle of preemptive action. It monitors load variables (disturbances) that affect a process and takes corrective action before these disturbances can impact the process variable. Rather than waiting for errors to manifest, feedforward control uses data from load sensors to predict when an upset is about to occur, then feeds that information forward to the final control element to counteract the load change proactively.
The feedback-feedforward controls hub serves as a central coordination point where these two control strategies converge and complement each other. As a product moves through its lifecycle, from development to commercial manufacturing, this control hub evolves based on accumulated knowledge and experience. Validation results, process monitoring data, and emerging risks all feed back into the control strategy, which in turn drives adjustments to design parameters and validation approaches.
Knowledge Management Maturity in Control Strategy Implementation
The effectiveness of control strategies is directly linked to an organization’s knowledge management maturity. Organizations with higher knowledge management maturity typically implement more robust, science-based control strategies that evolve effectively over time. Conversely, organizations with lower maturity often struggle with static control strategies that fail to incorporate learning and experience.
Common knowledge management gaps affecting control strategies include:
- Inadequate mechanisms for capturing tacit knowledge from subject matter experts
- Poor visibility of knowledge across organizational and lifecycle boundaries
- Ineffective lessons learned processes that fail to incorporate insights into control strategies
- Limited knowledge sharing between sites implementing similar control strategies
- Difficulty accessing historical knowledge that informed original control strategy design
Addressing these gaps through systematic knowledge management practices can significantly enhance control strategy effectiveness, leading to more robust processes, fewer deviations, and more efficient responses to change.
The examination of control strategies through a knowledge management lens reveals their fundamentally knowledge-dependent nature. Whether focused on contamination control, process parameters, or platform technologies, control strategies represent the formal mechanisms through which organizational knowledge is applied to ensure consistent pharmaceutical quality.
Organizations seeking to enhance their control strategy effectiveness should consider several key knowledge management principles:
- Recognize both explicit and tacit knowledge as essential components of effective control strategies
- Ensure knowledge flows seamlessly across functional boundaries and lifecycle phases
- Address all four pillars of knowledge management—people, process, technology, and governance
- Implement systematic methods for capturing lessons and insights that can enhance control strategies
- Foster a knowledge-sharing culture that supports continuous learning and improvement
By integrating these principles into control strategy development and implementation, organizations can create more robust, science-based approaches that continuously evolve based on accumulated knowledge and experience. This not only enhances regulatory compliance but also improves operational efficiency and product quality, ultimately benefiting patients through more consistent, high-quality pharmaceutical products.
The feedback-feedforward controls hub concept represents a particularly powerful framework for thinking about control strategies, emphasizing the dynamic, knowledge-driven nature of effective controls. By systematically capturing insights from process performance and proactively applying this knowledge to prevent issues, organizations can create truly learning control systems that become increasingly effective over time.
Conclusion: The Central Role of Control Strategies in Pharmaceutical Quality Management
Control strategies—whether focused on contamination prevention, process control, or technology platforms—serve as the intellectual foundation connecting high-level quality policies with detailed operational procedures. They embody scientific understanding, risk management decisions, and continuous improvement mechanisms in a coherent framework that ensures consistent product quality.
Regulatory Needs and Control Strategies
Regulatory guidelines like ICH Q8 and Annex 1 CCS underscore the importance of control strategies in ensuring product quality and compliance. ICH Q8 emphasizes a Quality by Design (QbD) approach, where product and process understanding drives the development of controls. Annex 1 CCS focuses on facility-wide contamination prevention, highlighting the need for comprehensive risk management and control systems. These regulatory expectations necessitate robust control strategies that integrate scientific knowledge with operational practices.
Knowledge Management: The Backbone of Effective Control Strategies
Knowledge management (KM) plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of control strategies. By systematically acquiring, analyzing, storing, and disseminating information related to products and processes, organizations can ensure that the right knowledge is available at the right time. This enables informed decision-making, reduces uncertainty, and ultimately decreases risk.
Risk Management and Control Strategies
Risk management is inextricably linked with control strategies. By identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can maintain a state of control and facilitate continual improvement. Control strategies must be designed to incorporate risk assessments and management processes, ensuring that they are proactive and adaptive.
The Interconnectedness of Control Strategies
Control strategies are not isolated entities but are interconnected with design, qualification/validation, and risk management processes. They form a feedback-feedforward controls hub that evolves over a product’s lifecycle, incorporating new insights and adjustments based on accumulated knowledge and experience. This dynamic approach ensures that control strategies remain effective and relevant, supporting both regulatory compliance and operational excellence.
Why Control Strategies Are Key
Control strategies are essential for several reasons:
- Regulatory Compliance: They ensure adherence to regulatory guidelines and standards, such as ICH Q8 and Annex 1 CCS.
- Quality Assurance: By integrating scientific understanding and risk management, control strategies guarantee consistent product quality.
- Operational Efficiency: Effective control strategies streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance productivity.
- Knowledge Management: They facilitate the systematic management of knowledge, ensuring that insights are captured and applied across the organization.
- Risk Mitigation: Control strategies proactively identify and mitigate risks, protecting both product quality and patient safety.
Control strategies represent the central mechanism through which pharmaceutical companies ensure quality, manage risk, and leverage knowledge. As the industry continues to evolve with new technologies and regulatory expectations, the importance of robust, science-based control strategies will only grow. By integrating knowledge management, risk management, and regulatory compliance, organizations can develop comprehensive quality systems that protect patients, satisfy regulators, and drive operational excellence.