The Cognitive Architecture of Risk Buy-Down
The concept of “buying down risk” through operational capability development fundamentally depends on addressing the cognitive foundations that underpin effective risk assessment and decision-making. There are three critical systematic vulnerabilities that plague risk management processes: unjustified assumptions, incomplete identification of risks, and inappropriate use of risk assessment tools. These failures represent more than procedural deficiencies—they expose cognitive and knowledge management vulnerabilities that can undermine even the most well-intentioned quality systems.
Unjustified assumptions emerge when organizations rely on historical performance data or familiar process knowledge without adequately considering how changes in conditions, equipment, or supply chains might alter risk profiles. This manifests through anchoring bias, where teams place undue weight on initial information, leading to conclusions like “This process has worked safely for five years, so the risk profile remains unchanged.” Confirmation bias compounds this issue by causing assessors to seek information confirming existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
Incomplete risk identification occurs when cognitive limitations and organizational biases inhibit comprehensive hazard recognition. Availability bias leads to overemphasis on dramatic but unlikely events while underestimating more probable but less memorable risks. Additionally, groupthink in risk assessment teams causes initial dissenting voices to be suppressed as consensus builds around preferred conclusions, limiting the scope of risks considered.
Inappropriate use of risk assessment tools represents the third systematic vulnerability, where organizations select methodologies based on familiarity rather than appropriateness for specific decision-making contexts. This includes using overly formal tools for trivial issues, applying generic assessment approaches without considering specific operational contexts, and relying on subjective risk scoring that provides false precision without meaningful insight. The misapplication often leads to risk assessments that fail to add value or clarity because they only superficially address root causes while generating high levels of subjectivity and uncertainty in outputs.
Traditional risk management approaches often focus on methodological sophistication while overlooking the cognitive realities that determine assessment effectiveness. Risk management operates fundamentally as a framework rather than a rigid methodology, providing structural architecture that enables systematic approaches to identifying, assessing, and controlling uncertainties. This framework distinction proves crucial because it recognizes that excellence emerges from the intersection of systematic process design with cognitive support systems that work with, rather than against, human decision-making patterns.
The Minimal Viable Risk Assessment Team: Beyond Compliance Theater
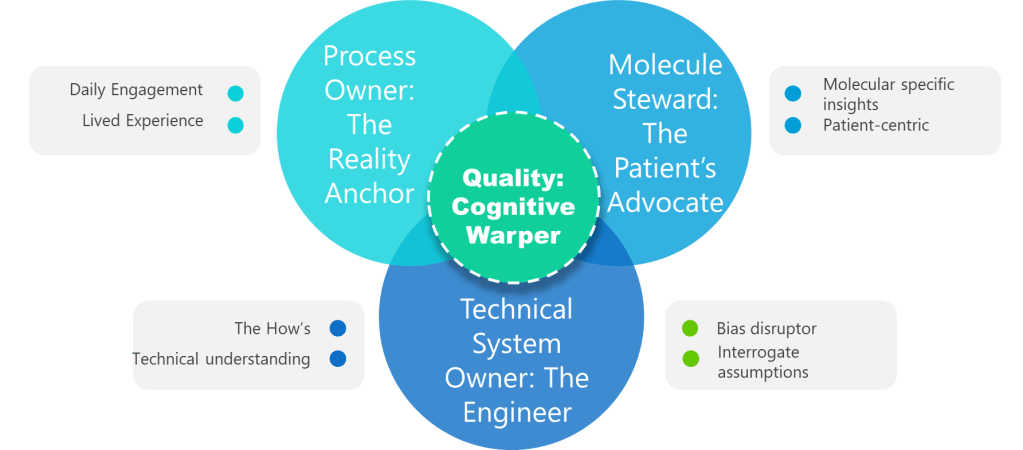
The foundation of cognitive excellence in risk management begins with assembling teams designed for cognitive rigor, knowledge depth, and psychological safety rather than mere compliance box-checking. The minimal viable risk assessment team concept challenges traditional approaches by focusing on four non-negotiable core roles that provide essential cognitive perspectives and knowledge anchors.
The Four Cognitive Anchors
Process Owner: The Reality Anchor represents lived operational experience rather than signature authority. This individual has engaged with the operation within the last 90 days and carries authority to change methods, budgets, and training. Authentic process ownership dismantles assumptions by grounding every risk statement in current operational facts, countering the tendency toward unjustified assumptions that plague many risk assessments.
Molecule Steward: The Patient’s Advocate moves beyond generic subject matter expertise to provide specific knowledge of how the particular product fails and can translate deviations into patient impact. When temperature drifts during freeze-drying, the molecule steward can explain whether a monoclonal antibody will aggregate or merely lose shelf life. Without this anchor, teams inevitably under-score hazards that never appear in generic assessment templates.
Technical System Owner: The Engineering Interpreter bridges the gap between equipment design intentions and operational realities. Equipment obeys physics rather than meeting minutes, and the system owner must articulate functional requirements, design limits, and engineering principles. This role prevents method-focused teams from missing systemic failures where engineering and design flaws could push entire batches outside critical parameters.
Quality Integrator: The Bias Disruptor forces cross-functional dialogue and preserves evidence of decision-making processes. Quality’s mission involves writing assumption logs, challenging confirmation bias, and ensuring dissenting voices are heard. This role maintains knowledge repositories so future teams are not condemned to repeat forgotten errors, directly addressing the knowledge management dimension of systematic risk assessment failure.
Knowledge Accessibility: The Missing Link in Risk Management
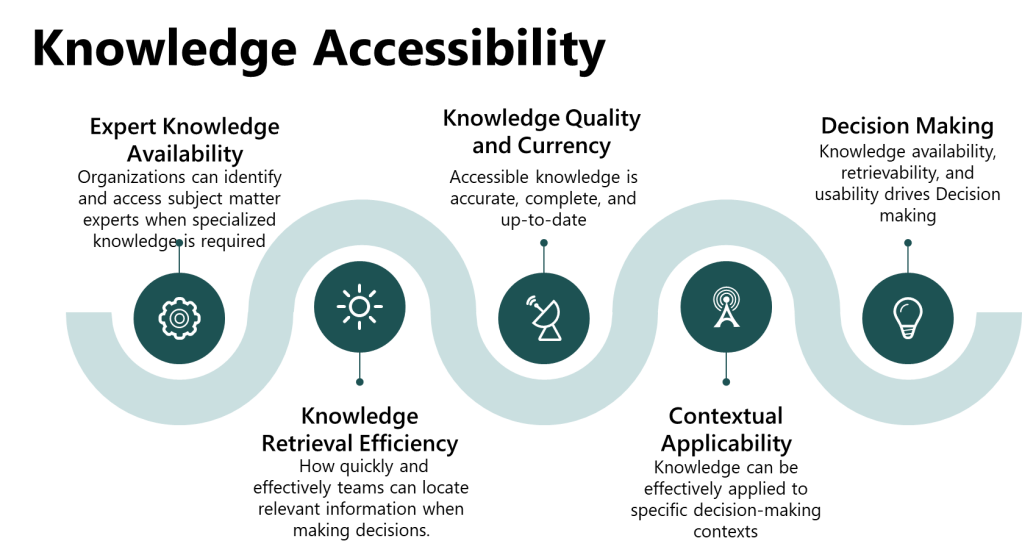
The Knowledge Accessibility Index (KAI) provides a systematic framework for evaluating how effectively organizations can access and deploy critical knowledge when decision-making requires specialized expertis. Unlike traditional knowledge management metrics focusing on knowledge creation or storage, the KAI specifically evaluates the availability, retrievability, and usability of knowledge at the point of decision-making.
Four Dimensions of Knowledge Accessibility
Expert Knowledge Availability assesses whether organizations can identify and access subject matter experts when specialized knowledge is required. This includes expert mapping and skill matrices, availability assessment during different operational scenarios, knowledge succession planning, and cross-training coverage for critical capabilities. The pharmaceutical environment demands that a qualified molecule steward be accessible within two hours for critical quality decisions, yet many organizations lack systematic approaches to ensuring this availability.
Knowledge Retrieval Efficiency measures how quickly and effectively teams can locate relevant information when making decisions. This encompasses search functionality effectiveness, knowledge organization and categorization, information architecture alignment with decision-making workflows, and access permissions balancing protection with accessibility. Time to find information represents a critical efficiency indicator that directly impacts the quality of risk assessment outcomes.
Knowledge Quality and Currency evaluates whether accessible knowledge is accurate, complete, and up-to-date through information accuracy verification processes, knowledge update frequency management, source credibility validation mechanisms, and completeness assessment relative to decision-making requirements. Outdated or incomplete knowledge can lead to systematic assessment failures even when expertise appears readily available.
Contextual Applicability assesses whether knowledge can be effectively applied to specific decision-making contexts through knowledge contextualization for operational scenarios, applicability assessment for different situations, integration capabilities with existing processes, and usability evaluation from end-user perspectives. Knowledge that exists but cannot be effectively applied provides little value during critical risk assessment activities.
Team Design as Knowledge Preservation Strategy
Effective risk assessment team design fundamentally serves as knowledge preservation, not just compliance fulfillment. Every effective risk team is a living repository of organizational critical process insights, technical know-how, and operational experience. When teams include process owners, technical system engineers, molecule stewards, and quality integrators with deep hands-on familiarity, they collectively safeguard hard-won lessons and tacit knowledge that are often lost during organizational transitions.
Combating organizational forgetting requires intentional, cross-functional team design that fosters active knowledge transfer. When risk teams bring together diverse experts who routinely interact, challenge assumptions, and share context from respective domains, they create dynamic environments where critical information is surfaced, scrutinized, and retained. This living dialogue proves more effective than static records because it allows continuous updating and contextualization of knowledge in response to new challenges, regulatory changes, and operational shifts.
Team design becomes a strategic defense against the silent erosion of expertise that can leave organizations exposed to avoidable risks. By prioritizing teams that embody both breadth and depth of experience, organizations create robust safety nets that catch subtle warning signs, adapt to evolving risks, and ensure critical knowledge endures beyond individual tenure. This transforms collective memory into competitive advantage and foundation for sustained quality.
Cultural Integration: Embedding Cognitive Excellence
The development of truly effective risk management capabilities requires cultural transformation that embeds cognitive excellence principles into organizational DNA. Organizations with strong risk management cultures demonstrate superior capability in preventing quality issues, detecting problems early, and implementing effective corrective actions that address root causes rather than symptoms.
Psychological Safety as Cognitive Infrastructure
Psychological safety creates the foundational environment where personnel feel comfortable challenging assumptions, raising concerns about potential risks, and admitting uncertainty or knowledge limitations. This requires organizational cultures that treat questioning and systematic analysis as valuable contributions rather than obstacles to efficiency. Without psychological safety, the most sophisticated risk assessment methodologies and team compositions cannot overcome the fundamental barrier of information suppression.
Leaders must model vulnerability by sharing personal errors and how systems, not individuals, failed. They must invite dissent early in meetings with questions like “What might we be overlooking?” and reward candor by recognizing people who halt production over questionable trends. Psychological safety converts silent observers into active risk sensors, dramatically improving the effectiveness of knowledge accessibility and risk identification processes.
Structured Decision-Making as Cultural Practice
Excellence in pharmaceutical quality systems requires moving beyond hoping individuals will overcome cognitive limitations through awareness alone. Instead, organizations must design structured decision-making processes that systematically counter known biases while supporting comprehensive risk identification and analysis.
Forced systematic consideration involves checklists, templates, and protocols requiring teams to address specific risk categories and evidence types before reaching conclusions. Rather than relying on free-form discussion influenced by availability bias or groupthink, these tools ensure comprehensive coverage of relevant factors.
Devil’s advocate processes systematically introduce alternative perspectives and challenge preferred conclusions. By assigning specific individuals to argue against prevailing views or identify overlooked risks, organizations counter confirmation bias and overconfidence while identifying blind spots.
Staged decision-making separates risk identification from evaluation, preventing premature closure and ensuring adequate time for comprehensive hazard identification before moving to analysis and control decisions.
Implementation Framework: Building Cognitive Resilience
Phase 1: Knowledge Accessibility Audit
Organizations must begin with systematic knowledge accessibility audits that identify potential vulnerabilities in expertise availability and access. This audit addresses expertise mapping to identify knowledge holders and capabilities, knowledge accessibility assessment evaluating how effectively relevant knowledge can be accessed, knowledge quality evaluation assessing currency and completeness, and cognitive bias vulnerability assessment identifying situations where biases most likely affect conclusions.
For pharmaceutical manufacturing organizations, this audit might assess whether teams can access qualified molecule stewards within two hours for critical quality decisions, whether current system architecture documentation is accessible and comprehensible to risk assessment teams, whether process owners with recent operational experience are available for participation, and whether quality professionals can effectively challenge assumptions and integrate diverse perspectives.
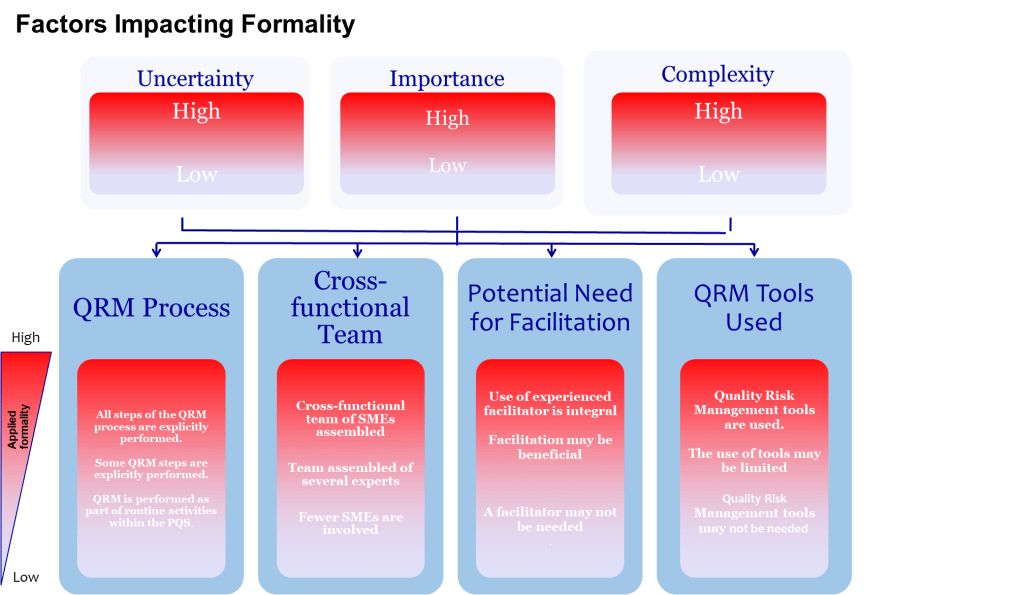
Phase 2: Team Charter and Competence Framework
Moving from compliance theater to protection requires assembling teams with clear charters focused on cognitive rigor rather than checklist completion. An excellent risk team exists to frame, analyze, and communicate uncertainty so businesses can make science-based, patient-centered decisions. Before naming people, organizations must document the decisions teams must enable, the degree of formality those decisions demand, and the resources management will guarantee.
Competence proving rather than role filling ensures each core seat demonstrates documented capabilities. The process owner must have lived the operation recently with authority to change methods and budgets. The molecule steward must understand how specific products fail and translate deviations into patient impact. The technical system owner must articulate functional requirements and design limits. The quality integrator must force cross-functional dialogue and preserve evidence.
Phase 3: Knowledge System Integration
Knowledge-enabled decision making requires structures that make relevant information accessible at decision points while supporting cognitive processes necessary for accurate analysis. This involves structured knowledge capture that explicitly identifies assumptions, limitations, and context rather than simply documenting conclusions. Knowledge validation systems systematically test assumptions embedded in organizational knowledge, including processes for challenging accepted wisdom and updating mental models when new evidence emerges.
Expertise networks connect decision-makers with relevant specialized knowledge when required rather than relying on generalist teams for all assessments. Decision support systems prompt systematic consideration of potential biases and alternative explanations, creating technological infrastructure that supports rather than replaces human cognitive capabilities.
Phase 4: Cultural Embedding and Sustainment
The final phase focuses on embedding cognitive excellence principles into organizational culture through systematic training programs that build both technical competencies and cognitive skills. These programs address not just what tools to use but how to think systematically about complex risk assessment challenges.
Continuous improvement mechanisms systematically analyze risk assessment performance to identify enhancement opportunities and implement improvements in methodologies, training, and support systems. Organizations track prediction accuracy, compare expected versus actual detectability, and feed insights into updated templates and training so subsequent teams start with enhanced capabilities.
Advanced Maturity: Predictive Risk Intelligence
Organizations achieving the highest levels of cognitive excellence implement predictive analytics, real-time bias detection, and adaptive systems that learn from assessment performance. These capabilities enable anticipation of potential risks and bias patterns before they manifest in assessment failures, including systematic monitoring of assessment performance, early warning systems for cognitive failures, and proactive adjustment of assessment approaches based on accumulated experience.
Adaptive learning systems continuously improve organizational capabilities based on performance feedback and changing conditions. These systems identify emerging patterns in risk assessment challenges and automatically adjust methodologies, training programs, and support systems to maintain effectiveness. Organizations at this maturity level contribute to industry knowledge and best practices while serving as benchmarks for other organizations.
From Reactive Compliance to Proactive Capability
The integration of cognitive science insights, knowledge accessibility frameworks, and team design principles creates a transformative approach to pharmaceutical risk management that moves beyond traditional compliance-focused activities toward strategic capability development. Organizations implementing these integrated approaches develop competitive advantages that extend far beyond regulatory compliance.
They build capabilities in systematic decision-making that improve performance across all aspects of pharmaceutical quality management. They create resilient systems that adapt to changing conditions while maintaining consistent effectiveness. Most importantly, they develop cultures of excellence that attract and retain exceptional talent while continuously improving capabilities.
The strategic integration of risk management practices with cultural transformation represents not merely an operational improvement opportunity but a fundamental requirement for sustained success in the evolving pharmaceutical manufacturing environment. Organizations implementing comprehensive risk buy-down strategies through systematic capability development will emerge as industry leaders capable of navigating regulatory complexity while delivering consistent value to patients, stakeholders, and society.
Excellence in this context means designing quality systems that work with human cognitive capabilities rather than against them. This requires integrating knowledge management principles with cognitive science insights to create environments where systematic, evidence-based decision-making becomes natural and sustainable. True elegance in quality system design comes from seamlessly integrating technical excellence with cognitive support, creating systems where the right decisions emerge naturally from the intersection of human expertise and systematic process.
Building Operational Capabilities Through Strategic Risk Management and Cultural Transformation
The Strategic Imperative: Beyond Compliance Theater
The fundamental shift from checklist-driven compliance to sustainable operational excellence grounded in robust risk management culture. Organizations continue to struggle with fundamental capability gaps that manifest as systemic compliance failures, operational disruptions, and ultimately, compromised patient safety.
The Risk Buy-Down Paradigm in Operations
The core challenge here is to build operational capabilities through proactively building systemic competencies that reduce the probability and impact of operational failures over time. Unlike traditional risk mitigation strategies that focus on reactive controls, risk buy-down emphasizes capability development that creates inherent resilience within operational systems.
This paradigm shifts the traditional cost-benefit equation from reactive compliance expenditure to proactive capability investment. Organizations implementing risk buy-down strategies recognize that upfront investments in operational excellence infrastructure generate compounding returns through reduced deviation rates, fewer regulatory observations, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced competitive positioning.
Economic Logic: Investment versus Failure Costs
The financial case for operational capability investment becomes stark when examining failure costs across the pharmaceutical industry. Drug development failures, inclusive of regulatory compliance issues, represent costs ranging from $500 to $900 million per program when accounting for capital costs and failure probabilities. Manufacturing quality failures trigger cascading costs including batch losses, investigation expenses, remediation efforts, regulatory responses, and market disruption.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers continue experiencing fundamental quality system failures despite decades of regulatory enforcement. These failures indicate insufficient investment in underlying operational capabilities, resulting in recurring compliance issues that generate exponentially higher long-term costs than proactive capability development would require.
Organizations successfully implementing risk buy-down strategies demonstrate measurable operational improvements. Companies with strong risk management cultures experience 30% higher likelihood of outperforming competitors while achieving 21% increases in productivity. These performance differentials reflect the compound benefits of systematic capability investment over reactive compliance expenditure.
Just look at the recent whitepaper published by the FDA to see the identified returns to this investment.
Regulatory Intelligence Framework Integration
The regulatory intelligence framework provides crucial foundation for risk buy-down implementation by enabling organizations to anticipate, assess, and proactively address emerging compliance requirements. Rather than responding reactively to regulatory observations, organizations with mature regulatory intelligence capabilities identify systemic capability gaps before they manifest as compliance violations.
Effective regulatory intelligence programs monitor FDA warning letter trends, 483 observations, and enforcement actions to identify patterns indicating capability deficiencies across industry segments. For example, persistent Quality Unit oversight failures across multiple geographic regions indicate fundamental organizational design issues rather than isolated procedural lapses8. This intelligence enables organizations to invest in Quality Unit empowerment, authority structures, and oversight capabilities before experiencing regulatory action.
The integration of regulatory intelligence with risk buy-down strategies creates a proactive capability development cycle where external regulatory trends inform internal capability investments, reducing both regulatory exposure and operational risk while enhancing competitive positioning through superior operational performance.
Culture as the Primary Risk Control
Organizational Culture as Foundational Risk Management
Organizational culture represents the most fundamental risk control mechanism within pharmaceutical operations, directly influencing how quality decisions are made, risks are identified and escalated, and operational excellence is sustained over time. Unlike procedural controls that can be circumvented or technical systems that can fail, culture operates as a pervasive influence that shapes behavior across all organizational levels and operational contexts.
Research demonstrates that organizations with strong risk management cultures are significantly less likely to experience damaging operational risk events and are better positioned to effectively respond when issues do occur.
The foundational nature of culture as a risk control becomes evident when examining quality system failures across pharmaceutical operations. Recent FDA warning letters consistently identify cultural deficiencies underlying technical violations, including insufficient Quality Unit authority, inadequate management commitment to compliance, and systemic failures in risk identification and escalation. These patterns indicate that technical compliance measures alone cannot substitute for robust quality culture.
Quality Culture Impact on Operational Resilience
Quality culture directly influences operational resilience by determining how organizations identify, assess, and respond to quality-related risks throughout manufacturing operations. Organizations with mature quality cultures demonstrate superior capability in preventing quality issues, detecting problems early, and implementing effective corrective actions that address root causes rather than symptoms.
Research in the biopharmaceutical industry reveals that integrating safety and quality cultures creates a unified “Resilience Culture” that significantly enhances organizational ability to sustain high-quality outcomes even under challenging conditions. This resilience culture is characterized by commitment to excellence, customer satisfaction focus, and long-term success orientation that transcends short-term operational pressures.
The operational impact of quality culture manifests through multiple mechanisms. Strong quality cultures promote proactive risk identification where employees at all levels actively surface potential quality concerns before they impact product quality. These cultures support effective escalation processes where quality issues receive appropriate priority regardless of operational pressures. Most importantly, mature quality cultures sustain continuous improvement mindsets where operational challenges become opportunities for systematic capability enhancement.
Dual-Approach Model: Leadership and Employee Ownership
Effective quality culture development requires coordinated implementation of top-down leadership commitment and bottom-up employee ownership, creating organizational alignment around quality principles and operational excellence. This dual-approach model recognizes that sustainable culture transformation cannot be achieved through leadership mandate alone, nor through grassroots initiatives without executive support.
Top-down leadership commitment establishes organizational vision, resource allocation, and accountability structures necessary for quality culture development. Research indicates that leadership commitment is vital for quality culture success and sustainability, with senior management responsible for initiating transformational change, setting quality vision, dedicating resources, communicating progress, and exhibiting visible support. Middle managers and supervisors ensure employees receive direct support and are held accountable to quality values.
Bottom-up employee ownership develops through empowerment, engagement, and competency development that enables staff to integrate quality considerations into daily operations. Organizations achieve employee ownership by incorporating quality into staff orientations, including quality expectations in job descriptions and performance appraisals, providing ongoing training opportunities, granting decision-making authority, and eliminating fear of consequences for quality-related concerns.
The integration of these approaches creates organizational conditions where quality culture becomes self-reinforcing. Leadership demonstrates commitment through resource allocation and decision-making priorities, while employees experience empowerment to make quality-focused decisions without fear of negative consequences for raising concerns or stopping production when quality issues arise.
Culture’s Role in Risk Identification and Response
Mature quality cultures fundamentally alter organizational approaches to risk identification and response by creating psychological safety for surfacing concerns, establishing systematic processes for risk assessment, and maintaining focus on long-term quality outcomes over short-term operational pressures. These cultural characteristics enable organizations to identify and address quality risks before they impact product quality or regulatory compliance.
Risk identification effectiveness depends critically on organizational culture that encourages transparency, values diverse perspectives, and rewards proactive concern identification. Research demonstrates that effective risk cultures promote “speaking up” where employees feel confident raising concerns and leaders demonstrate transparency in decision-making. This cultural foundation enables early risk detection that prevents minor issues from escalating into major quality failures.
Risk response effectiveness reflects cultural values around accountability, continuous improvement, and systematic problem-solving. Organizations with strong risk cultures implement thorough root cause analysis, develop comprehensive corrective and preventive actions, and monitor implementation effectiveness over time. These cultural practices ensure that risk responses address underlying causes rather than symptoms, preventing issue recurrence and building organizational learning capabilities.
The measurement of cultural risk management effectiveness requires systematic assessment of cultural indicators including employee engagement, incident reporting rates, management response to concerns, and the quality of corrective action implementation. Organizations tracking these cultural metrics can identify areas requiring improvement and monitor progress in cultural maturity over time.
Continuous Improvement Culture and Adaptive Capacity
Continuous improvement culture represents a fundamental organizational capability that enables sustained operational excellence through systematic enhancement of processes, systems, and capabilities over time. This culture creates adaptive capacity by embedding improvement mindsets, methodologies, and practices that enable organizations to evolve operational capabilities in response to changing requirements and emerging challenges.
Research demonstrates that continuous improvement culture significantly enhances operational performance through multiple mechanisms. Organizations with strong continuous improvement cultures experience increased employee engagement, higher productivity levels, enhanced innovation, and superior customer satisfaction. These performance improvements reflect the compound benefits of systematic capability development over time.
The development of continuous improvement culture requires systematic investment in employee competencies, improvement methodologies, data collection and analysis capabilities, and organizational learning systems. Organizations achieving mature improvement cultures provide training in improvement methodologies, establish improvement project pipelines, implement measurement systems that track improvement progress, and create recognition systems that reward improvement contributions.
Adaptive capacity emerges from continuous improvement culture through organizational learning mechanisms that capture knowledge from improvement projects, codify successful practices, and disseminate learning across the organization. This learning capability enables organizations to build institutional knowledge that improves response effectiveness to future challenges while preventing recurrence of past issues.
Integration with Regulatory Intelligence and Preventive Action
The integration of continuous improvement methodologies with regulatory intelligence capabilities creates proactive capability development systems that identify and address potential compliance issues before they manifest as regulatory observations. This integration represents advanced maturity in organizational quality management where external regulatory trends inform internal improvement priorities.
Regulatory intelligence provides continuous monitoring of FDA warning letters, 483 observations, enforcement actions, and guidance documents to identify emerging compliance trends and requirements. This intelligence enables organizations to anticipate regulatory expectations and proactively develop capabilities that address potential compliance gaps before they are identified through inspection.
Trending analysis of regulatory observations across industry segments reveals systemic capability gaps that multiple organizations experience. For example, persistent citations for Quality Unit oversight failures indicate industry-wide challenges in Quality Unit empowerment, authority structures, and oversight effectiveness. Organizations with mature regulatory intelligence capabilities use this trending data to assess their own Quality Unit capabilities and implement improvements before experiencing regulatory action.
The implementation of preventive action based on regulatory intelligence creates competitive advantage through superior regulatory preparedness while reducing compliance risk exposure. Organizations systematically analyzing regulatory trends and implementing capability improvements demonstrate regulatory readiness that supports inspection success and enables focus on operational excellence rather than compliance remediation.
The Integration Framework
Aligning Risk Management with Operational Capability Development
The strategic alignment of risk management principles with operational capability development creates synergistic organizational systems where risk identification enhances operational performance while operational excellence reduces risk exposure. This integration requires systematic design of management systems that embed risk considerations into operational processes while using operational data to inform risk management decisions.
Risk-based quality management approaches provide structured frameworks for integrating risk assessment with quality management processes throughout pharmaceutical operations. These approaches move beyond traditional compliance-focused quality management toward proactive systems that identify, assess, and mitigate quality risks before they impact product quality or regulatory compliance.
The implementation of risk-based approaches requires organizational capabilities in risk identification, assessment, prioritization, and mitigation that must be developed through systematic training, process development, and technology implementation. Organizations achieving mature risk-based quality management demonstrate superior performance in preventing quality issues, reducing deviation rates, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Operational capability development supports risk management effectiveness by creating robust processes, competent personnel, and effective oversight systems that reduce the likelihood of risk occurrence while enhancing response effectiveness when risks do materialize. This capability development includes technical competencies, management systems, and organizational culture elements that collectively create operational resilience.
Efficiency-Excellence-Resilience Nexus
The strategic integration of efficiency, excellence, and resilience objectives creates organizational capabilities that simultaneously optimize resource utilization, maintain high-quality standards, and sustain performance under challenging conditions. This integration challenges traditional assumptions that efficiency and quality represent competing objectives, instead demonstrating that properly designed systems achieve superior performance across all dimensions.
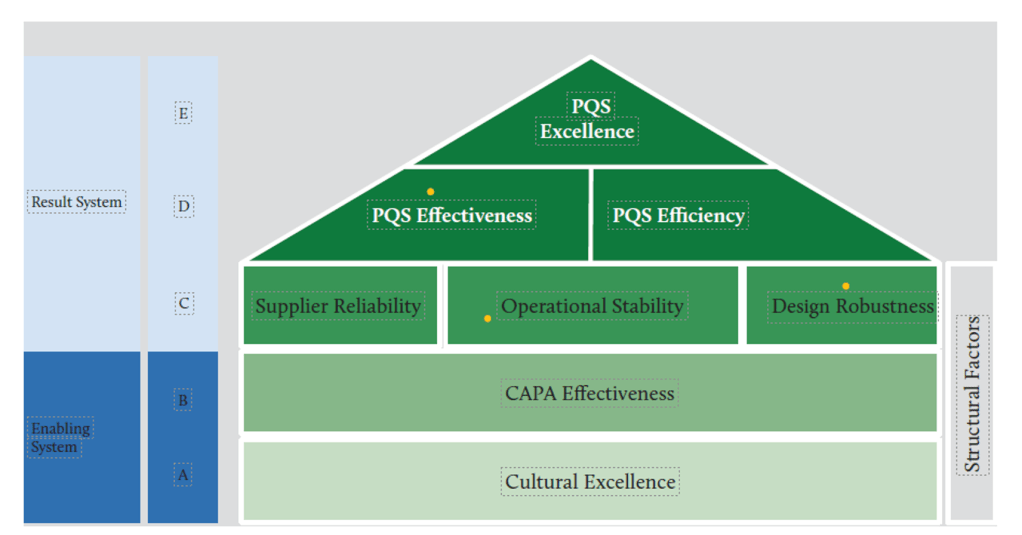
Operational efficiency emerges from systematic elimination of waste, optimization of processes, and effective resource utilization that reduces operational costs while maintaining quality standards.
Operational excellence encompasses consistent achievement of high-quality outcomes through robust processes, competent personnel, and effective management systems.
Operational resilience represents the capability to maintain performance under stress, adapt to changing conditions, and recover effectively from disruptions. Resilience emerges from the integration of efficiency and excellence capabilities with adaptive capacity, redundancy planning, and organizational learning systems that enable sustained performance across varying conditions.
Measurement and Monitoring of Cultural Risk Management
The development of comprehensive measurement systems for cultural risk management enables organizations to track progress, identify improvement opportunities, and demonstrate the business value of culture investments. These measurement systems must capture both quantitative indicators of cultural effectiveness and qualitative assessments of cultural maturity across organizational levels.
Quantitative cultural risk management metrics include employee engagement scores, incident reporting rates, training completion rates, corrective action effectiveness measures, and regulatory compliance indicators. These metrics provide objective measures of cultural performance that can be tracked over time and benchmarked against industry standards.
Qualitative cultural assessment approaches include employee surveys, focus groups, management interviews, and observational assessments that capture cultural nuances not reflected in quantitative metrics. These qualitative approaches provide insights into cultural strengths, improvement opportunities, and the effectiveness of cultural transformation initiatives.
The integration of quantitative and qualitative measurement approaches creates comprehensive cultural assessment capabilities that inform management decision-making while demonstrating progress in cultural maturity. Organizations with mature cultural measurement systems can identify cultural risk indicators early, implement targeted interventions, and track improvement effectiveness over time.
Risk culture measurement frameworks must align with organizational risk appetite, regulatory requirements, and business objectives to ensure relevance and actionability. Effective frameworks establish clear definitions of desired cultural behaviors, implement systematic measurement processes, and create feedback mechanisms that inform continuous improvement in cultural effectiveness.
Common Capability Gaps Revealed Through FDA Observations
Analysis of FDA warning letters and 483 observations reveals persistent capability gaps across pharmaceutical manufacturing operations that reflect systemic weaknesses in organizational design, management systems, and quality culture. These capability gaps manifest as recurring regulatory observations that persist despite repeated enforcement actions, indicating fundamental deficiencies in operational capabilities rather than isolated procedural failures.
Quality Unit oversight failures represent the most frequently cited deficiency in FDA warning letters. These failures encompass insufficient authority to ensure CGMP compliance, inadequate resources for effective oversight, poor documentation practices, and systematic failures in deviation investigation and corrective action implementation. The persistence of Quality Unit deficiencies across multiple geographic regions indicates industry-wide challenges in Quality Unit design and empowerment.
Data integrity violations represent another systematic capability gap revealed through regulatory observations, including falsified records, inappropriate data manipulation, deleted electronic records, and inadequate controls over data generation and review. These violations indicate fundamental weaknesses in data governance systems, personnel training, and organizational culture around data integrity principles.
Deviation investigation and corrective action deficiencies appear consistently across FDA warning letters, reflecting inadequate capabilities in root cause analysis, corrective action development, and implementation effectiveness monitoring. These deficiencies indicate systematic weaknesses in problem-solving methodologies, investigation competencies, and management systems for tracking corrective action effectiveness.
Manufacturing process control deficiencies including inadequate validation, insufficient process monitoring, and poor change control implementation represent persistent capability gaps that directly impact product quality and regulatory compliance. These deficiencies reflect inadequate technical capabilities, insufficient management oversight, and poor integration between manufacturing and quality systems.
GMP Culture Translation to Operational Resilience
The five pillars of GMP – People, Product, Process, Procedures, and Premises – provide comprehensive framework for organizational capability development that addresses all aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing operations. Effective GMP culture ensures that each pillar receives appropriate attention and investment while maintaining integration across all operational elements.
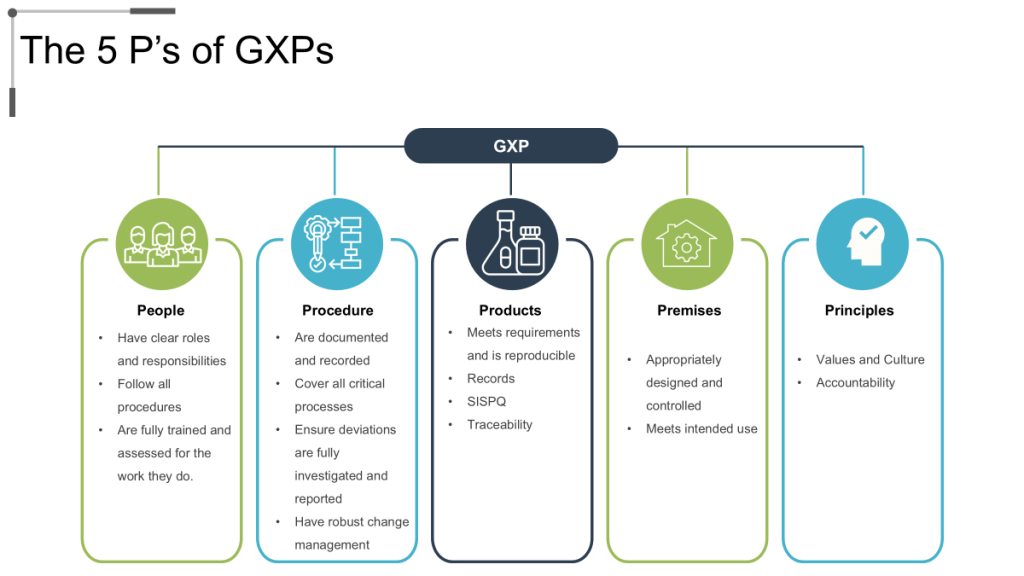
Personnel competency development represents the foundational element of GMP culture, encompassing technical training, quality awareness, regulatory knowledge, and continuous learning capabilities that enable employees to make appropriate quality decisions across varying operational conditions. Organizations with mature GMP cultures invest systematically in personnel development while creating career advancement opportunities that retain quality expertise.
Process robustness and validation ensure that manufacturing operations consistently produce products meeting quality specifications while providing confidence in process capability under normal operating conditions. GMP culture emphasizes process understanding, validation effectiveness, and continuous monitoring that enables proactive identification and resolution of process issues before they impact product quality.
Documentation systems and data integrity support all aspects of GMP implementation by providing objective evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements while enabling effective investigation and corrective action when issues occur. Mature GMP cultures emphasize documentation accuracy, completeness, and accessibility while implementing controls that prevent data integrity issues.
Risk-Based Quality Management as Operational Capability
Risk-based quality management represents advanced organizational capability that integrates risk assessment principles with quality management processes to create proactive systems that prevent quality issues while optimizing resource allocation. This capability enables organizations to focus quality oversight activities on areas with greatest potential impact while maintaining comprehensive quality assurance across all operations.
The implementation of risk-based quality management requires organizational capabilities in risk identification, assessment, prioritization, and mitigation that must be developed through systematic training, process development, and technology implementation. Organizations achieving mature risk-based capabilities demonstrate superior performance in preventing quality issues, reducing deviation rates, and maintaining regulatory compliance efficiency.
Critical process identification and control strategy development represent core competencies in risk-based quality management that enable organizations to focus resources on processes with greatest potential impact on product quality. These competencies require deep process understanding, risk assessment capabilities, and systematic approaches to control strategy optimization.
Continuous monitoring and trending analysis capabilities enable organizations to identify emerging quality risks before they impact product quality while providing data for systematic improvement of risk management effectiveness. These capabilities require data collection systems, analytical competencies, and management processes that translate monitoring results into proactive risk mitigation actions.
Supplier Management and Third-Party Risk Capabilities
Supplier management and third-party risk management represent critical organizational capabilities that directly impact product quality, regulatory compliance, and operational continuity. The complexity of pharmaceutical supply chains requires sophisticated approaches to supplier qualification, performance monitoring, and risk mitigation that go beyond traditional procurement practices.
Supplier qualification processes must assess not only technical capabilities but also quality culture, regulatory compliance history, and risk management effectiveness of potential suppliers. This assessment requires organizational capabilities in audit planning, execution, and reporting that provide confidence in supplier ability to meet pharmaceutical quality requirements consistently.
Performance monitoring systems must track supplier compliance with quality requirements, delivery performance, and responsiveness to quality issues over time. These systems require data collection capabilities, analytical competencies, and escalation processes that enable proactive management of supplier performance issues before they impact operations.
Risk mitigation strategies must address potential supply disruptions, quality failures, and regulatory compliance issues across the supplier network. Effective risk mitigation requires contingency planning, alternative supplier development, and inventory management strategies that maintain operational continuity while ensuring product quality.
The integration of supplier management with internal quality systems creates comprehensive quality assurance that extends across the entire value chain while maintaining accountability for product quality regardless of manufacturing location or supplier involvement. This integration requires organizational capabilities in supplier oversight, quality agreement management, and cross-functional coordination that ensure consistent quality standards throughout the supply network.
Implementation Roadmap for Cultural Risk Management Development
Staged Approach to Cultural Risk Management Development
The implementation of cultural risk management requires systematic, phased approach that builds organizational capabilities progressively while maintaining operational continuity and regulatory compliance. This staged approach recognizes that cultural transformation requires sustained effort over extended timeframes while providing measurable progress indicators that demonstrate value and maintain organizational commitment.
Phase 1: Foundation Building and Assessment establishes baseline understanding of current culture state, identifies immediate improvement opportunities, and creates infrastructure necessary for systematic cultural development. This phase includes comprehensive cultural assessment, leadership commitment establishment, initial training program development, and quick-win implementation that demonstrates early value from cultural investment.
Cultural assessment activities encompass employee surveys, management interviews, process observations, and regulatory compliance analysis that provide comprehensive understanding of current cultural strengths and improvement opportunities. These assessments establish baseline measurements that enable progress tracking while identifying specific areas requiring focused attention during subsequent phases.
Leadership commitment development ensures that senior management understands cultural transformation requirements, commits necessary resources, and demonstrates visible support for cultural change initiatives. This commitment includes resource allocation, communication of cultural expectations, and integration of cultural objectives into performance management systems.
Phase 2: Capability Development and System Implementation focuses on building specific competencies, implementing systematic processes, and creating organizational infrastructure that supports sustained cultural improvement. This phase includes comprehensive training program rollout, process improvement implementation, measurement system development, and initial culture champion network establishment.
Training program implementation provides employees with knowledge, skills, and tools necessary for effective participation in cultural transformation while creating shared understanding of quality expectations and risk management principles. These programs must be tailored to specific roles and responsibilities while maintaining consistency in core cultural messages.
Process improvement implementation creates systematic approaches to risk identification, assessment, and mitigation that embed cultural values into daily operations. These processes include structured problem-solving methodologies, escalation procedures, and continuous improvement practices that reinforce cultural expectations through routine operational activities.
Phase 3: Integration and Sustainment emphasizes cultural embedding, performance optimization, and continuous improvement capabilities that ensure long-term cultural effectiveness. This phase includes advanced measurement system implementation, culture champion network expansion, and systematic review processes that maintain cultural momentum over time.
Leadership Engagement Strategies for Sustainable Change
Leadership engagement represents the most critical factor in successful cultural transformation, requiring systematic strategies that ensure consistent leadership behavior, effective communication, and sustained commitment throughout the transformation process. Effective leadership engagement creates organizational conditions where cultural change becomes self-reinforcing while providing clear direction and resources necessary for transformation success.
Visible Leadership Commitment requires leaders to demonstrate cultural values through daily decisions, resource allocation priorities, and personal behavior that models expected cultural norms. This visibility includes regular communication of cultural expectations, participation in cultural activities, and recognition of employees who exemplify desired cultural behaviors.
Leadership communication strategies must provide clear, consistent messages about cultural expectations while demonstrating transparency in decision-making and responsiveness to employee concerns. Effective communication includes regular updates on cultural progress, honest discussion of challenges, and celebration of cultural achievements that reinforce the value of cultural investment.
Leadership Development Programs ensure that managers at all levels possess competencies necessary for effective cultural leadership including change management skills, coaching capabilities, and performance management approaches that support cultural transformation. These programs must be ongoing rather than one-time events to ensure sustained leadership effectiveness.
Change management competencies enable leaders to guide employees through cultural transformation while addressing resistance, maintaining morale, and sustaining momentum throughout extended change processes. These competencies include stakeholder engagement, communication planning, and resistance management approaches that facilitate smooth cultural transitions.
Accountability Systems ensure that leaders are held responsible for cultural outcomes within their areas of responsibility while providing support and resources necessary for cultural success. These systems include cultural metrics integration into performance management systems, regular cultural assessment processes, and recognition programs that reward effective cultural leadership.
Training and Development Frameworks
Comprehensive training and development frameworks provide employees with competencies necessary for effective participation in risk-based quality culture while creating organizational learning capabilities that support continuous cultural improvement. These frameworks must be systematic, role-specific, and continuously updated to reflect evolving regulatory requirements and organizational capabilities.
Foundational Training Programs establish basic understanding of quality principles, risk management concepts, and regulatory requirements that apply to all employees regardless of specific role or function. This training creates shared vocabulary and understanding that enables effective cross-functional collaboration while ensuring consistent application of cultural principles.
Quality fundamentals training covers basic concepts including customer focus, process thinking, data-driven decision making, and continuous improvement that form the foundation of quality culture. This training must be interactive, practical, and directly relevant to employee daily responsibilities to ensure engagement and retention.
Risk management training provides employees with capabilities in risk identification, assessment, communication, and escalation that enable proactive risk management throughout operations. This training includes both conceptual understanding and practical tools that employees can apply immediately in their work environment.
Role-Specific Advanced Training develops specialized competencies required for specific positions while maintaining alignment with overall cultural objectives and organizational quality strategy. This training addresses technical competencies, leadership skills, and specialized knowledge required for effective performance in specific roles.
Management training focuses on leadership competencies, change management skills, and performance management approaches that support cultural transformation while achieving operational objectives. This training must be ongoing and include both formal instruction and practical application opportunities.
Technical training ensures that employees possess current knowledge and skills required for effective job performance while maintaining awareness of evolving regulatory requirements and industry best practices. This training includes both initial competency development and ongoing skill maintenance programs.
Continuous Learning Systems create organizational capabilities for identifying training needs, developing training content, and measuring training effectiveness that ensure sustained competency development over time. These systems include needs assessment processes, content development capabilities, and effectiveness measurement approaches that continuously improve training quality.
Metrics and KPIs for Tracking Capability Maturation
Comprehensive measurement systems for cultural capability maturation provide objective evidence of progress while identifying areas requiring additional attention and investment. These measurement systems must balance quantitative indicators with qualitative assessments to capture the full scope of cultural development while providing actionable insights for continuous improvement.
Leading Indicators measure cultural inputs and activities that predict future cultural performance including training completion rates, employee engagement scores, participation in improvement activities, and leadership behavior assessments. These indicators provide early warning of cultural issues while demonstrating progress in cultural development activities.
Employee engagement measurements capture employee commitment to organizational objectives, satisfaction with work environment, and confidence in organizational leadership that directly influence cultural effectiveness. These measurements include regular survey processes, focus group discussions, and exit interview analysis that provide insights into employee perspectives on cultural development.
Training effectiveness indicators track not only completion rates but also competency development, knowledge retention, and application of training content in daily work activities. These indicators ensure that training investments translate into improved job performance and cultural behavior.
Lagging Indicators measure cultural outcomes including quality performance, regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction that reflect the ultimate impact of cultural investments. These indicators provide validation of cultural effectiveness while identifying areas where cultural development has not yet achieved desired outcomes.
Quality performance metrics include deviation rates, customer complaints, product recalls, and regulatory observations that directly reflect the effectiveness of quality culture in preventing quality issues. These metrics must be trended over time to identify improvement patterns and areas requiring additional attention.
Operational efficiency indicators encompass productivity measures, cost performance, delivery performance, and resource utilization that demonstrate the operational impact of cultural improvements. These indicators help demonstrate the business value of cultural investments while identifying opportunities for further improvement.
Integrated Measurement Systems combine leading and lagging indicators into comprehensive dashboards that provide management with complete visibility into cultural development progress while enabling data-driven decision making about cultural investments. These systems include automated data collection, trend analysis capabilities, and exception reporting that focus management attention on areas requiring intervention.
Benchmarking capabilities enable organizations to compare their cultural performance against industry standards and best practices while identifying opportunities for improvement. These capabilities require access to industry data, analytical competencies, and systematic comparison processes that inform cultural development strategies.
Future-Facing Implications for the Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Emerging Regulatory Trends and Capability Requirements
The regulatory landscape continues evolving toward increased emphasis on risk-based approaches, data integrity requirements, and organizational culture assessment that require corresponding evolution in organizational capabilities and management approaches. Organizations must anticipate these regulatory developments and proactively develop capabilities that address future requirements rather than merely responding to current regulations.
Enhanced Quality Culture Focus in regulatory inspections requires organizations to demonstrate not only technical compliance but also cultural effectiveness in sustaining quality performance over time. This trend requires development of cultural measurement capabilities, cultural audit processes, and systematic approaches to cultural development that provide evidence of cultural maturity to regulatory inspectors.
Risk-based inspection approaches focus regulatory attention on areas with greatest potential risk while requiring organizations to demonstrate effective risk management capabilities throughout their operations. This evolution requires mature risk assessment capabilities, comprehensive risk mitigation strategies, and systematic documentation of risk management effectiveness.
Technology Integration and Cultural Adaptation
Technology integration in pharmaceutical manufacturing creates new opportunities for operational excellence while requiring cultural adaptation that maintains human oversight and decision-making capabilities in increasingly automated environments. Organizations must develop cultural approaches that leverage technology capabilities while preserving the human judgment and oversight essential for quality decision-making.
Digital quality systems enable real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and automated decision support that enhance quality management effectiveness while requiring new competencies in system operation, data interpretation, and technology-assisted decision making. Cultural adaptation must ensure that technology enhances rather than replaces human quality oversight capabilities.
Data Integrity in Digital Environments requires sophisticated understanding of electronic systems, data governance principles, and cybersecurity requirements that go beyond traditional paper-based quality systems. Cultural development must emphasize data integrity principles that apply across both electronic and paper systems while building competencies in digital data management.
Building Adaptive Organizational Capabilities
The increasing pace of change in regulatory requirements, technology capabilities, and market conditions requires organizational capabilities that enable rapid adaptation while maintaining operational stability and quality performance. These adaptive capabilities must be embedded in organizational culture and management systems to ensure sustained effectiveness across changing conditions.
Learning Organization Capabilities enable systematic capture, analysis, and dissemination of knowledge from operational experience, regulatory changes, and industry developments that inform continuous organizational improvement. These capabilities include knowledge management systems, learning processes, and cultural practices that promote organizational learning and adaptation.
Scenario planning and contingency management capabilities enable organizations to anticipate potential future conditions and develop response strategies that maintain operational effectiveness across varying circumstances. These capabilities require analytical competencies, strategic planning processes, and risk management approaches that address uncertainty systematically.
Change Management Excellence encompasses systematic approaches to organizational change that minimize disruption while maximizing adoption of new capabilities and practices. These capabilities include change planning, stakeholder engagement, communication strategies, and performance management approaches that facilitate smooth organizational transitions.
Resilience building requires organizational capabilities that enable sustained performance under stress, rapid recovery from disruptions, and systematic strengthening of organizational capabilities based on experience with challenges. These capabilities encompass redundancy planning, crisis management, business continuity, and systematic approaches to capability enhancement based on lessons learned.
The future pharmaceutical manufacturing environment will require organizations that combine operational excellence with adaptive capability, regulatory intelligence with proactive compliance, and technical competence with robust quality culture. Organizations successfully developing these integrated capabilities will achieve sustainable competitive advantage while contributing to improved patient outcomes through reliable access to high-quality pharmaceutical products.
The strategic integration of risk management practices with cultural transformation represents not merely an operational improvement opportunity but a fundamental requirement for sustained success in the evolving pharmaceutical manufacturing environment. Organizations implementing comprehensive risk buy-down strategies through systematic capability development will emerge as industry leaders capable of navigating regulatory complexity while delivering consistent value to patients, stakeholders, and society.