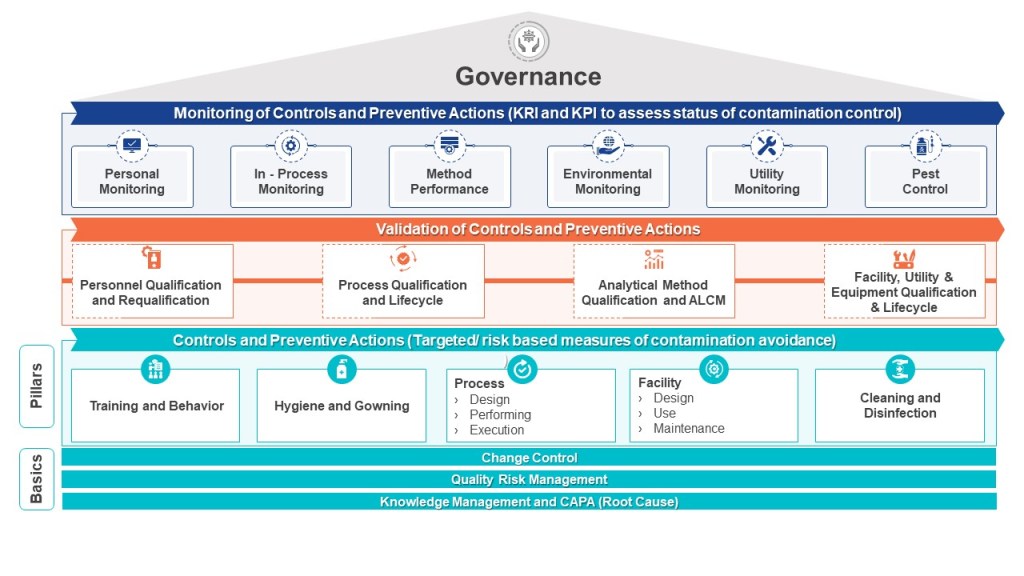
In the previous post, we discussed the critical importance of thorough investigations into deviations, as highlighted by the recent FDA warning letter to Sanofi. Let us delve deeper into a specific aspect of these investigations: determining whether an invalidated out-of-specification (OOS) result for bioburden, endotoxin, or environmental monitoring action limit excursions conclusively demonstrates causative laboratory error.
When faced with an OOS result in microbiological testing, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough investigation before invalidating the result. The FDA expects companies to provide scientific justification and evidence that conclusively demonstrates a causative laboratory error if a result is to be invalidated.
Key Steps in Evaluating Laboratory Error
1. Review of Test Method and Procedure
- Examine the standard operating procedure (SOP) for the test method
- Verify that all steps were followed correctly
- Check for any deviations from the established procedure
2. Evaluation of Equipment and Materials
Evaluation of Equipment and Materials is a critical step in determining whether laboratory error caused an out-of-specification (OOS) result, particularly for bioburden, endotoxin, or environmental monitoring tests. Here’s a detailed approach to performing this evaluation:
Equipment Assessment
Functionality Check
- Run performance verification tests on key equipment used in the analysis
- Review equipment logs for any recent malfunctions or irregularities
- Verify that all equipment settings were correct for the specific test performed
Calibration Review
- Check calibration records to ensure equipment was within its calibration period
- Verify that calibration standards used were traceable and not expired
- Review any recent calibration data for trends or shifts
Maintenance Evaluation
- Examine maintenance logs for adherence to scheduled maintenance
- Look for any recent repairs or adjustments that could affect performance
- Verify that all preventive maintenance tasks were completed as required
Materials Evaluation
Reagent Quality Control
- Check expiration dates of all reagents used in the test
- Review storage conditions to ensure reagents were stored properly
- Verify that quality control checks were performed on reagents before use
Media Assessment (for Bioburden and Environmental Monitoring)
- Review growth promotion test results for culture media
- Check pH and sterility of prepared media
- Verify that media was stored at the correct temperature
Water Quality (for Endotoxin Testing)
- Review records of water quality used for reagent preparation
- Check for any recent changes in water purification systems
- Verify endotoxin levels in water used for testing
Environmental Factors
Laboratory Conditions
- Review temperature and humidity logs for the testing area
- Check for any unusual events (e.g., power outages, HVAC issues) around the time of testing
- Verify that environmental conditions met the requirements for the test method
Contamination Control
- Examine cleaning logs for the laboratory area and equipment
- Review recent environmental monitoring results for the testing area
- Check for any breaches in aseptic technique during testing
Documentation Review
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Verify that the most current version of the SOP was used
- Check for any recent changes to the SOP that might affect the test
- Ensure all steps in the SOP were followed and documented
Equipment and Material Certifications
- Review certificates of analysis for critical reagents and standards
- Check equipment qualification documents (IQ/OQ/PQ) for compliance
- Verify that all required certifications were current at the time of testing
By thoroughly evaluating equipment and materials using these detailed steps, laboratories can more conclusively determine whether an OOS result was due to laboratory error or represents a true product quality issue. This comprehensive approach helps ensure the integrity of microbiological testing and supports robust quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
3. Assessment of Analyst Performance
Here are key aspects to consider when evaluating analyst performance during an OOS investigation:
Review Training Records
- Examine the analyst’s training documentation to ensure they are qualified to perform the specific test method.
- Verify that the analyst has completed all required periodic refresher training.
- Check if the analyst has demonstrated proficiency in the particular test method recently.
Evaluate Recent Performance History
- Review the analyst’s performance on similar tests over the past few months.
- Look for any patterns or trends in the analyst’s results, such as consistently high or low readings.
- Compare the analyst’s results with those of other analysts performing the same tests.
Conduct Interviews
- Interview the analyst who performed the test to gather detailed information about the testing process.
- Ask open-ended questions to encourage the analyst to describe any unusual occurrences or deviations from standard procedures.
- Inquire about the analyst’s workload and any potential distractions during testing.
Observe Technique
- If possible, have the analyst demonstrate the test method while being observed by a supervisor or senior analyst.
- Pay attention to the analyst’s technique, including sample handling, reagent preparation, and equipment operation.
- Note any deviations from standard operating procedures (SOPs) or good practices.
Review Documentation Practices
- Examine the analyst’s laboratory notebooks and test records for completeness and accuracy.
- Verify that all required information was recorded contemporaneously.
- Check for any unusual notations or corrections in the documentation.
Assess Knowledge of Method and Equipment
- Quiz the analyst on critical aspects of the test method and equipment operation.
- Verify their understanding of acceptance criteria, potential sources of error, and troubleshooting procedures.
- Ensure the analyst is aware of recent changes to SOPs or equipment calibration requirements.
Evaluate Workload and Environment
- Consider the analyst’s workload at the time of testing, including any time pressures or competing priorities.
- Assess the laboratory environment for potential distractions or interruptions that could have affected performance.
- Review any recent changes in the analyst’s responsibilities or work schedule.
Perform Comparative Testing
- Have another qualified analyst repeat the test using the same sample and equipment, if possible.
- Compare the results to determine if there are significant discrepancies between analysts.
- If discrepancies exist, investigate potential reasons for the differences.
Review Equipment Use Records
- Check equipment logbooks to verify proper use and any noted issues during the time of testing.
- Confirm that the analyst used the correct equipment and that it was properly calibrated and maintained.
Consider Human Factors
- Assess any personal factors that could have affected the analyst’s performance, such as fatigue, illness, or personal stress.
- Review the analyst’s work schedule leading up to the OOS result for any unusual patterns or extended hours.
By thoroughly assessing analyst performance using these methods, investigators can determine whether human error contributed to the OOS result and identify areas for improvement in training, procedures, or work environment. It’s important to approach this assessment objectively and supportively, focusing on systemic improvements rather than individual blame.
4. Examination of Environmental Factors
- Review environmental monitoring data for the testing area
- Check for any unusual events or conditions that could have affected the test
5. Data Analysis and Trending
- Compare the OOS result with historical data and trends
- Look for any patterns or anomalies that might explain the result
Conclusive vs. Inconclusive Evidence
Conclusive Evidence of Laboratory Error
To conclusively demonstrate laboratory error, you should be able to:
- Identify a specific, documented error in the testing process
- Reproduce the error and show how it leads to the OOS result
- Demonstrate that correcting the error leads to an in-specification result
Examples of conclusive evidence might include:
- Documented use of an expired reagent
- Verified malfunction of testing equipment
- Confirmed contamination of a negative control
Inconclusive Evidence
If the investigation reveals potential issues but cannot definitively link them to the OOS result, the evidence is considered inconclusive. This might include:
- Minor deviations from SOPs that don’t clearly impact the result
- Slight variations in environmental conditions
- Analyst performance issues that aren’t directly tied to the specific test
Special Considerations for Microbiological Testing
Bioburden, endotoxin, and environmental monitoring tests present unique challenges due to their biological nature.
Bioburden Testing
- Consider the possibility of sample contamination during collection or processing
- Evaluate the recovery efficiency of the test method
- Assess the potential for microbial growth during sample storage
Endotoxin Testing
- Review the sample preparation process, including any dilution steps
- Evaluate the potential for endotoxin masking or enhancement
- Consider the impact of product formulation on the test method
Environmental Monitoring
- Assess the sampling technique and equipment used
- Consider the potential for transient environmental contamination
- Evaluate the impact of recent cleaning or maintenance activities
Documenting the Investigation
Regardless of the outcome, it’s crucial to thoroughly document the investigation process. This documentation should include:
- A clear description of the OOS result and initial observations
- Detailed accounts of all investigative steps taken
- Raw data and analytical results from the investigation
- A comprehensive analysis of the evidence
- A scientifically justified conclusion
Conclusion
Determining whether an invalidated OOS result conclusively demonstrates causative laboratory error requires a systematic, thorough, and well-documented investigation. For microbiological tests like bioburden, endotoxin, and environmental monitoring, this process can be particularly challenging due to the complex and sometimes variable nature of biological systems.
Remember, the goal is not to simply invalidate OOS results, but to understand the root cause and implement corrective and preventive actions. Only through rigorous investigation and continuous improvement can we ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. When investigating environmental and in-process results we are investigating the whole house of contamination control.