Hopefully, you’ve been following my journey through the ever-changing world of validation. In that case, you’ll recognize that our field is undergoing transformation under the dual drivers of digital transformation and shifting regulatory expectations. Halfway through 2025, we have another annual report from Kneat, and it is clear that while some of those core challenges remain, companies are reporting that new priorities are emerging—driven by the rapid pace of digital adoption and evolving compliance landscapes.
Audit Readiness Overtakes Compliance Burden as Top Challenge
The 2025 validation landscape reveals a striking reversal: audit readiness has dethroned compliance burden as the industry’s primary concern , marking a fundamental shift in how organizations prioritize regulatory preparedness. While compliance burden dominated in 2024—a reflection of teams grappling with evolving standards during active projects—this year’s data signals a maturation of validation programs. As organizations transition from project execution to operational stewardship, the scramble to pass audits has given way to the imperative to sustain readiness.
Why the Shift Matters
The surge in audit readiness aligns with broader quality challenges outlined in The Challenges Ahead for Quality (2023) , where data integrity and operational resilience emerged as systemic priorities.
Table: Top Validation Challenges (2022–2025)
| Rank | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Human resources | Human resources | Compliance burden | Audit readiness |
| 2 | Efficiency | Efficiency | Audit readiness | Compliance burden |
| 3 | Technological gaps | Technological gaps | Data integrity | Data integrity |
This reversal mirrors a lifecycle progression. During active validation projects, teams focus on navigating procedural requirements (compliance burden). Once operational, the emphasis shifts to sustaining inspection-ready systems—a transition fraught with gaps in metadata governance and decentralized workflows. As noted in Health of the Validation Program, organizations often discover latent weaknesses in change control or data traceability only during audits, underscoring the need for proactive systems.
Next year it could flop back, to be honest these are just two sides of the same coin.
Operational Realities Driving the Change
The 2025 report highlights two critical pain points:
- Documentation traceability : 69% of teams using digital validation tools cite automated audit trails as their top benefit, yet only 13% integrate these systems with project management platform . This siloing creates last-minute scrambles to reconcile disparate records.
- Experience gaps : With 42% of professionals having 6–15 years of experience, mid-career teams lack the institutional knowledge to prevent audit pitfalls—a vulnerability exacerbated by retiring senior experts .
Organizations that treated compliance as a checkbox exercise now face operational reckoning, as fragmented systems struggle to meet the FDA’s expectations for real-time data access and holistic process understanding.
Similarly, teams that relied on 1 or 2 full-time employees, and leveraged contractors, also struggle with building and retaining expertise.
Strategic Implications
To bridge this gap, forward-thinking teams continue to adopt risk-adaptive validation models that align with ICH Q10’s lifecycle approach. By embedding audit readiness into daily work organizations can transform validation from a cost center to a strategic asset. As argued in Principles-Based Compliance, this shift requires rethinking quality culture: audit preparedness is not a periodic sprint but a byproduct of robust, self-correcting systems.
In essence, audit readiness reflects validation’s evolution from a tactical compliance activity to a cornerstone of enterprise quality—a theme that will continue to dominate the profession’s agenda and reflects the need to drive for maturity.
Digital Validation Adoption Reaches Tipping Point
Digital validation systems have seen a 28% adoption increase since 2024, with 58% of organizations now using these tools . By 2025, 93% of firms either use or plan to adopt digital validation, signaling and sector-wide transformation. Early adopters report significant returns: 63% meet or exceed ROI expectations, achieving 50% faster cycle times and reduced deviations. However, integration gaps persist, as only 13% connect digital validation with project management tools, highlighting siloed workflows.
None of this should be a surprise, especially since Kneat, a provider of an electronic validation management system, sponsored the report.
Table 2: Digital Validation Adoption Metrics (2025)
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Organizations using digital systems | 58% |
| ROI expectations met/exceeded | 63% |
| Integration with project tools | 13% |
For me, the real challenge here, as I explored in my post “Beyond Documents: Embracing Data-Centric Thinking“, is not just settling for paper-on-glass but to start thinking of your validation data as a larger lifecycle.
Leveraging Data-Centric Thinking for Digital Validation Transformation
The shift from document-centric to data-centric validation represents a paradigm shift in how regulated industries approach compliance, as outlined in Beyond Documents: Embracing Data-Centric Thinking. This transition aligns with the 2025 State of Validation Report’s findings on digital adoption trends and addresses persistent challenges like audit readiness and workforce pressures.
The Paper-on-Glass Trap in Validation
Many organizations remain stuck in “paper-on-glass” validation models, where digital systems replicate paper-based workflows without leveraging data’s full potential. This approach perpetuates inefficiencies such as:
- Manual data extraction requiring hours to reconcile disparate records
- Inflated validation cycles due to rigid document structures that limit adaptive testing
- Increased error rates from static protocols that cannot dynamically respond to process deviations
Principles of Data-Centric Validation
True digital transformation requires reimagining validation through four core data-centric principles:
- Unified Data Layer Architecture: The adoption of unified data layer architectures marks a paradigm shift in validation practices, as highlighted in the 2025 State of Validation Report. By replacing fragmented document-centric models with centralized repositories, organizations can achieve real-time traceability and automated compliance with ALCOA++ principles. The transition to structured data objects over static PDFs directly addresses the audit readiness challenges discussed above, ensuring metadata remains enduring and available across decentralized teams.
- Dynamic Protocol Generation: AI-driven dynamic protocol generation may reshape validation efficiency. By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning, the hope is to have systems analyze historical protocols and regulatory guidelines to auto-generate context-aware test scripts. However, regulatory acceptance remains a barrier—only 10% of firms integrate validation systems with AI analytics, highlighting the need for controlled pilots in low-risk scenarios before broader deployment.
- Continuous Process Verification: Continuous Process Verification (CPV) has emerged as a cornerstone of the industry as IoT sensors and real-time analytics enabling proactive quality management. Unlike traditional batch-focused validation, CPV systems feed live data from manufacturing equipment into validation platforms, triggering automated discrepancy investigations when parameters exceed thresholds. By aligning with ICH Q10’s lifecycle approach, CPV transforms validation from a compliance exercise into a strategic asset.
- Validation as Code: The validation-as-code movement, pioneered in semiconductor and nuclear industries, represents the next frontier in agile compliance. By representing validation requirements as machine-executable code, teams automate regression testing during system updates and enable Git-like version control for protocols. The model’s inherent auditability—with every test result linked to specific code commits—directly addresses the data integrity priorities ranked #1 by 63% of digital validation adopters.
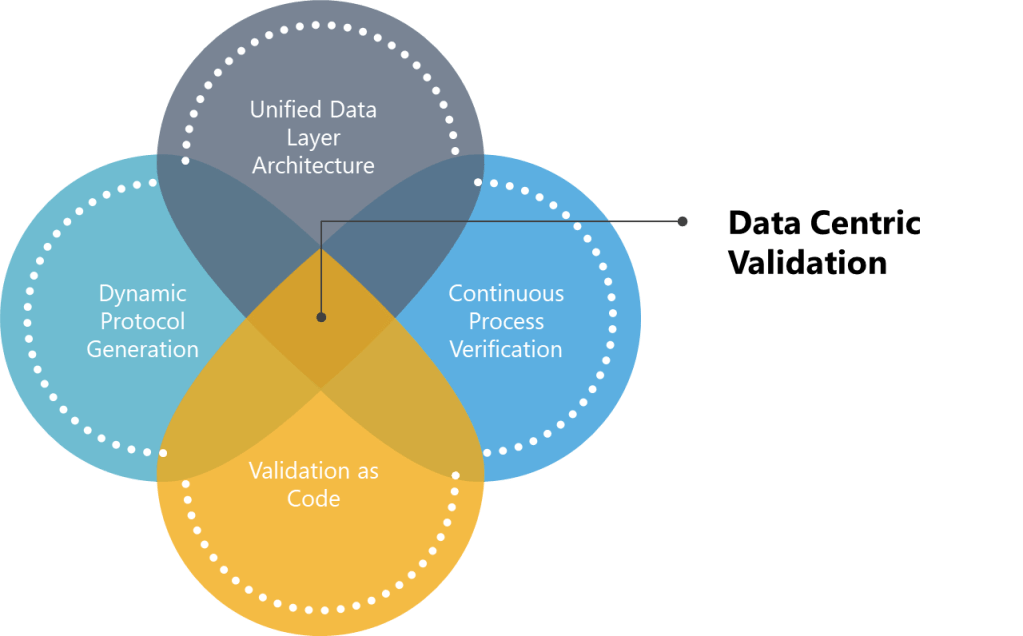
Table 1: Document-Centric vs. Data-Centric Validation Models
| Aspect | Document-Centric | Data-Centric |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Artifact | PDF/Word Documents | Structured Data Objects |
| Change Management | Manual Version Control | Git-like Branching/Merging |
| Audit Readiness | Weeks of Preparation | Real-Time Dashboard Access |
| AI Compatibility | Limited (OCR-Dependent) | Native Integration (eg, LLM Fine-Tuning) |
| Cross-System Traceability | Manual Matrix Maintenance | Automated API-Driven Links |
Implementation Roadmap
Organizations progressing towards maturity should:
- Conduct Data Maturity Assessments
- Map existing validation data flows
- Perform a maturity assessment
- Adopt Modular Validation Platforms
- Implement cloud-native solutions
- Reskill Teams for Data Fluency
- Establish Data Governance Frameworks
AI in Validation: Early Adoption, Strategic Potential
Artificial intelligence (AI) adoption and validation are still in the early stages, though the outlook is promising. Currently, much of the conversation around AI is driven by hype, and while there are encouraging developments, significant questions remain about the fundamental soundness and reliability of AI technologies.
In my view, AI is something to consider for the future rather than immediate implementation, as we still need to fully understand how it functions. There are substantial concerns regarding the validation of AI systems that the industry must address, especially as we approach more advanced stages of integration. Nevertheless, AI holds considerable potential, and leading-edge companies are already exploring a variety of approaches to harness its capabilities.
Table 3: AI Adoption in Validation (2025)
| AI Application | Adoption Rate | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol generation | 12% | 40% faster drafting |
| Risk assessment automation | 9% | 30% reduction in deviations |
| Predictive analytics | 5% | 25% improvement in audit readiness |
Workforce Pressures Intensify Amid Resource Constraints
Workloads increased for 66% of teams in 2025, yet 39% operate with 1–3 members, exacerbating talent gaps . Mid-career professionals (42% with 6–15 years of experience) dominate the workforce, signaling a looming “experience gap” as senior experts retire. This echoes 2023 quality challenges, where turnover risks and knowledge silos threaten operational resilience. Outsourcing has become a critical strategy, with 70% of firms relying on external partners for at least 10% of validation work.
Smart organizations have talent and competency building strategies.
Emerging Challenges and Strategic Responses
From Compliance to Continuous Readiness
Organizations are shifting from reactive compliance to building “always-ready” systems.
From Firefighting to Future-Proofing: The Strategic Shift to “Always-Ready” Quality Systems
The industry’s transition from reactive compliance to “always-ready” systems represents a fundamental reimagining of quality management. This shift aligns with the Excellence Triad framework—efficiency, effectiveness, and elegance—introduced in my 2025 post on elegant quality systems, where elegance is defined as the seamless integration of intuitive design, sustainability, and user-centric workflows. Rather than treating compliance as a series of checkboxes to address during audits, organizations must now prioritize systems that inherently maintain readiness through proactive risk mitigation , real-time data integrity , and self-correcting workflows .
Elegance as the Catalyst for Readiness
The concept of “always-ready” systems draws heavily from the elegance principle, which emphasizes reducing friction while maintaining sophistication. .
Principles-Based Compliance and Quality
The move towards always-ready systems also reflects lessons from principles-based compliance , which prioritizes regulatory intent over prescriptive rules.
Cultural and Structural Enablers
Building always-ready systems demands more than technology—it requires a cultural shift. The 2021 post on quality culture emphasized aligning leadership behavior with quality values, a theme reinforced by the 2025 VUCA/BANI framework , which advocates for “open-book metrics” and cross-functional transparency to prevent brittleness in chaotic environments. F
Outcomes Over Obligation
Ultimately, always-ready systems transform compliance from a cost center into a strategic asset. As noted in the 2025 elegance post , organizations using risk-adaptive documentation practices and API-driven integrations report 35% fewer audit findings, proving that elegance and readiness are mutually reinforcing. This mirrors the semiconductor industry’s success with validation-as-code, where machine-readable protocols enable automated regression testing and real-time traceability.
By marrying elegance with enterprise-wide integration, organizations are not just surviving audits—they’re redefining excellence as a state of perpetual readiness, where quality is woven into the fabric of daily operations rather than bolted on during inspections.
Workforce Resilience in Lean Teams
The imperative for cross-training in digital tools and validation methodologies stems from the interconnected nature of modern quality systems, where validation professionals must act as “system gardeners” nurturing adaptive, resilient processes. This competency framework aligns with the principles outlined in Building a Competency Framework for Quality Professionals as System Gardeners, emphasizing the integration of technical proficiency, regulatory fluency, and collaborative problem-solving.
Competency: Digital Validation Cross-Training
Definition : The ability to fluidly navigate and integrate digital validation tools with traditional methodologies while maintaining compliance and fostering system-wide resilience.
Dimensions and Elements
1. Adaptive Technical Mastery
Elements :
- Tool Agnosticism : Proficiency across validation platforms and core systems (eQMS, etc) with ability to map workflows between systems.
- System Literacy : Competence in configuring integrations between validation tools and electronic systems, such as an MES.
- CSA Implementation : Practical application of Computer Software Assurance principles and GAMP 5.
2. Regulatory-DNA Integration
Elements :
- ALCOA++ Fluency : Ability to implement data integrity controls that satisfy FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11.
- Inspection Readiness : Implementation of inspection readiness principles
- Risk-Based AI Validation : Skills to validate machine learning models per FDA 2024 AI/ML Validation Draft Guidance.
3. Cross-Functional Cultivation
Elements :
- Change Control Hybridization : Ability to harmonize agile sprint workflows with ASTM E2500 and GAMP 5 change control requirements.
- Knowledge Pollination : Regular rotation through manufacturing/QC roles to contextualize validation decisions.
Validation’s Role in Broader Quality Ecosystems
Data Integrity as a Strategic Asset
The axiom “we are only as good as our data” encapsulates the existential reality of regulated industries, where decisions about product safety, regulatory compliance, and process reliability hinge on the trustworthiness of information. The ALCOA++ framework— Attributable, Legible, Contemporary, Original, Accurate, Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available —provides the architectural blueprint for embedding data integrity into every layer of validation and quality systems. As highlighted in the 2025 State of Validation Report , organizations that treat ALCOA++ as a compliance checklist rather than a cultural imperative risk systemic vulnerabilities, while those embracing it as a strategic foundation unlock resilience and innovation.
Cultural Foundations: ALCOA++ as a Mindset, Not a Mandate
The 2025 validation landscape reveals a stark divide: organizations treating ALCOA++ as a technical requirement struggle with recurring findings, while those embedding it into their quality culture thrive. Key cultural drivers include:
- Leadership Accountability : Executives who tie KPIs to data integrity metrics (eg, % of unattributed deviations) signal its strategic priority, aligning with Principles-Based Compliance.
- Cross-Functional Fluency : Training validation teams in ALCOA++-aligned tools bridges the 2025 report’s noted “experience gap” among mid-career professionals .
- Psychological Safety : Encouraging staff to report near-misses without fear—a theme in Health of the Validation Program —prevents data manipulation and fosters trust.
The Cost of Compromise: When Data Integrity Falters
The 2025 report underscores that 25% of organizations spend >10% of project budgets on validation—a figure that balloons when data integrity failures trigger rework. Recent FDA warning letters cite ALCOA++ breaches as root causes for:
- Batch rejections due to unverified temperature logs (lack of original records).
- Clinical holds from incomplete adverse event reporting (failure of Complete ).
- Import bans stemming from inconsistent stability data across sites (breach of Consistent ).
Conclusion: ALCOA++ as the Linchpin of Trust
In an era where AI-driven validation and hybrid inspections redefine compliance, ALCOA++ principles remain the non-negotiable foundation. Organizations must evolve beyond treating these principles as static rules, instead embedding them into the DNA of their quality systems—as emphasized in Pillars of Good Data. When data integrity drives every decision, validation transforms from a cost center into a catalyst for innovation, ensuring that “being as good as our data” means being unquestionably reliable.
Future-Proofing Validation in 2025
The 2025 validation landscape demands a dual focus: accelerating digital/AI adoption while fortifying human expertise . Key recommendations include:
- Prioritize Integration : Break down silos by connecting validation tools to data sources and analytics platforms.
- Adopt Risk-Based AI : Start with low-risk AI pilots to build regulatory confidence.
- Invest in Talent Pipelines : Address mid-career gaps via academic partnerships and reskilling programs.
As the industry navigates these challenges, validation will increasingly serve as a catalyst for quality innovation—transforming from a cost center to a strategic asset.

